In-depth understanding of die casting materials and analysis of advantages and disadvantages
As one of the most popular manufacturing technologies today, die casting has significant advantages. This metal casting process combines a mold cavity with high pressure to create an engineering part or product. The molds used are made of alloys with high strength properties and use non-ferrous metals such as copper, zinc, magnesium, aluminum, tin, lead and many other alloys. It is widely used in many industries such as automobiles, industry, lighting, home and medical.
1.Commonly used materials for die casting process
(1) Copper alloys
The copper alloys used for die casting are H58, H59, H62, H65 and H68. Copper alloys are known for their excellent electrical conductivity and relative corrosion resistance. These two properties make them a good choice for die castings.
(2) Aluminum alloys
Typical examples of aluminum alloy die castings include ADC12, ADC1, A360, A380, A413, B390, EN AC 43500 and A356. Like standard aluminum, these alloys are known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for lightweight parts that require a certain amount of strength. They are also corrosion resistant and have first-rate thermal conductivity, making them an ideal choice. In addition, aluminum castings maintain dimensional stability even under harsh conditions.
(3) Zinc Alloys
Typical zinc alloys used for casting are ZDC3 and ZDC5. These zinc alloys are known for their low melting points (less than 800 degrees Fahrenheit), making them an excellent choice. In addition, zinc castings have high ductility, good thermal conductivity, and dimensional stability, which makes them suitable for manufacturing parts with complex structures.
(4) Magnesium Alloys
The standard magnesium alloy used for casting is AZ91D. Its main property is its light weight, making it a popular choice for parts in the aerospace industry, where low density is a key criterion. However, due to magnesium’s flammability, its use in production is somewhat limited.

Advantages and disadvantages of die casting
(1) Advantages
1) High efficiency:
The process is simple, with a high degree of automation and high productivity, which is particularly suitable for mass production of products.
2) Excellent precision and smooth surface:
With high tolerance and high precision, the product quality is high and the surface finish is good. It can be used directly or processed in small quantities, which improves the utilization rate of the alloy and saves processing costs.
3) High mechanical properties:
During die casting, the molten metal cools and crystallizes rapidly under pressure. The crystal particles on the surface of the injection molded parts are usually dense and fine, which is conducive to improving the strength and hardness of the products.
4) Complex thin-walled parts:
Complex thin-walled structures with thinner walls than metal mold casting and sand casting can be produced.
5) Integrated materials:
Complex inserts and fasteners can be integrated into the final product, saving material and processing costs, improving component functions, and even allowing the production of the most complex shapes.
6) Easy to mass produce:
Dimensionally stable and durable castings can be produced, so little or no processing is required.
7) Various surface textures:
There are different surface and finishing methods, and it may have a textured or smooth surface.

(2) Disadvantages
1) Only supports non-ferrous metals:
This is one of the main disadvantages. Although it is not impossible to cast ferrous metals, manufacturers usually avoid it due to its difficulty.
2) Extremely high initial investment:
Many small companies and startups cannot afford the high initial investment.
3) Prone to defects:
If not carefully designed, parts are prone to defects such as pores, deflection, cold shut, etc.
4) Not suitable for small projects:
Most large suppliers are not interested in die casting solutions for small projects, and small projects may be more expensive than other methods.
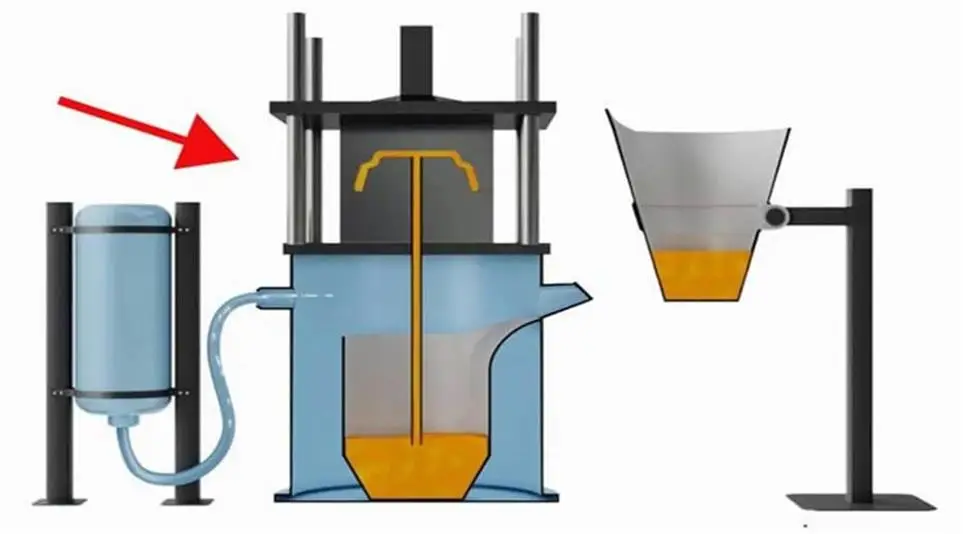
3.How to minimize defects in die casting
(1) Porosity is a common defect form, and strict quality control must be maintained at multiple stages of production. During the metal smelting process, additives can be used to release gases dissolved in the metal; after each casting, lubricants are added to the mold to reduce the possibility of pores forming on the surface; forming a vacuum during the casting process can significantly reduce the possibility of air accumulation in hard-to-reach areas of the part.
(2) At the same time, properly designing the mold and performing mold flow analysis to determine the appropriate shot blasting speed can avoid turbulence caused by improper design and excessive injection speed. Porosity. Taking the above steps will also help solve defects such as cold sealing and underfilling that may occur when filling the mold cavity.
During the solidification process, poor design or timing may cause shrinkage defects and damage to the casting and mold, which can be corrected by improving the part and mold design, such as eliminating hot spots in the design and adding runners and risers to the casting.
4. Conclusion
Die casting is an important metal part manufacturing process that is widely used and cost-effective. It can efficiently manufacture parts of different shapes, structures and precision standards. It is a valuable industrial production technology. However, while the die casting process is relatively simple, it requires specialized knowledge to achieve the desired results. Therefore, it is necessary to work with a reliable service provider to ensure that the production meets all the necessary design specifications. LVXUN is a professional injection molding service provider with knowledgeable technicians who can ensure that the injection molded products are suitable for the intended purpose. If necessary, you can always contact us for injection molding services for your parts.



What do you think?
[…] Die casting machines have various classifications and characteristics, and each type has its unique advantages and application scenarios. Choosing the right machine is the key to ensuring production efficiency and product quality. […]
Comments are closed.