Precision machined parts: A comprehensive guide from design to finished product
Precision machined parts are an indispensable and important part of modern industry, and their application areas cover a wide range of industries such as aerospace, medical devices, automobile manufacturing, electronic communications, optical instruments, and chemicals.
The quality of precision machined parts directly affects the performance, reliability, and service life of the product. This article will take you through a comprehensive understanding of precision machined parts and provide you with a comprehensive guide from design to finished product.
1.Design stage: the foundation of precision machined parts
The design of precision machined parts is the premise of the entire manufacturing process. The following key factors need to be considered in the design stage:
(1) Clarify requirements and analyze functions:
1) Clarify part functions:
First, clarify the role and function of the part in the final product, such as bearing loads, transmitting motion, sealing, etc.
2) Analyze the working environment:
Determine the working environment of the part, such as temperature, pressure, corrosive media, etc., in order to select appropriate materials and surface treatment processes.
3) Determine performance indicators:
Based on the function of the part and the working environment, determine key performance indicators, such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.

(2) Material selection:
Different application scenarios have different requirements for material properties. The following are several common metal materials and their application fields:
1) Stainless steel
Features: Excellent corrosion resistance and strength.
Applicable fields: medical equipment, food processing equipment, chemical equipment.
2) Aluminum alloy
Features: Lightweight, high strength and corrosion resistance.
Applicable fields: aerospace, automobile manufacturing, electronic products.
3) Titanium alloy
Features: High strength, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
Applicable fields: aerospace, military industry, high-end medical equipment.

4) Tool steel
Features: High hardness and wear resistance.
Applicable fields: cutting tools, molds, mechanical parts.
5) Brass
Features: Good processability and corrosion resistance.
Applicable fields: electronic components, pipe fittings, watch parts.
6) Zirconium alloy
Features: High temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
Applicable fields: nuclear energy, chemical equipment, marine engineering.
(3) Structural design:
1) Determine the shape and size of the part:
Determine the shape and size of the part according to the function and assembly requirements of the part, and use CAD software to draw a three-dimensional model.
2) Consider the processing technology:
Structural design needs to consider the limitations of the processing technology, such as avoiding complex shapes and narrow spaces that are difficult to process.
(4) Tolerance and surface roughness design:
1) Determine the tolerance grade:
Tolerance refers to the allowable dimensional deviation range. It is necessary to determine a reasonable tolerance grade based on the functional requirements of the part and the level of processing technology.
2) Determine the surface roughness:
Surface roughness refers to the microscopic unevenness of the surface of the part. It is necessary to determine a reasonable surface roughness based on the functional requirements of the part and the surface treatment process.
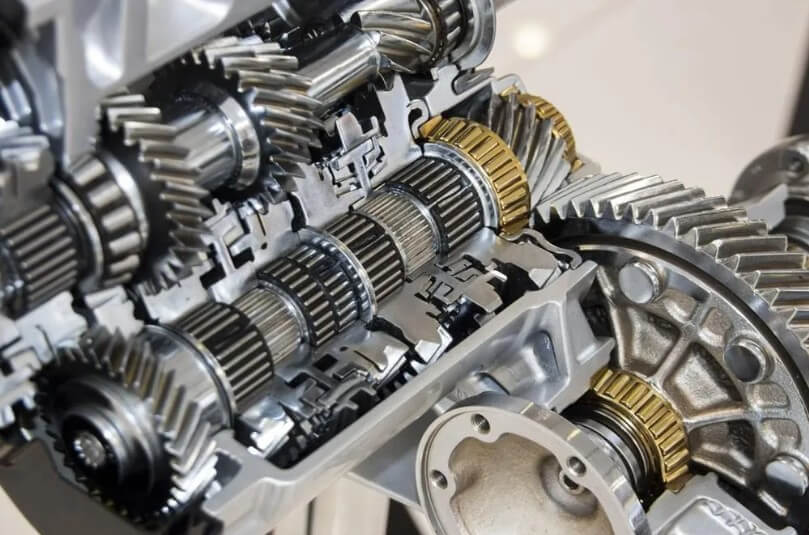
2.Processing technology of precision machined parts: turning design into reality
After the design is completed, it is necessary to select a suitable processing technology to transform the design drawings into physical objects. The following are four common production processes and characteristics of precision machining parts:
(1) CNC turning:
Process principle: Use CNC lathes to process rotating workpieces, and complete various shapes by controlling the tool’s moving path and cutting parameters.
Suitable parts: cylindrical, conical, threaded and other rotating parts.
Processing capabilities: outer circle, inner hole, end face, thread, groove, etc.
Advantages: high precision, high efficiency, suitable for mass production.
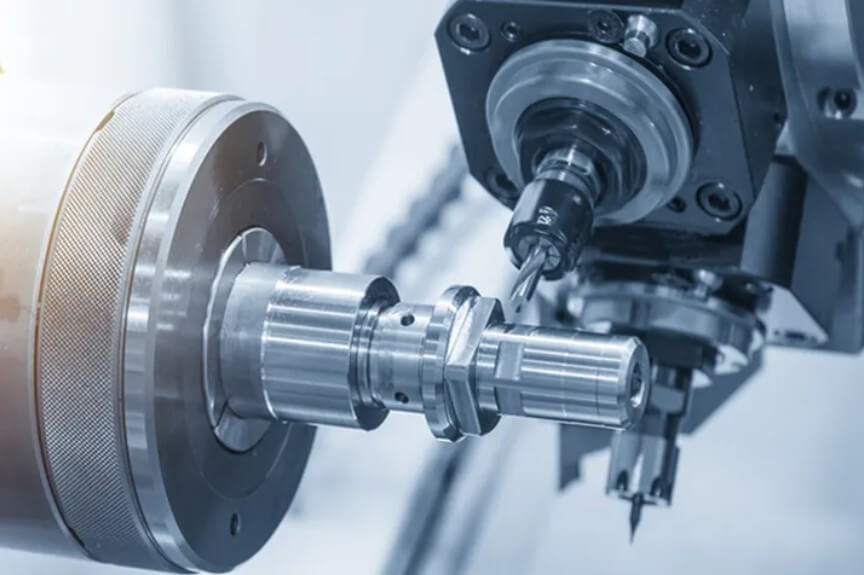
(2) CNC milling:
Process principle: Use CNC milling machines to perform multi-axis linkage processing on workpieces, and complete complex shape processing by controlling the tool’s moving path and cutting parameters.
Suitable parts: planes, curved surfaces, grooves, gears and other complex shape parts.
Processing capabilities: plane milling, contour milling, cavity milling, drilling, tapping, etc.
Advantages: strong flexibility, suitable for multi-variety and small batch production.
(3) Swiss Turning:
Process principle: Use Swiss lathes for high-precision machining, support the workpiece through guide sleeves, reduce vibration, and achieve high-precision and high-finish machining.
Suitable parts: Small, slender, high-precision shaft parts.
Processing capabilities: External circles, internal holes, end faces, threads, grooves, etc., especially suitable for mass production.
Advantages: High precision, high finish, suitable for small parts with complex shapes.
(4) Five-axis milling:
Process principle: Use five-axis linkage CNC milling machines to perform multi-angle machining on the workpiece, and complete the machining of complex surfaces by controlling the moving path and angle of the tool.
Suitable parts: Complex curved surface parts in the fields of aerospace, medical equipment, etc.
Processing capabilities: Complex curved surface machining, multi-angle drilling, contour machining, etc.
Advantages: High precision, high efficiency, suitable for the machining of complex curved surfaces.
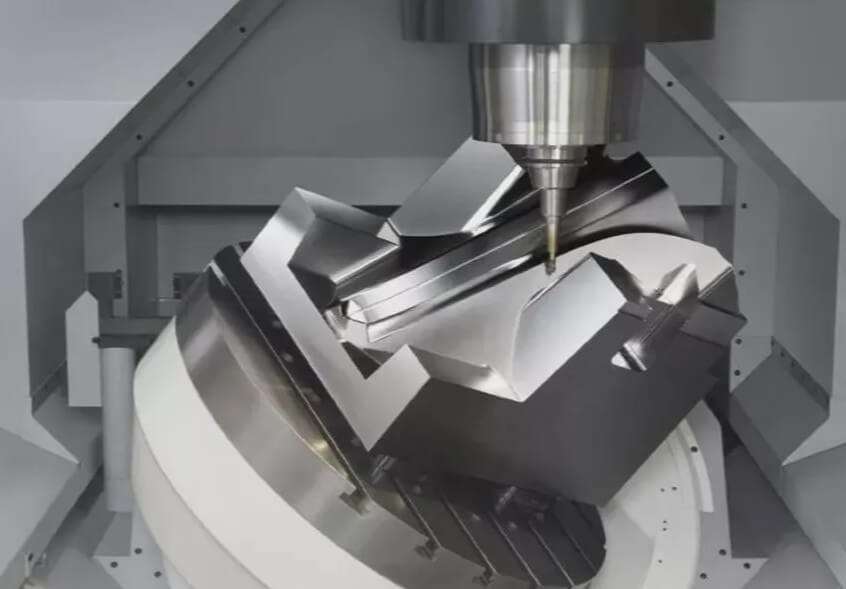

3.Quality control: ensuring the quality of precision machined parts
Quality control of precision machined parts is crucial and directly related to the performance and reliability of the product. Quality control mainly includes the following aspects:
(1) Testing equipment:
Common testing equipment includes three-dimensional coordinate measuring machines, profilometers, surface roughness meters, etc. These devices can accurately measure the size, shape and surface quality of parts to ensure that they meet the design requirements.
(2) Quality assurance system:
Establishing a sound quality assurance system is the key to ensuring the stability of part quality. Common quality assurance systems include ISO9001, AS9100, etc.
4.Fields with demand for precision machined parts and their components
The application fields of precision machined parts are very wide. The following are several typical application fields and their key components:
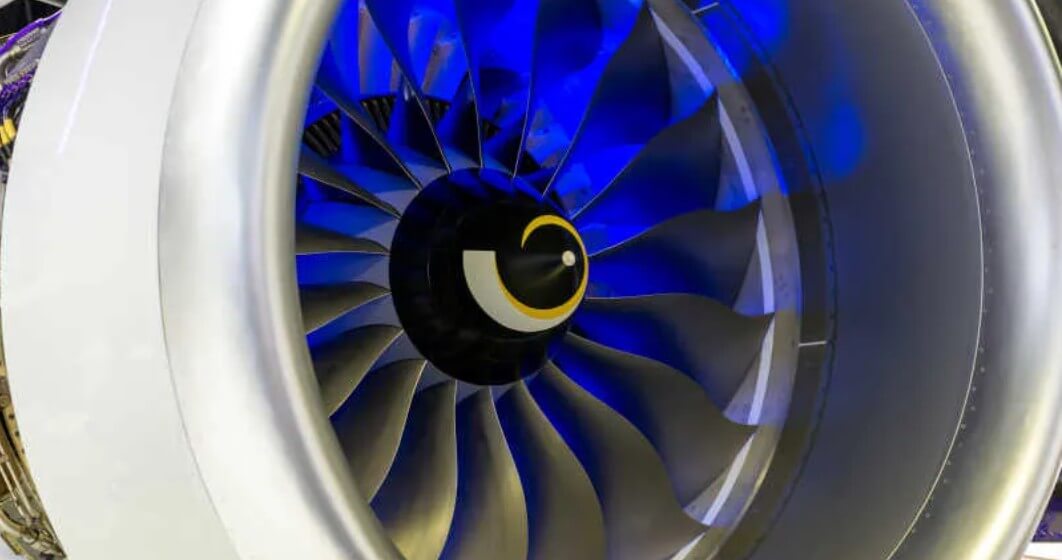
(1) Aerospace:
Engine blades, turbine discs, landing gear components, hydraulic system parts, etc.
These components need to withstand extreme working environments, so they have extremely high requirements for material properties, processing accuracy and surface quality.

(2) Medical devices:
Surgical instruments, implants, prostheses, diagnostic equipment parts, etc.
These parts are directly related to the life safety of patients, so they need to have good biocompatibility, high cleanliness and high precision.
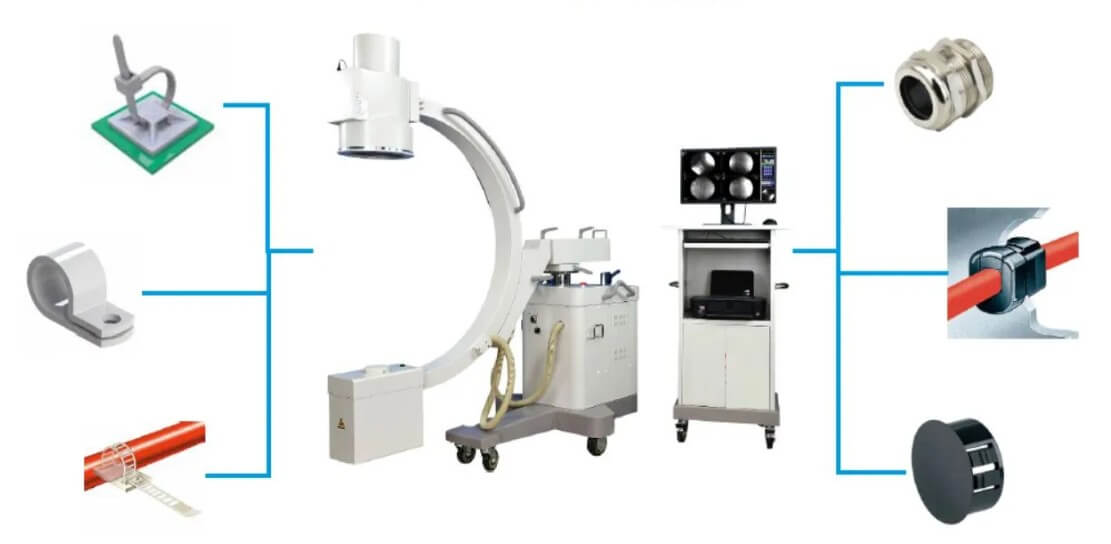
(3) Automobile manufacturing:
Engine cylinder, gearbox gear, steering system parts, sensor housing, etc.
With the development of the automobile industry, the demand for precision machining parts is also increasing, such as lightweight, high precision, high reliability, etc.
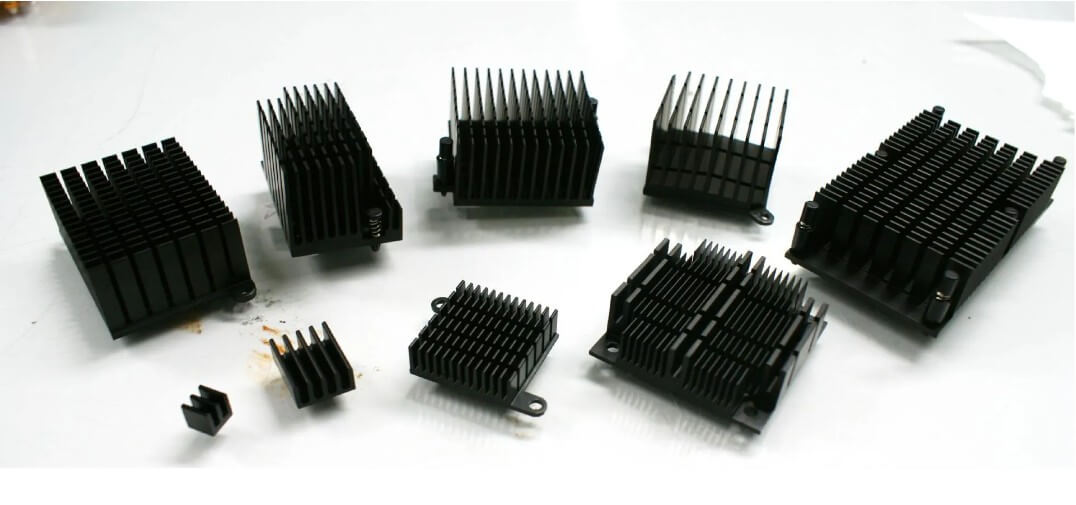
(4) Electronic communication:
Mobile phone housing, connector, heat sink, semiconductor device, etc.
The demand for precision machining parts in electronic communication equipment is mainly concentrated in high precision, miniaturization and high reliability.

(5) Optical instruments:
Lens, prism, reflector, laser parts, etc.
The demand for precision machining parts in optical instruments is mainly concentrated in high precision, high surface finish and low defect rate.
(6) Chemical industry:
Valves, pump bodies, seals, reactor parts, etc.
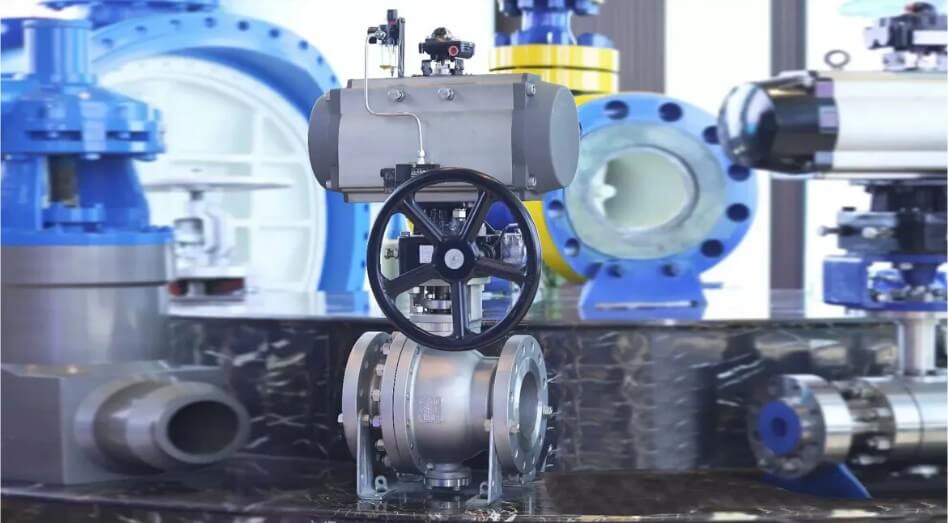

Although the demand for precision machining in the chemical industry is relatively low, some key parts still require high-precision machining, such as corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, high pressure resistance, high sealing, etc.
5.Conclusion
By understanding the design, material selection, processing technology and quality control process of precision machined parts, we can have a deeper understanding of this complex and high-precision manufacturing process. With the advancement of science and technology, precision machining technology will continue to break through the limits and provide better quality and more reliable parts for all walks of life.





What do you think?
[…] (2) The core role of precision machined parts […]
[…] parts with complex shapes, use CNC machine tools for precision machining to improve machining […]
[…] CNC machining a core link in their manufacturing process. The following are the applications of CNC machining in the manufacturing of several typical […]
[…] machine tools are the core equipment for plumbing component precision machined parts, mainly used for machining flanges, elbows, joints, valve bodies and other […]
[…] Reduce cutting speed and feed rate, improve surface quality, and ensure the dimensional accuracy of the workpiece. […]