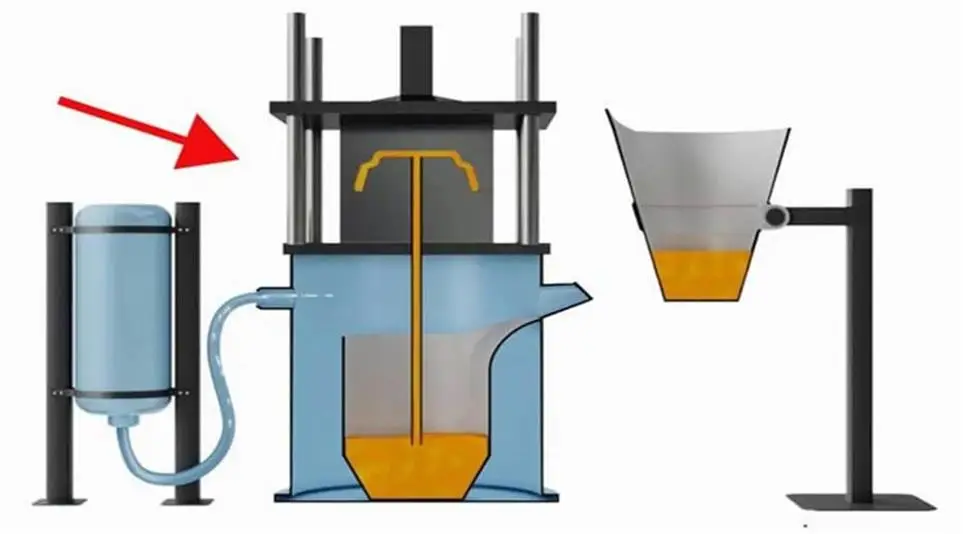
Investment casting process: the perfect presentation of precision technology
Investment casting process is a precision metal casting method. This process can produce parts with precise dimensions and high surface finish. It is widely used in aviation, automobiles, medical equipment and other fields. This article will introduce in detail the definition of investment casting, process flow, precautions during operation, differences from ordinary casting process and application fields.
1.Definition of investment casting
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting or precision casting, is an advanced process that can produce high-precision and complex-shaped metal parts. The basic principle of this process is to use fusible materials (such as wax) to make a precise pattern, and then coat the pattern with multiple layers of refractory materials to form a shell. After hardening and heating treatment, the pattern is melted and flows out to form a cavity, and finally molten metal is injected. After cooling, the desired casting is obtained.
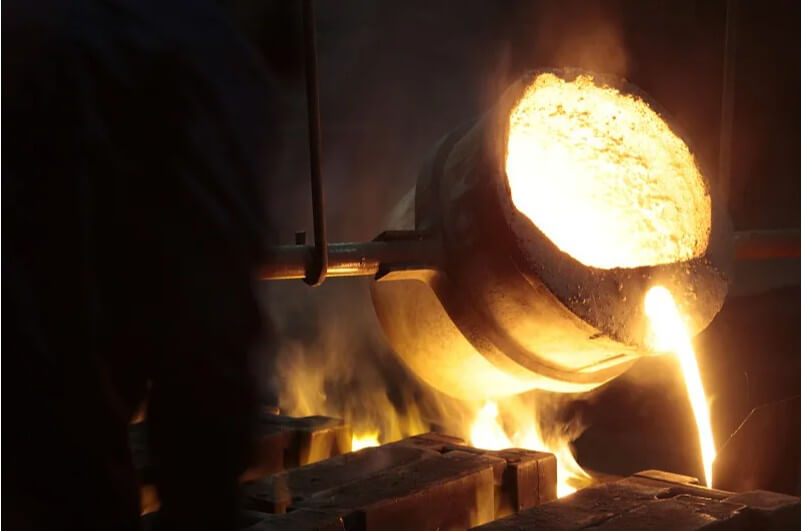

2.Investment casting process
(1) Mold making
1) Modeling:
First, make a prototype model according to the desired casting shape, usually using materials such as wax or silicone.
2) Molding:
Heat the wax to a plastic state, then pour it into the pre-prepared mold, and remove the wax mold after cooling.
(2) Crusting
1) Slurrying:
Evenly apply a layer of special slurry on the surface of the wax mold.
2) Sanding:
Before the slurry dries, sprinkle a layer of fine quartz sand or other refractory materials to make it adhere to the slurry.
3) Hardening:
Repeat the slurrying and sanding steps, usually 5 to 6 layers are required to form a mold shell of sufficient thickness.
4) Dewaxing:
Put the completed mold shell in a high-temperature furnace for baking, so that the wax mold melts and flows out, leaving only the mold shell.
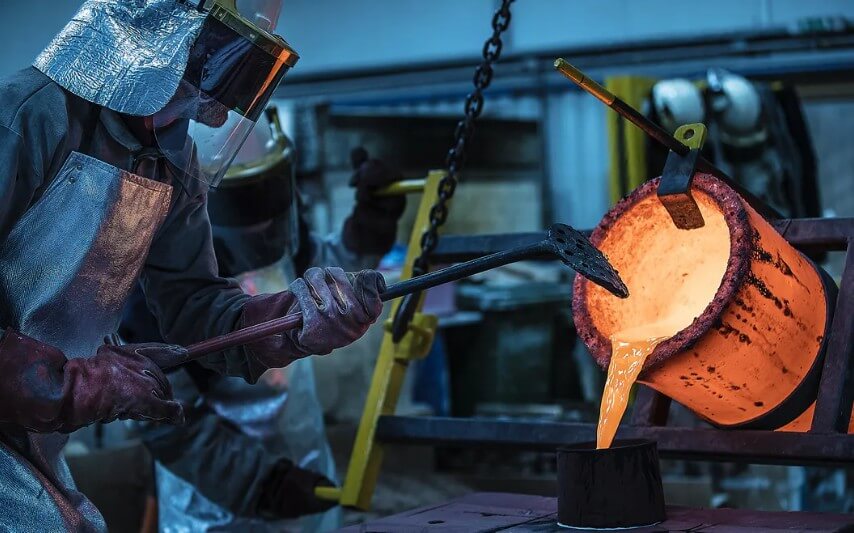
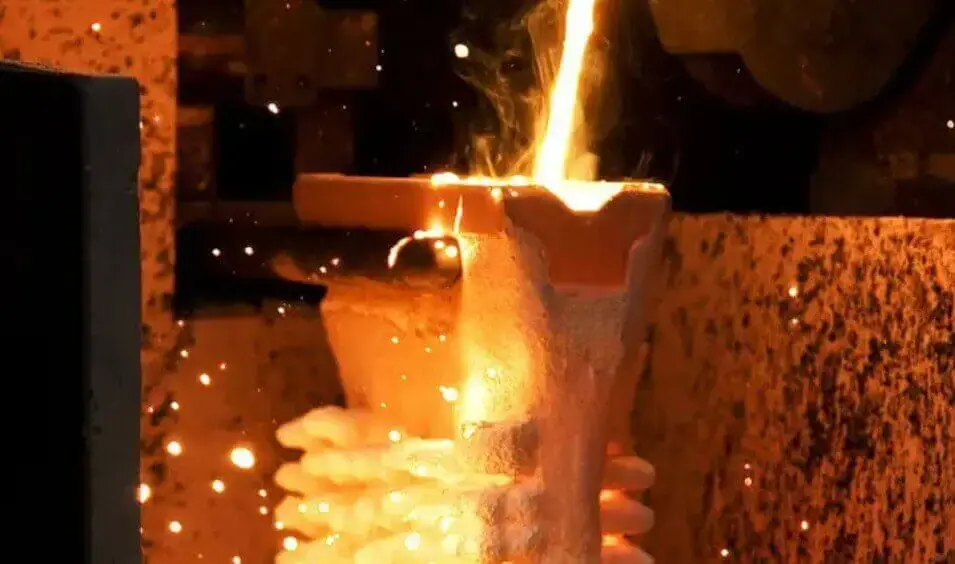
(3) Casting
1) Baking:
After dewaxing, continue to heat the mold shell to a high temperature to remove residues and increase the strength of the mold shell.
2) Casting:
Pour molten metal liquid (such as copper, aluminum, etc.) into the preheated mold shell.
3) Cooling:
After the metal liquid cools and solidifies, break the shell and take out the casting.
(4) Molding
1) Welding:
If the casting has multiple parts, it may need to be welded together.
2) Grinding:
Grind the surface of the casting to remove burrs and unevenness.
3) Polishing:
Further polish the casting to make its surface smooth.
4) Coloring:
Perform surface treatment as needed, such as coloring, electroplating, etc.
3.Precautions when using investment casting process
(1) Wax mold making
1) The temperature of the wax mold should be moderate. Too high may cause the wax liquid to overflow, and too low may not fill the mold.
2) The wax mold should be carefully trimmed to ensure a smooth surface without defects.
(2) Shell making
1) The ratio of slurry and sand should be appropriate to ensure the strength and air permeability of the shell.
2) Each layer of slurry and sand should be fully dried after gluing to avoid cracking of the shell.
(3) Dewaxing and roasting
1) The dewaxing temperature should be gradually increased to avoid the shell from cracking due to sudden temperature changes.
2) The roasting time should be sufficient to ensure that the wax model is completely volatilized.
(4) Casting
1) The temperature of the molten metal should be moderate. Too high may damage the shell, and too low may not fill the cavity.
2) The casting speed should be uniform to avoid the formation of pores and slag inclusions.
(5) Post-processing
1) Pay attention to operating safety during welding and grinding to prevent burns and other injuries.
2) Polishing and coloring should be processed according to specific requirements to ensure the appearance quality of the casting.
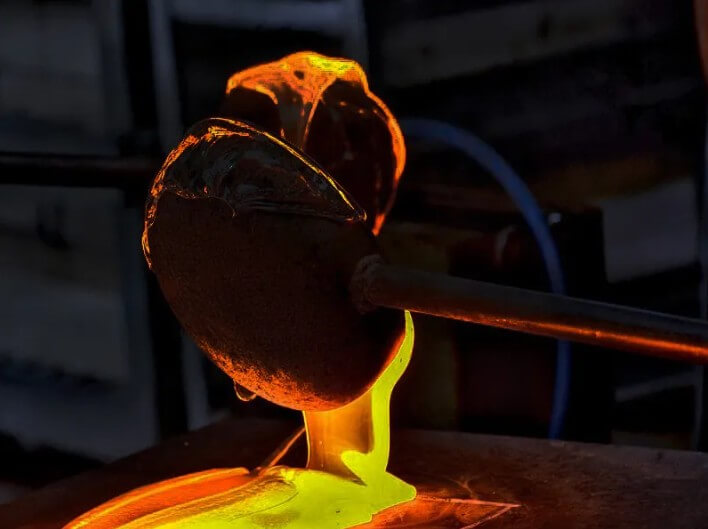

Summary:
Although the investment casting process is complex, high-precision and high-quality castings can be produced through strict process control and meticulous operation. Replaceable value.
4.Differences between investment casting and ordinary casting processes
There are significant differences between investment casting and ordinary casting processes in many aspects. These differences are mainly reflected in process flow, precision, scope of application, cost and production efficiency.
(1) Process Flow
Investment Casting: Investment casting is a precision casting process, the process mainly includes making wax molds, coating refractory materials, hardening shells, melting lost wax molds, baking shells and pouring molten metal. The production of wax molds is a key step in investment casting, and high-precision molds are required to ensure the accuracy of the size and shape of the wax molds.
Ordinary Casting: The process of ordinary casting mainly includes making sand molds, melting metal, pouring and cooling. Sand molds are usually made with sand and binders, and are molded by hand or machine.
(2) Precision
Investment Casting: Due to the high precision of the wax mold and the protection of the shell, investment casting can achieve very high dimensional accuracy and surface finish. The accuracy of the casting can usually reach CT4 to CT6, and the surface roughness can reach Ra 1.6 to 12.5 microns.
Ordinary Casting: The precision of ordinary casting is relatively low. Due to the limitations of sand mold materials and manufacturing processes, the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of castings are usually not as good as those of investment casting.
(3) Scope of application
Investment casting: Suitable for the production of small parts with complex shapes, high precision requirements, and difficult to manufacture by other processing methods, such as turbine engine blades, precision medical equipment parts, etc.
Conventional casting: Suitable for the production of parts with relatively simple shapes and large sizes, such as machine bases, pipe fittings, etc.
(4) Cost
Investment casting: Due to the complex process flow, expensive materials, and the need for high-precision equipment and molds, the cost of investment casting is relatively high.
Conventional casting: The process flow is relatively simple and the material cost is low, so the overall cost is lower than investment casting.
(5) Production efficiency
Investment casting: Although the production cost of a single piece is high, due to its high precision, it can usually reduce or eliminate subsequent machining, thus having certain advantages in overall production efficiency. However, for mass production, the production cycle of investment casting is longer.
Conventional casting: Suitable for mass production, with a short production cycle, but more subsequent machining may be required.
Summary:
Through the above comparison, it can be seen that the investment casting process and the conventional casting process each have their own advantages and applicable scenarios. The choice of process depends on the specific application requirements, cost budget and production scale.
5.Application fields of investment casting process
Investment casting technology is widely used in many fields, especially in the following aspects:
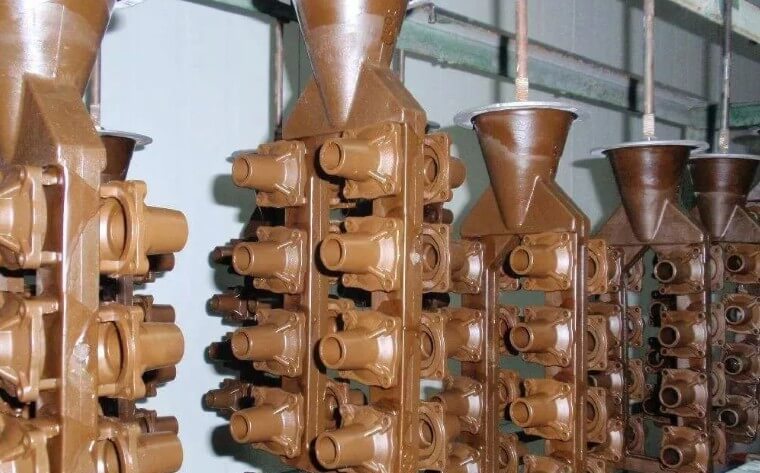

(1) Aerospace:
It is used to manufacture key components such as engine blades and turbines, which require high precision and good mechanical properties.
(2) Medical devices:
Due to its high precision and surface finish, it is suitable for manufacturing precision medical devices and implants.
(3) Automotive industry:
Produce engine parts, exhaust systems, etc. with complex shapes.
(4) Art and jewelry:
In artistic creation and jewelry making, it is used to make fine sculptures and ornaments.
6.Summary
With its unique advantages, the investment casting process occupies an irreplaceable position in modern manufacturing. With the continuous advancement and innovation of technology, investment casting technology will show its huge potential and value in more fields.