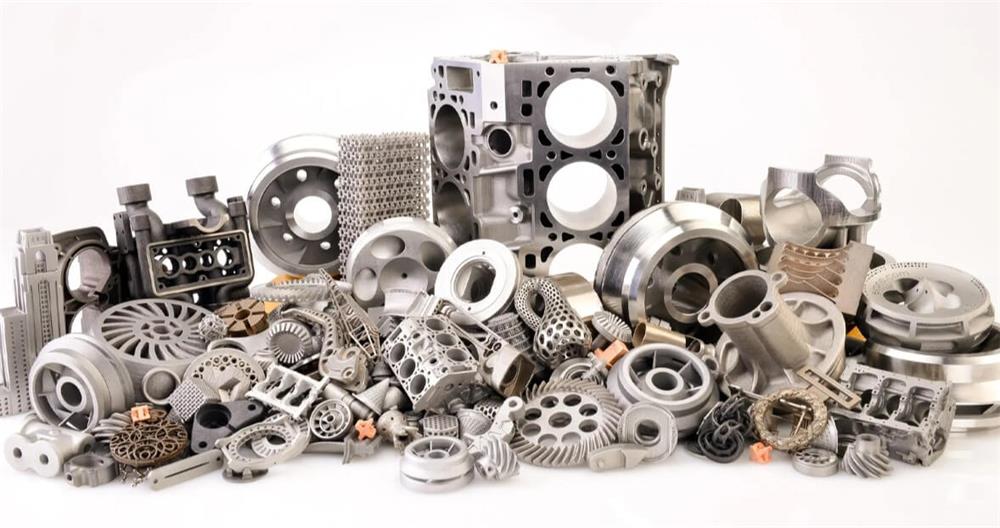
Stainless steel investment casting: full process quality control
Stainless steel investment casting is a high-precision metal forming process that is widely used in aviation, medical equipment, automobiles and other fields. Due to the characteristics of stainless steel materials themselves and their behavior at high temperatures, quality control in the stainless steel investment casting process is particularly important. This article will analyze in detail the material control, process control, post-processing control, and common casting defect types, characteristics, causes and solutions in stainless steel investment casting.
Common defect types, explore their causes, and propose corresponding quality control measures to ensure that the quality of castings meets high standards.
1.Material selection and control of stainless steel investment casting
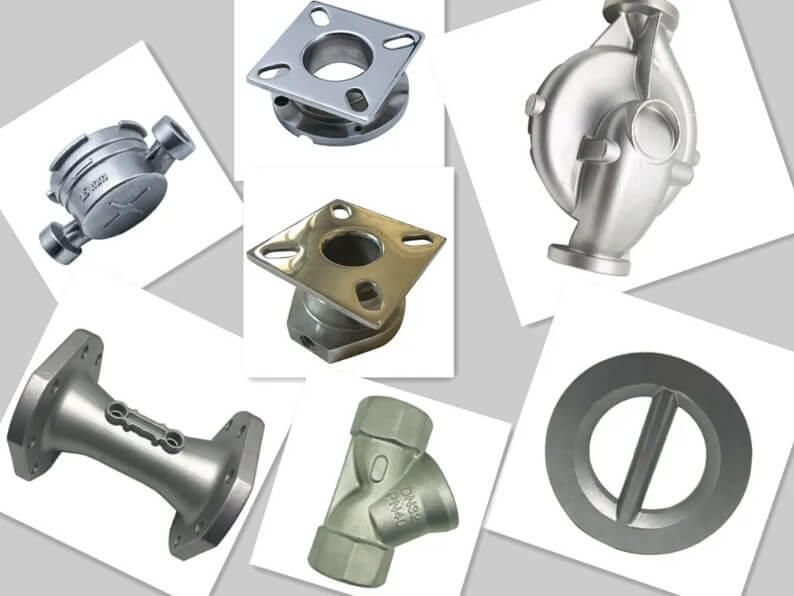

(1) Characteristics and application fields of stainless steel materials
Stainless steel has become the preferred material for many high-end equipment manufacturing due to its excellent corrosion resistance and high temperature strength. Stainless steel investment casting plays an irreplaceable role in the fields of aircraft engines, medical equipment, automotive parts, etc.
1) In the aviation field, stainless steel castings are mainly used to manufacture engine parts, such as turbine blades, combustion chambers, etc. These parts need to work in extreme environments of high temperature and high pressure, so the performance requirements of the material are extremely high.
2) In the field of medical devices, stainless steel’s corrosion resistance and biocompatibility are used to manufacture key components such as surgical instruments and artificial joints.
3) In the automotive industry, stainless steel investment casting parts are widely used in exhaust systems, turbochargers and other parts, improving the safety and reliability of automobiles.
(2) Material quality control
1) Composition control:
Ensure that the chemical composition of the selected stainless steel material meets relevant standards, such as ASTM, EN, etc. Through spectral analysis and other detection methods, the key elements such as C, Cr, Ni, Mo, etc. of the material are precisely controlled to avoid performance defects caused by composition deviation.
2) Purity control:
The purity of stainless steel materials directly affects the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of castings. Through advanced smelting technologies such as vacuum melting and electroslag remelting, harmful impurities and gases in the material are effectively removed to improve the purity of the material.
3) Raw material inspection:
Establish a strict raw material inspection system, conduct chemical composition analysis, mechanical property testing and surface quality inspection on each batch of raw materials entering the factory to ensure stable and reliable raw material quality.
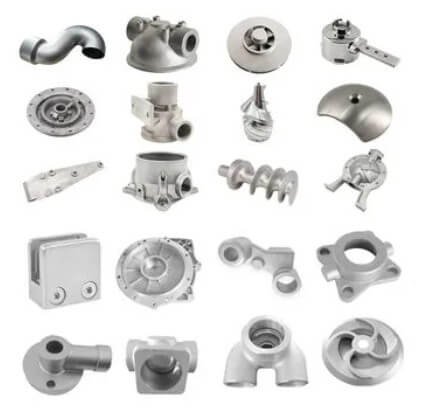

2.Stainless steel investment casting process control
(1) Melting process control
1) Melting temperature control:
Precisely control the melting temperature to avoid material burning and composition segregation due to excessive temperature. Use advanced temperature control system to achieve precise control and stability of temperature.
2) Deoxidation treatment:
Effective deoxidation treatment is carried out during the smelting process to reduce the oxygen content in the molten steel and improve the density and mechanical properties of the casting. Commonly used deoxidizers include aluminum, silicon calcium, etc.
3) Pre-furnace rapid analysis:
Perform pre-furnace rapid analysis before pouring to ensure that the composition of the molten steel meets the requirements, adjust the composition deviation in time, and ensure the stability of the quality of stainless steel investment casting parts.
(2) Pouring process control

1) Pouring temperature control:
Strictly control the pouring temperature to avoid casting defects caused by too high or too low temperature. Through the temperature measurement and control system, the pouring temperature can be accurately controlled.
2) Pouring speed control:
Reasonably control the pouring speed to avoid casting defects caused by too fast or too slow pouring speed. According to the structure and wall thickness of the casting, formulate reasonable pouring process parameters.
3) Riser design:
Reasonably design the riser to ensure that the casting is fully compensated for shrinkage during the solidification process and reduce defects such as shrinkage cavities and shrinkage porosity. Optimize the riser position and size through simulation analysis.
3.Subsequent treatment of stainless steel investment casting
(1) Heat treatment process
1) Solution treatment:
Through solution treatment, the carbides in the casting are fully dissolved to improve the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the casting. Formulate reasonable heat treatment process parameters to ensure the heat treatment effect.
2) Aging treatment:
Aging treatment is performed on certain grades of stainless steel castings to precipitate strengthening phases and improve the strength and hardness of the castings. According to specific materials and requirements, formulate appropriate aging treatment processes.
(2) Surface treatment
1) Sandblasting:
Through sandblasting, the oxide scale and adhesion on the surface of stainless steel investment casting parts are removed to improve the surface finish and aesthetics of the casting. Select appropriate abrasives and sandblasting parameters to ensure the treatment effect.
2) Polishing:
Polish castings with higher requirements to achieve a mirror-like surface. According to the casting material and surface requirements, select the appropriate polishing method and process parameters.
4.Common defect types, characteristics, causes and measures of stainless steel investment casting
(1) Surface pitting defects
1) Characteristic description:
Surface pitting is manifested as small depressions on the surface of the casting, usually hemispherical, small in size but may be large in number, affecting the appearance quality of the casting.
2) Cause analysis:
Surface pitting is mainly caused by unqualified shell materials. For example, when the shell material contains impurities or insufficient refractoriness, the shell material may undergo chemical reactions or decomposition during high-temperature pouring, thereby forming pitting on the surface of the casting. In addition, improper preparation and treatment of shell materials, such as uneven mixing and poor coating fluidity, may also lead to the formation of surface pitting.
3) Prevention of surface pits
① Strictly screen high-quality shell materials:
Select shell materials with high refractoriness and low impurity content to ensure the stability of the shell at high temperatures.
② Control the chemical composition and purity of the shell materials:
Through strict chemical analysis, ensure the quality of the shell materials and avoid chemical reactions at high temperatures.
(2) Depression defects
1) Defect description:
The depression defect is manifested as a local depression on the surface of the casting, which is usually more common in the hot spot, affecting the dimensional accuracy and appearance quality of the casting.
2) Cause analysis:
The depression defect is mainly caused by the degradation of the shell material performance. During the high-temperature pouring process of stainless steel investment casting, if the shell material has insufficient high-temperature resistance, thermal expansion or deformation may occur, resulting in depressions on the casting surface. In addition, improper shell design and manufacturing, such as uneven thickness and unreasonable structure, may also lead to depression defects.
3) Control strategy for sinking defects
① Improve the high temperature resistance of the shell material:
Choose a shell material with better high temperature resistance to ensure that it is not easy to deform during high temperature pouring.
② Rationally design the shell structure:
Optimize the thickness and structure of the shell to reduce the impact of thermal expansion on the casting.

(3) Shrinkage defects
1) Defect characteristics:
Shrinkage defects are manifested as depressions on the surface or inside of the casting, usually caused by the shrinkage of the molten metal during the cooling process, affecting the structural integrity and mechanical properties of the casting.
2) Cause analysis:
Shrinkage defects are mainly caused by improper pouring temperature control. If the pouring temperature is too high, the shrinkage rate of the molten metal will increase, causing the casting to shrink during the cooling process. In addition, unreasonable design of the pouring system, such as insufficient shrinkage channels, may also lead to shrinkage defects.
3) Solutions to shrinkage defects
① Accurately control the pouring temperature:
Through accurate temperature control, ensure that the molten metal is poured at an appropriate temperature to reduce shrinkage.
②Optimize the design of the pouring system:
Reasonably design the structure and size of the pouring system to ensure uniform filling and shrinkage compensation of the molten metal.
(3) Black spot defects
1) Defect manifestation:
Black spot defects usually appear on the surface of the casting, appearing as small black spots, affecting the appearance and surface finish of the casting.
2) Cause analysis:
Black spot defects are mainly caused by non-metallic inclusions in the molten steel. During the smelting and pouring process, if the purity of the molten steel is not enough, it contains non-metallic inclusions such as oxides and sulfides. These inclusions will remain in the casting after pouring and form black spots. In addition, unreasonable design of the pouring system, such as improper positioning of the gate and riser, may also lead to the introduction of non-metallic inclusions.
3) Measures to reduce black spot defects
① Improve the purity of the molten steel and reduce non-metallic inclusions:
Use efficient deoxidation and desulfurization processes in the melting process of stainless steel investment casting to ensure the purity of the molten steel.
② Optimize the deoxidation process:
Select the appropriate deoxidizer and add it at the appropriate time to maximize the removal of oxygen from the molten steel.
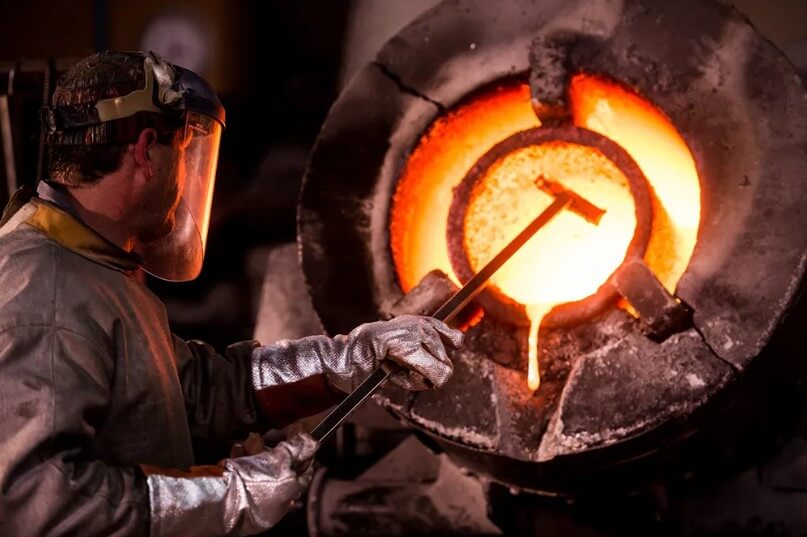
5.Summary
Through strict quality control measures, the stainless steel investment casting process can produce more stable and reliable casting products. The selection of raw materials, the fine operation of the process and post-processing, the prevention and resolution of defects, each link is an important guarantee to ensure the quality of the final product. In the future, with the continuous advancement and innovation of technology, we have reason to believe that the stainless steel investment casting process will play a more important role in the field of precision manufacturing.





What do you think?
[…] 4.Factors affecting the dimensional accuracy of stainless steel investment casting parts […]
Comments are closed.