What is the difference between annealed and heat treated?A comprehensive analysis
What is the difference between annealed and heat treated?This is a question that is often asked in the field of metal processing, and it often confuses beginners. Although annealing and heat treatment are closely related, they each have their own unique features.
Annealing, as a special heat treatment process, focuses on optimizing the hardness and plasticity of metal materials through precise temperature control and cooling rate. In contrast, heat treatment is a broader concept, including but not limited to annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering, each of which is aimed at improving specific properties. Based on the question “What is the difference between annealed and heat treated?”, this article will conduct an in-depth analysis of the purpose, types, procedures, and applications of the two.
What is the difference between annealed and heat treated——first analyze the definition, purpose, type, and method separately, and then conduct a comprehensive analysis.
1.Definition and purpose of annealing
(1) Definition of annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process in which a metal or alloy is heated to an appropriate temperature, maintained for a certain period of time, and then slowly cooled. This process is mainly used to improve the microstructure of metal materials in order to adjust the material properties. During the annealing process, the material is heated to a specific temperature, usually above the critical temperature, to promote internal atomic rearrangement and form a uniform microstructure.

(2) Purpose of annealing
The main purpose of annealing is to reduce hardness, improve plasticity, facilitate cutting or pressure processing, reduce or eliminate internal residual stress, and stabilize size. Through these processes, the mechanical properties of the material can be improved, making it more suitable for subsequent processing or use. Annealing can also refine the grains, make the structure and composition of the steel uniform, improve the performance of the steel or prepare for subsequent heat treatment.
2.Types and methods of annealing
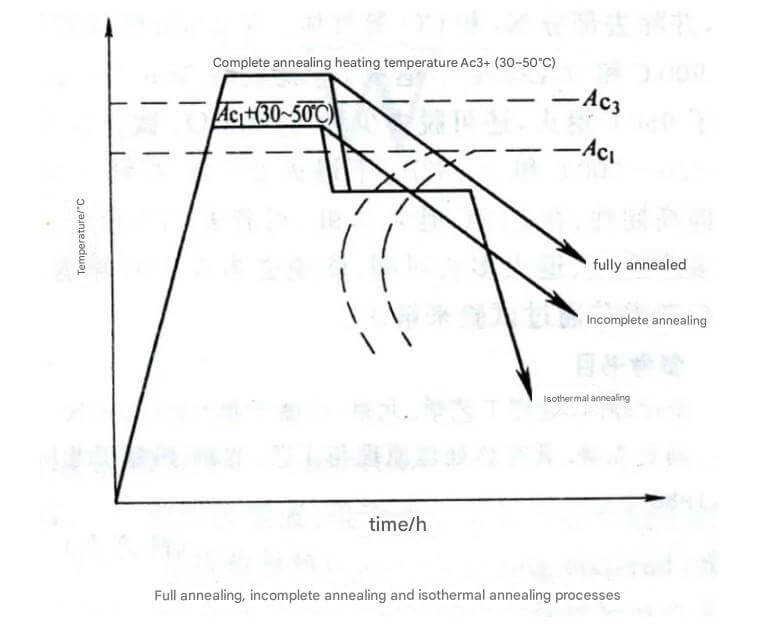
(1) Complete annealing
Complete annealing is mainly used for hypoeutectoid steel and eutectoid steel. It is heated to a temperature above Ac3 and then slowly cooled to obtain a balanced structure. This method helps to refine the grains, make the structure uniform, reduce hardness, and improve plasticity.
(2) Isothermal annealing
Isothermal annealing is used to form a uniform pearlite structure. The steel is heated to a temperature higher than Ac1 and then is isothermally maintained at a temperature below Ar1. This method can shorten the annealing time and improve production efficiency.
(3) Spheroidizing annealing
Spheroidizing annealing is mainly used for hypereutectoid steel. It is heated to 20-30℃ above Ac1 to spheroidize cementite and obtain granular pearlite. Spheroidizing annealing can reduce the hardness of the material, improve cutting performance, and prepare for subsequent quenching.
(4) Stress relief annealing
Stress relief annealing is used to eliminate residual stress in castings, forgings, welded parts and cold-processed parts. By low-temperature heating and slow cooling, the stress concentration inside the material can be effectively reduced to prevent deformation or cracking during use.

3.Definition and purpose of heat treatment
(1) Definition of heat treatment
Heat treatment is a process of changing the internal structure of solid metals or alloys by heating and cooling them, thereby improving the performance of the material. The heat treatment process includes three basic processes: heating, insulation and cooling. By precisely controlling these three stages, the hardness, strength, toughness and other mechanical properties of the material can be adjusted.
(2) Purpose of heat treatment
The purpose of heat treatment is to obtain the desired structure and performance, such as improving strength, hardness and toughness. Heat treatment is widely used in material modification of steel, nonferrous metals and their alloys, and is an indispensable part of modern manufacturing. Through heat treatment, the comprehensive performance of materials can be significantly improved, the service life of parts can be extended, and the needs of various engineering applications can be met.

4.Types and methods of heat treatment
(1) Normalizing
Normalizing is to heat steel to above the critical temperature and then cool it in air to obtain a fine pearlite structure. The normalizing process can improve the strength and toughness of steel and improve cutting performance. It is suitable for low-carbon and medium-carbon steels and low-alloy steels.
(2) Quenching
Quenching is to heat steel to a temperature above Ac3 or Ac1 and quickly cool it to obtain a martensitic structure to improve hardness and strength. Quenching is an important means to improve the hardness and wear resistance of steel parts. It is often used in the treatment of tool steel and structural steel.
(3) Tempering
Tempering is a subsequent treatment of quenched steel, which is heated to a temperature below Ac1 to improve the plasticity and toughness of the steel. Tempering can reduce the internal stress generated during quenching, improve the toughness of steel, and prevent brittle fracture during use.

5.What is the difference between annealed and heat treated: Summary
What is the difference between annealed and heat treated? Annealing and heat treatment are two metal processing processes commonly used to improve the properties of metal materials. Although annealing is a type of heat treatment, there are obvious differences between the two in terms of operation process, purpose and application.
(1) Process differences:
1) Heat treatment:
It is a broad concept, usually including three steps of heating, heat preservation and cooling, and sometimes only two processes of heating and cooling. The heat treatment process can be adjusted according to specific needs to change the overall or surface properties of the material.
2) Annealing:
As a specific heat treatment process, it emphasizes slowly heating the metal to a certain temperature, keeping it for a sufficient time, and then cooling it at an appropriate rate, often cooling it with the furnace or burying it in sand or lime.

(2) Different purposes:
1) Heat treatment:
It aims to change the surface or internal chemical composition and organizational structure of the material to obtain the desired properties, such as hardness, strength and wear resistance. Heat treatment processes include quenching, normalizing, tempering, etc., and each process has its specific purpose.
2) Annealing:
The main purpose is to reduce the hardness of the metal, improve plasticity, eliminate internal stress, refine the grains, and make the composition uniform in preparation for subsequent processing or heat treatment.
(3) Different structural transformations
1) Heat treatment:
During the heat treatment process, the microstructure inside the metal will undergo significant changes, such as austenitization and martensite transformation, in order to obtain the required mechanical properties.
2) Annealing:
During the annealing process, the microstructure inside the metal mainly undergoes recovery and recrystallization to eliminate internal stress, reduce hardness, and improve cutting performance.

(4) Differences in cooling speed:
1) Heat treatment:
The cooling speed varies depending on the process. Normalizing has a faster cooling speed, quenching has an even faster cooling speed, and annealing has the slowest cooling speed, usually cooling with the furnace to allow the internal structure of the metal to reach or approach a state of equilibrium.
2) Annealing:
The cooling speed of annealing is the slowest, and the purpose is to allow the internal structure of the metal to reach or approach a state of equilibrium and obtain good process performance and performance.
(5) Temperature selection:
1) Heat treatment:
The heating temperature varies depending on the metal material being treated and the purpose of the heat treatment, but it is generally heated to above the phase change temperature to obtain the required structure.
2) Annealing:
The heating temperature of annealing is usually selected above or below the phase change temperature of the material. The specific temperature depends on the type of material and the type of annealing.

(6) Scope of application:
1) Heat treatment:
It is widely used in various metal materials. According to different treatment processes, it can improve the cutting performance, mechanical properties or chemical properties of the material.
2) Annealing:
It is mainly used to improve the process properties of metals, such as reducing hardness to facilitate cutting and eliminating internal stress during forging, welding and other processes.
6.Summary
In summary, the question “What is the difference between annealed and heat treated?” has been systematically answered. It can be seen that although annealing and heat treatment overlap in some aspects, they have different focuses on process details, purposes and applications. Understanding these differences will help to correctly select the processing technology in practical applications to achieve the required material properties.





What do you think?
Admiring the commitment you put into your site and detailed information you provide.
It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same
out of date rehashed material. Fantastic read!
I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google
account.
[…] Annealing is an important heat treatment process that can change the microstructure and mechanical properties of metal materials through heating, insulation and cooling processes. The following are the main effects of annealing stainless steel on its material structure and properties: […]
[…] mainly includes raw material preparation, glass melting, glass forming, and annealing treatment. Annealing treatment is a key link. By controlling the cooling rate, the stress inside the glass is […]