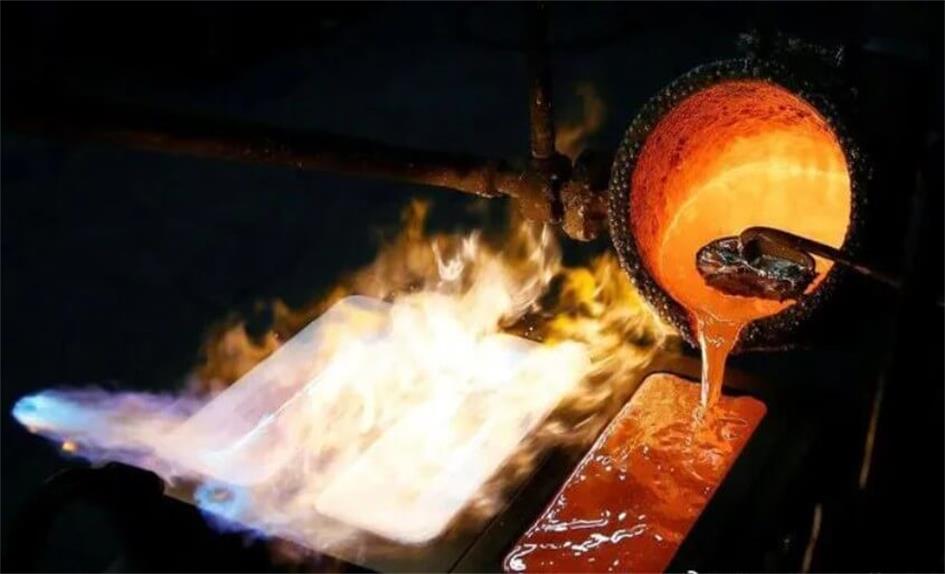
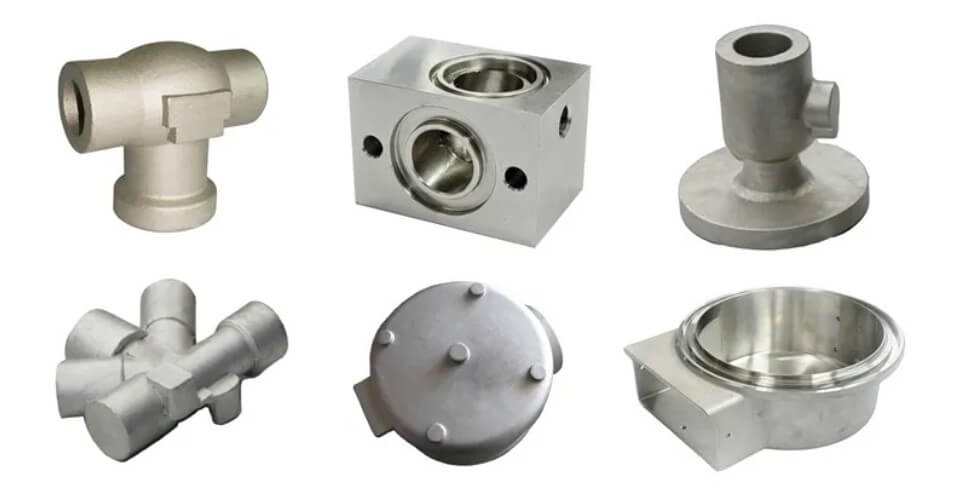
Comprehensive Guide to Liquid Steel: Characteristics, Production, Processing and Application
In modern industry, liquid steel plays a vital role as a basic material. From the construction of high-rise buildings to the manufacture of precision machinery, liquid steel is everywhere. However, it is not easy to fully master this material. This article aims to provide a detailed comprehensive guide to liquid steel, covering the entire process from its characteristics, production, processing to application, to help readers better understand and use this magical material.
1.Definition and basic concepts of liquid steel
Liquid steel, usually refers to the molten state of steel at high temperature. It is a molten steel formed under specific high temperature conditions. In this state, the steel has good fluidity and can be cast into various shapes. It is a key form in the steel production process. Liquid steel not only plays a vital role in steel production, but also has important research value in the field of materials science and engineering.
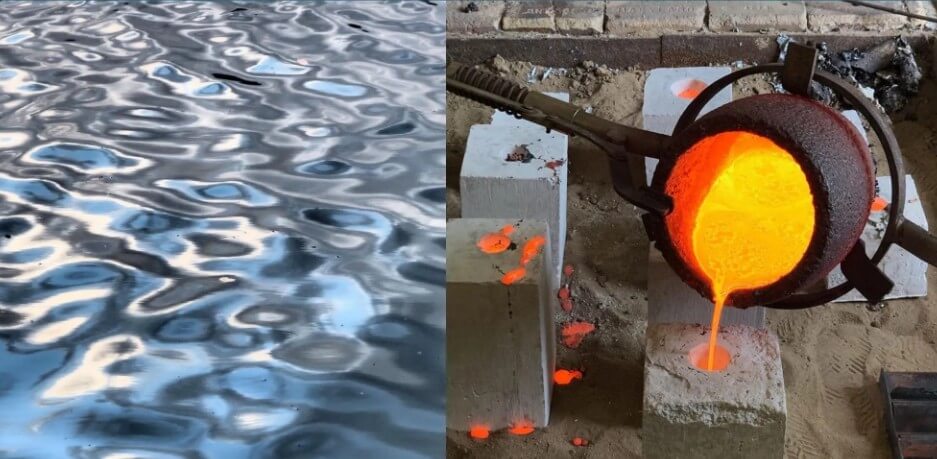

2.Characteristics and advantages of liquid steel
(1) High temperature fluidity
Liquid steel has good fluidity at high temperatures, which enables it to be made into various complex shapes and structures through the casting process. This fluidity is the basis for forming a uniform structure during steel production and is also a key factor in achieving efficient casting.
(2) Thermal conductivity
Liquid steel has excellent thermal conductivity and can dissipate heat quickly and evenly during cooling, which is crucial for controlling the microstructure and mechanical properties of steel products. Good thermal conductivity can also reduce thermal stress during casting and avoid defects such as cracks inside the material.
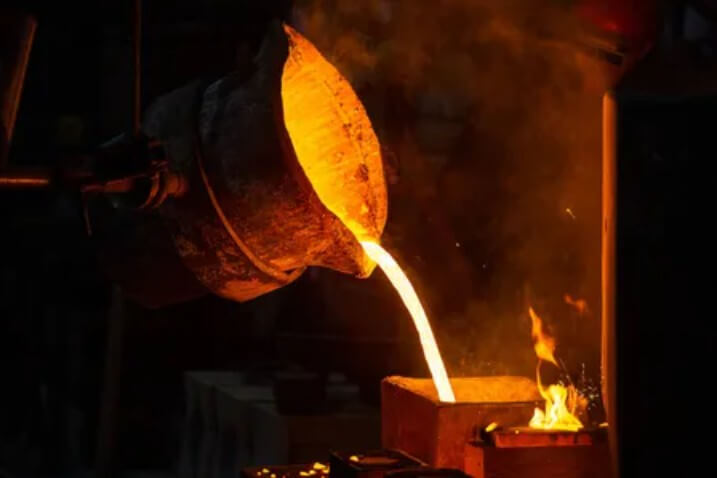

(3) Chemical stability
Liquid steel has high chemical stability at high temperatures and can resist corrosion from oxidation and other chemical reactions. This property ensures the purity of the molten steel during pouring and solidification, thereby ensuring the quality and performance of the final product.
(4) Mechanical properties
By controlling the cooling rate and solidification conditions of liquid steel, its microstructure can be adjusted to optimize its mechanical properties, such as strength and toughness. This gives liquid steel a significant advantage in manufacturing high-strength and high-durability structural materials.
3.Main production technology of liquid steel
The production of liquid steel is mainly achieved by heating raw materials such as iron ore and carbon at high temperatures to melt them into molten steel. This process is usually carried out in steelmaking furnaces, including converters and electric arc furnaces. The following is an overview of the two technologies:
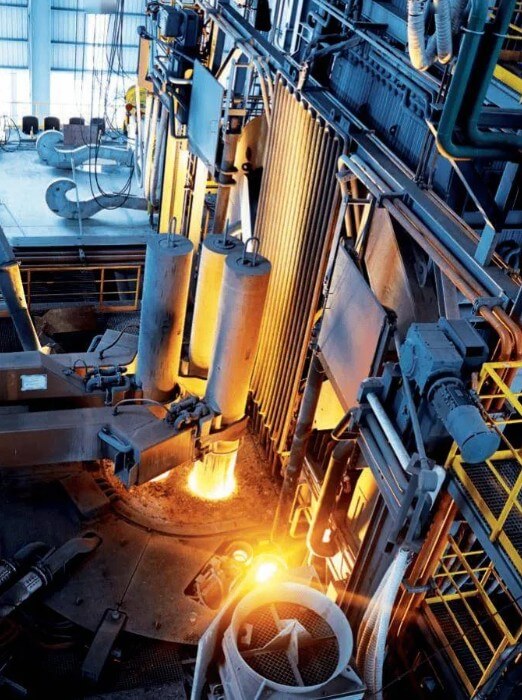

(1) Converter steelmaking technology:
The converter converts molten iron into molten steel by blowing pure oxygen into it to react with carbon, silicon, manganese and other elements in the molten iron to produce CO and CO2 gases. Converter steelmaking has the advantages of high production efficiency and low cost, and is the main method for large-scale steel production. Modern converter steelmaking technology is constantly developing in the direction of automation and intelligence to improve production efficiency and product quality.
(2) Electric arc furnace steelmaking technology:
The electric arc furnace is a device that uses the high temperature of the arc generated between the electrode and the scrap steel to melt steel. This technology is flexible and efficient, and can quickly adjust the composition of steel. It is widely used in the production of special steel and high-alloy steel. Electric arc furnace steelmaking technology continuously improves production efficiency and product quality by optimizing the power supply curve and improving the furnace lining material.
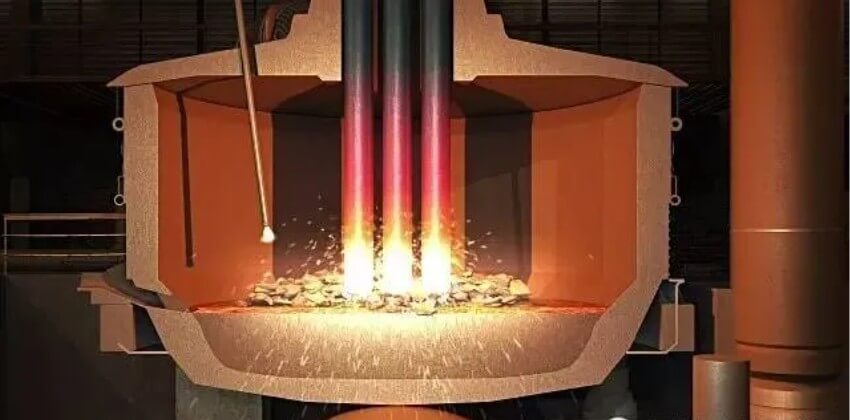

Summary:
The converter blows oxygen into the molten iron to oxidize and remove carbon and other impurities to obtain molten steel. The electric arc furnace heats scrap steel through an electric arc to melt it into molten steel.
Each of these two processes has its own advantages and disadvantages. The converter process has high production efficiency and low cost, but has a greater impact on the environment. Although the electric arc furnace process has a higher production cost, it has less pollution to the environment and can better control the quality of molten steel.
4.Main processing technologies for liquid steel
As a metal in a high-temperature molten state, liquid steel has extremely high plasticity and fluidity, which provides a variety of possibilities for its processing. The following will focus on the three main processing technologies for liquid steel: casting technology, forging technology, and heat treatment technology.
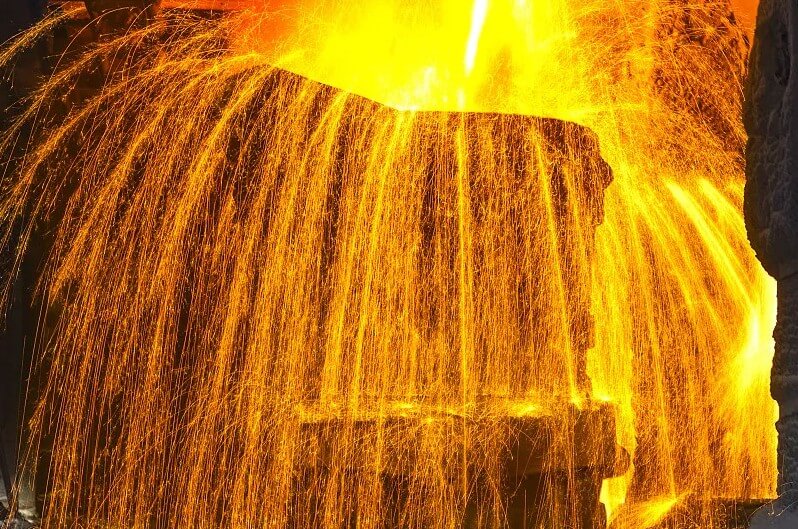

(1) Casting technology
Casting is a process method in which liquid steel is injected into a pre-prepared mold and, after cooling and solidification, a blank or part of the desired shape and size is obtained. Modern liquid steel casting technology mainly includes sand casting, precision casting, and pressure casting.
1) Sand casting:
This is one of the most traditional casting methods and is suitable for steel parts with complex shapes and large sizes. Sand casting has a simple process and low cost, but the surface of the casting is rough and the dimensional accuracy is not high.
2) Investment casting:
This technology uses fusible models (such as wax models) for modeling, which can obtain castings with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface. Investment casting is widely used in the manufacture of high-performance parts in the fields of aerospace, automobiles, etc.
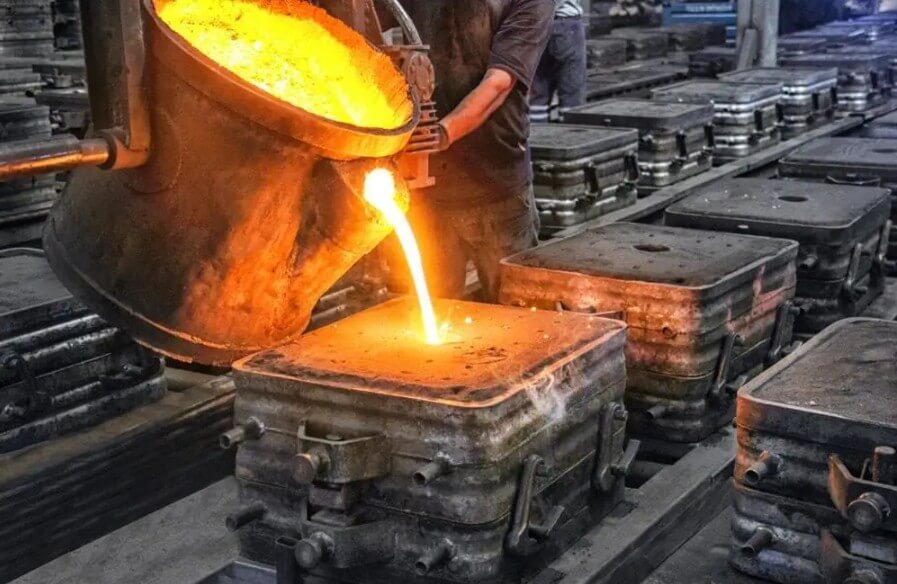

3) Die casting:
Die casting is a method of quickly pressing liquid steel into a metal mold under high pressure to form it. Its advantages are high production efficiency, good dimensional accuracy and surface quality of castings, but the cost of equipment and molds is high, and it is not suitable for the production of large castings.
(2) Forging technology
Forging is a processing method that applies external force to solid or liquid metal to cause it to undergo plastic deformation to obtain the desired shape, size and performance. The forging technology of liquid steel mainly includes liquid die forging and semi-solid forging.
1) Liquid die forging:
Liquid steel is directly injected into the mold and solidified and deformed under high pressure. Liquid die forging combines the advantages of casting and forging, and can obtain forgings with dense structure and excellent mechanical properties.
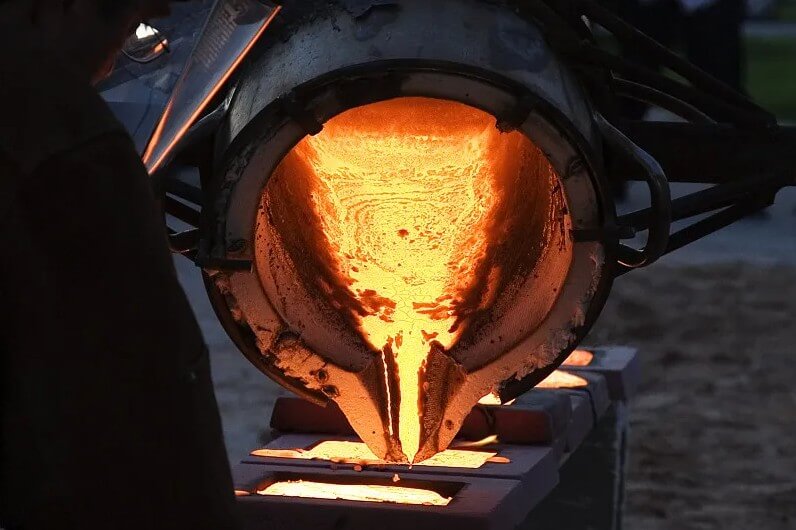

2) Semi-solid forging:
The liquid steel is cooled to a semi-solid state (a state where solid and liquid phases coexist), and then forging is performed. Semi-solid forging has the advantages of low forming force and good forging quality, and is an important development direction of liquid steel forging technology in the future.
(3) Heat treatment technology
Heat treatment is a method of changing the internal structure of steel through heating, heat preservation and cooling, thereby improving its performance. The heat treatment technology of liquid steel mainly includes the following:
1) Normalizing:
The steel is heated to above the austenitizing temperature, and then air-cooled after heat preservation. Normalizing can refine the grains and improve the strength and toughness of the steel.
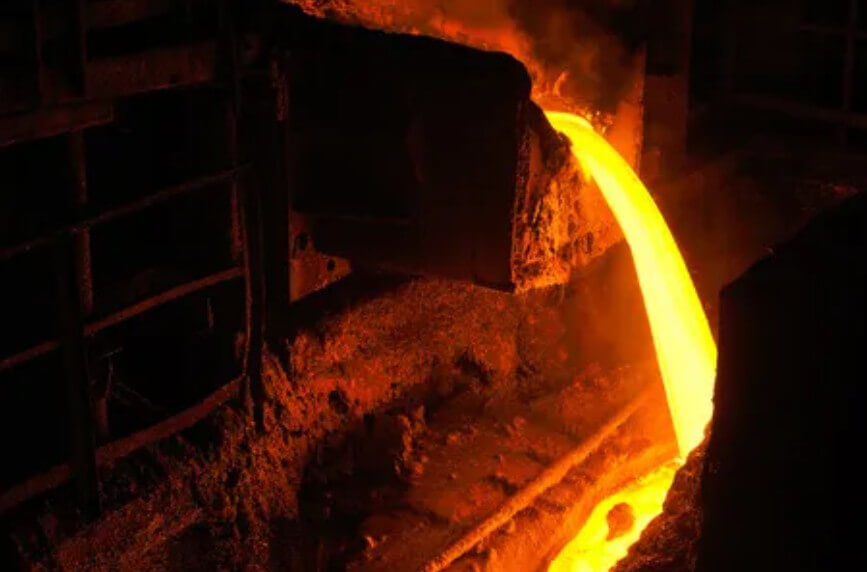

2) Quenching:
The steel is heated to above the austenitizing temperature, and then quickly cooled after heat preservation (such as water cooling or oil cooling). Quenching can significantly improve the hardness and wear resistance of the steel, but it will also increase its brittleness.
3) Tempering:
The quenched steel is reheated to a certain temperature, and then cooled after heat preservation. Tempering can reduce the brittleness of steel and adjust its comprehensive properties such as hardness, strength and toughness.
Summary:
The processing technology of liquid steel is one of the key technologies in modern industrial production. By continuously innovating and improving these technologies, we can further improve the quality and performance of steel parts and meet the needs of various industries for high-performance metal materials.
5.Application areas of liquid steel
(1) Construction and infrastructure
Liquid steel is widely used in construction and infrastructure construction due to its excellent mechanical properties. For example, the steel bars in reinforced concrete structures are cast from liquid steel, which can significantly improve the bearing capacity and earthquake resistance of buildings.
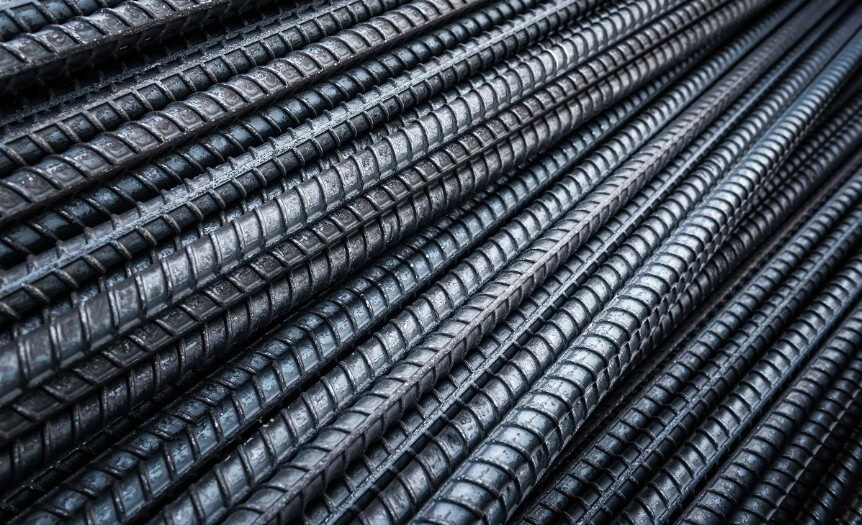

In addition, liquid steel is also used to manufacture key components of large-scale infrastructure such as bridges and tunnels to ensure the stability and safety of these structures.
(2) Automobile industry
In the automobile manufacturing industry, liquid steel is used to produce high-strength automobile parts such as frames, suspension systems and body structures. These parts not only need to have high strength and good toughness, but also need to be able to reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, thereby improving fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.
The application of liquid steel enables automobile manufacturers to produce safer and more energy-efficient vehicles.
(3) Shipbuilding and marine engineering
The application of liquid steel in the fields of shipbuilding and marine engineering cannot be ignored. The hull structure of ships and the supporting components of offshore platforms all require the use of high-strength and high-corrosion-resistant steel.
Liquid steel can meet the use requirements in these special environments through precise casting and forging processes, ensuring the safety and reliability of ships and offshore platforms.

(4) Tool and mold manufacturing
Liquid steel is widely used in tool and mold manufacturing due to its high hardness and high wear resistance. For example, the tools of machine tools such as lathes and milling machines and the molds of plastic products all need to be made of high-hardness steel to ensure that they can be used for a long time without failure.
Liquid steel can produce high-performance tools and molds through precise casting and heat treatment processes to meet the needs of industrial production.
6.Summary
Through this comprehensive analysis of liquid steel, we not only understand its unique physical and chemical properties, but also deeply explore its production, processing technology and wide range of applications. As a pillar material of modern industry, the importance of liquid steel is self-evident. Mastering relevant knowledge about it is of great significance to promote scientific and technological progress and promote industrial development. I hope this comprehensive guide can provide useful reference for relevant practitioners and enthusiasts.