Zinc die casting process guide: from entry to mastery
Zinc die casting is an efficient and precise metal forming technology. This article will provide you with a comprehensive process guide to take you from entry to mastery of zinc die casting.
1.Characteristics of zinc alloy
Zinc alloy is an important metal material that has been widely used in modern industry due to its unique properties. The following are the main characteristics of zinc alloy:
(1) Excellent mechanical properties:
Zinc alloy has high strength and hardness, which can meet a variety of engineering needs. Its elastic modulus and yield strength are high, and it performs well when bearing loads.
(2) Good corrosion resistance:
The surface of zinc alloy can form a stable oxide film, which effectively protects the internal metal from corrosion. This makes zinc alloy widely used in the fields of external parts, automotive parts, etc.
(3) Good machinability:
Zinc alloy is easy to process and form, and can be made into various parts with complex shapes and structures through hot die casting, cold die casting, injection molding and other methods.

(4) Good electrical and thermal conductivity:
Zinc alloy has good electrical and thermal conductivity and is suitable for manufacturing electronic devices, circuit boards, radiators and other products.
(5) Low melting point:
Zinc alloy has a low melting point and is easy to process and cast. It is suitable for some applications that require low temperature conditions.
(6) Environmental protection:
Zinc is a recyclable material. Therefore, zinc alloy has good environmental protection and biocompatibility and is suitable for use in biomedicine and food contact.
(7) Lightweight:
Compared with traditional cast iron and steel materials, zinc alloy is lighter and is an ideal choice for manufacturing lightweight parts.

2.Advantages and disadvantages of zinc die casting
As a process widely used in modern manufacturing, zinc die casting has advantages and disadvantages that cannot be ignored. Understanding these characteristics will help us better apply this technology.
(1) Advantages
1) Good casting performance:
Zinc alloy has a low melting point of only 385°C, which makes it easy to die cast. In addition, zinc alloy has excellent fluidity and can die-cast complex and thin-walled precision parts. The surface of the casting is smooth, which greatly reduces the subsequent machining process.
2) High dimensional accuracy:
Zinc die-cast parts have high dimensional accuracy and surface finish, which can reach level 6~7 or even level 4. This makes die-cast parts have excellent interchangeability, reduces the need for machining, and improves production efficiency.
3) Easy surface treatment:
Zinc die-cast parts can undergo a variety of surface treatments, such as electroplating, spraying, and painting, which not only improves the appearance of the product, but also enhances its corrosion resistance.
4) Good material compatibility:
During the melting and die casting process, zinc alloy does not absorb iron, does not corrode the die, and does not stick to the mold, which extends the service life of the mold and reduces production costs.

5) Material recyclability:
Zinc alloy scraps are easy to recycle and remelt, reducing material waste and environmental pollution, and have good economic and environmental benefits.
6) High production efficiency:
The die casting machine has high productivity, one mold with multiple cavities, and can realize mechanized and automated production, which is very suitable for mass production.
(2) Disadvantages
1) Poor corrosion resistance:
Zinc alloy is more sensitive to impurity elements such as lead, cadmium, and tin. When these elements exceed the standard, the casting is prone to intergranular corrosion, resulting in dimensional changes and decreased mechanical properties.
2) Low creep strength:
Zinc alloy has low creep strength, and is prone to dimensional changes caused by natural aging during long-term use, affecting the stability of the product.
3) Temperature limit:
Zinc die casting parts should not be used in high and low temperature environments, because under these conditions, their mechanical properties will be significantly reduced.

4) High cost:
The specific gravity of zinc alloy is relatively large, about 2.5 times that of aluminum alloy, and the price is relatively high, making the material cost high.
3.Zinc die casting process principle and process flow
Zinc die casting process is an efficient, precise and reliable metal forming technology, widely used in automobiles, electronics, home appliances, aerospace and other fields. The following is a detailed introduction to the principle and process of zinc die casting:
(1) Process principle
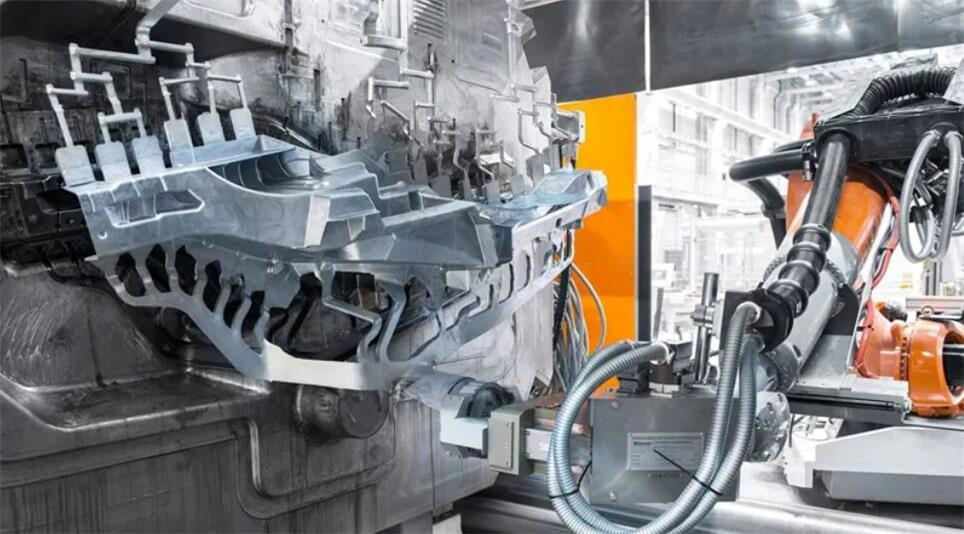
The basic principle of zinc die casting is to heat the zinc alloy to a liquid state and then inject it into a mold under high pressure. In the mold, the zinc alloy quickly cools and solidifies to form a casting with the same shape as the mold. This process has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency, and high strength, and is suitable for the production of parts and products of various complex shapes.
(2) Zinc die casting process flow
1) Raw material smelting
Put the zinc alloy raw material into a furnace for melting. The initial set temperature is generally between 435°C and 440°C, and after melting, it is adjusted to 420°C to 430°C for insulation. The alloy composition needs to be strictly controlled, such as the content of elements such as aluminum, copper, and magnesium, to ensure the quality of the casting.
2) Mold preheating
Before die casting, the mold needs to be preheated to 150°C to 200°C to ensure that the zinc alloy molten metal can quickly fill the mold cavity after being injected into the mold and reduce thermal stress.

3) Spraying release agent
Spray release agent on the mold surface so that the casting can be ejected from the mold smoothly after cooling. Commonly used release agents are mixed with water in a ratio of 1:200.
4) Mold closing and injection
After the mold is closed, the molten zinc alloy is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure through the die casting machine. The injection pressure ratio is generally set at 45 to 50 kg/cm², and the injection speed and filling time need to be precisely controlled.
5) Solidification and ejection
After the zinc alloy melt is injected into the mold, it is quickly cooled and solidified. After solidification, the casting is ejected from the mold by the ejector. The cooling time is generally from a few seconds to more than ten seconds.
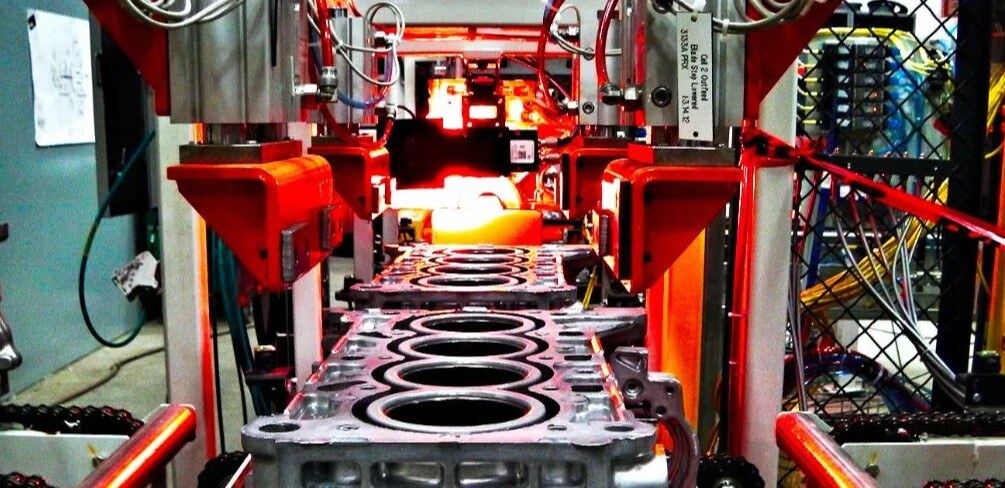

6) Post-processing of castings
Deburring and burring: remove excess burrs and burrs on the casting.
Surface treatment: including polishing, electroplating, spraying, etc. Polishing is usually divided into initial polishing, rough polishing and fine polishing to improve surface finish. Electroplating and spraying can enhance the corrosion resistance and aesthetics of castings.
Inspection: Inspect castings in terms of size, surface quality, mechanical properties, etc. to ensure product quality.
4.Design and optimization of zinc die casting process parameters
(1) Control of injection speed:
Injection speed is one of the key factors affecting the quality of zinc die-cast parts. Low-speed injection helps reduce gas entrapment and avoids the formation of pores inside the casting. High-speed injection can ensure that the molten metal fills the cavity in a short time and prevents cold shut defects.
Usually, low-speed injection is used in the initial filling stage, and high-speed injection is switched when the molten metal is close to being filled. The optimized injection speed curve needs to be adjusted according to the casting structure and wall thickness.
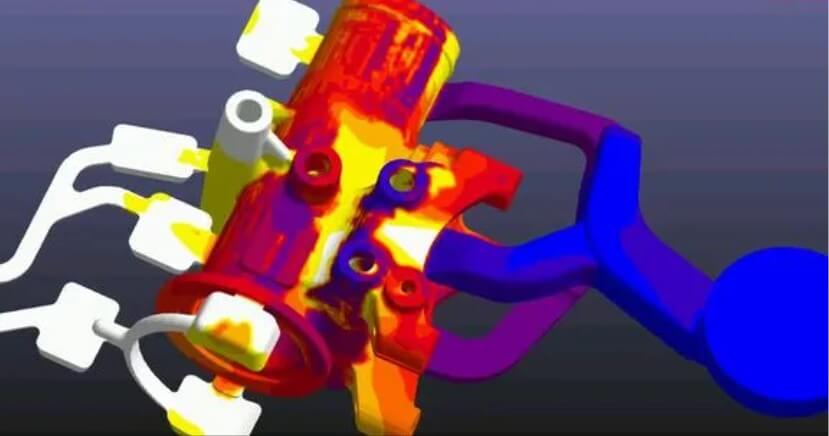
(2) Setting of injection pressure:
The injection pressure determines the filling capacity of the molten metal and the shrinkage compensation effect during solidification. Higher injection pressure helps to obtain a dense casting structure, but too high pressure may cause problems such as flash and mold damage.
Usually, the appropriate injection pressure is selected according to the complexity and wall thickness of the casting, generally between 30-70 MPa. For thin-walled complex parts, the injection pressure can be appropriately increased.
(3) Management of mold temperature:
The mold temperature directly affects the cooling rate and surface quality of the casting. Too low mold temperature will cause the casting surface to be rough, and even produce cold shuts and cracks; while too high temperature may cause mold sticking and casting deformation.
Usually, the mold temperature is controlled between 180-250℃ and accurately adjusted by the mold cooling system or heating system. For large and complex castings, it is necessary to simulate and analyze the mold temperature field to achieve uniform cooling.

(4) Selection of alloy composition:
The composition of zinc alloy has an important influence on the die casting process performance and casting performance. Commonly used zinc alloys include Zn-4Al, Zn-3Cu-0.5Mg, etc. By adjusting the alloy composition, the fluidity, strength and corrosion resistance can be improved. For example, adding an appropriate amount of aluminum can improve the fluidity of the alloy, while adding copper and magnesium can enhance the mechanical properties of the alloy.
(5) Design of the pouring system:
The design of the pouring system directly affects the flow path and filling effect of the molten metal. A reasonable pouring system should ensure that the molten metal fills the cavity smoothly and quickly, avoiding defects caused by gas entrapment and stream confluence. When designing, factors such as the shape, size and wall thickness of the casting need to be considered to optimize the position and size of the runner, cross runner and inner gate.
(6) Use of release agent:
The release agent helps to reduce the friction between the casting and the mold and prevent mold sticking. Commonly used release agents include water-based release agents and oil-based release agents. Selecting a suitable release agent and controlling its spraying amount can effectively improve the surface quality of the casting and the life of the mold.
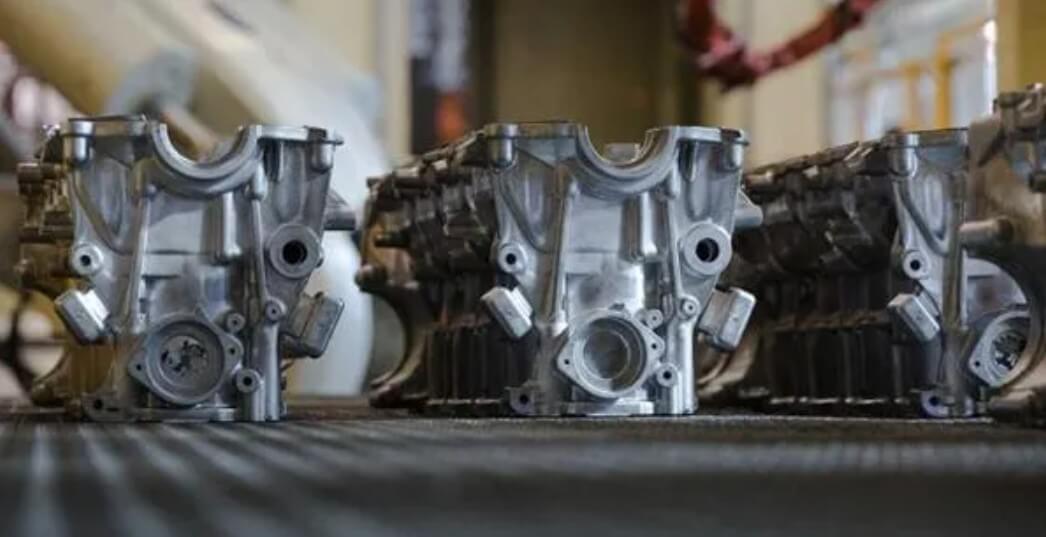

5.Precautions in zinc die casting
(1) Control of alloy composition
Ensure that the proportion of pure zinc ingots in the zinc alloy is greater than 94%, and strictly control the content of impurity elements such as lead, cadmium and tin to prevent aging and deformation of the casting.
The ratio of aluminum, copper, magnesium and other elements in the conventional alloy composition must meet the standard requirements to maintain the good performance of the zinc alloy.
(2) Strict melting temperature
Zinc alloy has a low melting point, and the melting temperature should be controlled at 415-430℃, and the maximum should not exceed 430℃ to prevent the loss of aluminum and magnesium and quality problems of die casting parts.
Check the furnace temperature regularly to ensure the accuracy of temperature control.
(3) Prevent corrosion and aging
Zinc alloy has poor corrosion resistance, and die casting parts should avoid being used in high and low temperature (below 0℃) environments.
Pay attention to storage conditions. The warehouse should be ventilated, dry and tidy to prevent oxidation and corrosion on the surface of zinc alloy die casting parts.
(4) Optimize die casting process
Use stainless steel tools for operation to avoid iron impurities affecting the quality of zinc alloy.
During the zinc die casting process, the clamping force and mold strength need to be reasonably controlled to prevent the surface of the casting from bursting.
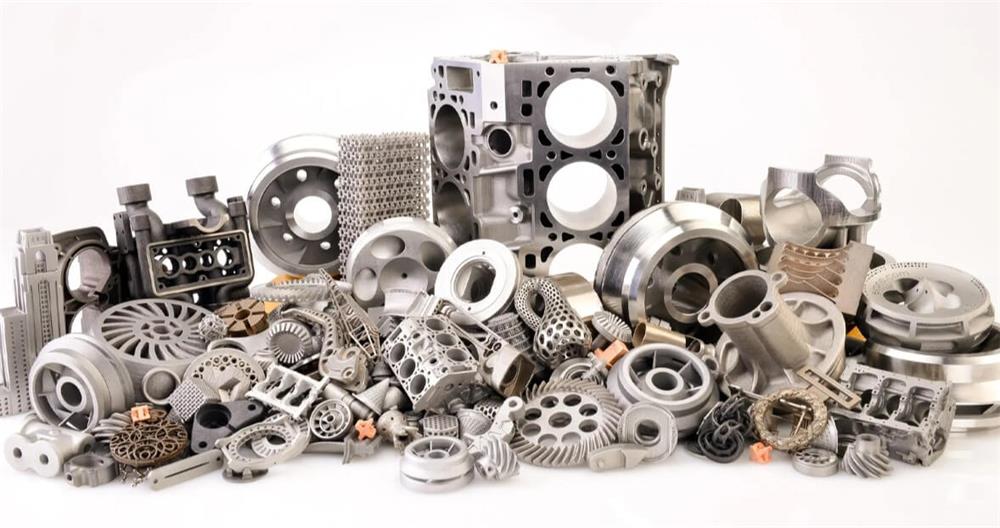
6.Application fields of zinc die casting parts
Zinc die casting parts occupy an important position in modern manufacturing industry due to their excellent physical properties, good plasticity and high efficiency production characteristics. The following are specific applications of zinc die casting parts in various industries:
(1) Automobile manufacturing industry
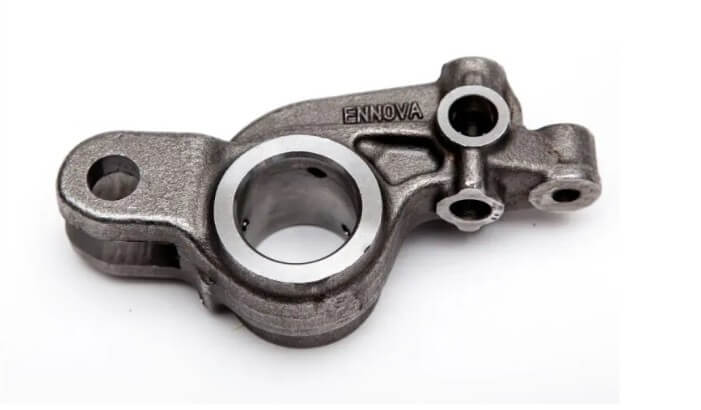
1) Engine parts:
Such as cylinder heads, valve rocker arms, valve supports, etc. These parts need to withstand high temperatures and high pressures. The high strength and good thermal conductivity of zinc alloys make them an ideal choice.

2) Chassis structure:
Including key components in the transmission system and suspension system, zinc die casting parts can provide the necessary strength and durability.
3) Body components:
Such as door handles, window frames, car door locks, etc., which not only ensure aesthetics but also improve safety.
(2) Electronic communication industry
1) Mobile phone housing:
Zinc die casting parts can provide good hand feel and appearance texture, and at the same time have certain protective properties.
2) Connectors:
Used in the connection part of electronic equipment, high precision and good conductivity are required. Zinc die cast parts can meet these requirements.
3) Keys:
Such as mobile phone keys, computer keyboards, etc., with good elasticity and durability.
(3) Building hardware
1) Door handles:
Zinc die casting parts are beautiful, durable and corrosion-resistant, and are widely used in various types of buildings.
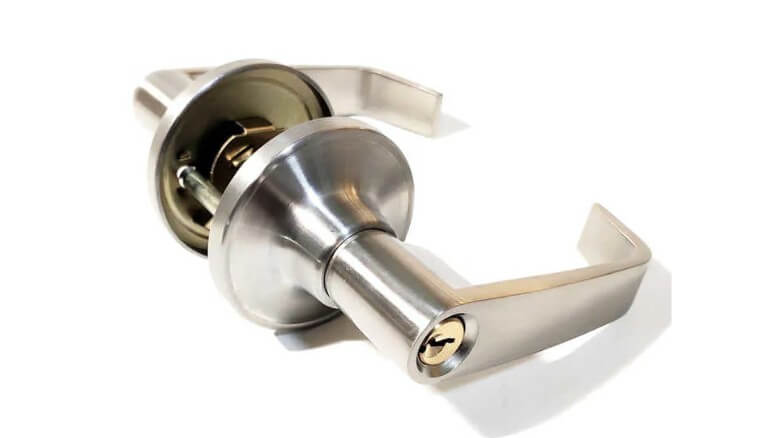

2) Window handles:
Similar to door handles, zinc die casting parts can provide long-term and stable use effects.
3) Hinges:
Used for the rotating parts of doors and windows, the high strength of zinc alloy ensures its durability.
(4) Daily consumer goods
1) Furniture accessories:
Such as drawer slides, hinges, etc., zinc die casting parts can provide smooth movement and long service life.
2) Lamps:
The good plasticity of zinc die casting parts enables it to be made into lamp housings of various shapes.
3) Toys:
Zinc die casting can produce toy parts with complex structures and durability.
(5) Medical devices
1) Implants:
Such as orthopedic fixation parts, the material is required to have high safety and biocompatibility. Zinc alloy can meet these requirements through surface treatment.
2) Surgical tools:
Such as surgical forceps, scissors, etc., the high precision of zinc die casting parts ensures the accuracy and reliability of the tools.
7.Summary
Through the detailed introduction of this article, I believe you have a deeper understanding of zinc die casting. Mastering these key steps, techniques and applications will help you become more handy in actual operations and promote the continuous advancement of zinc die casting technology.




