Investment casting materials: Do you know these four major categories of materials?
The selection of investment casting materials involves multiple process steps. The selection of each material is crucial and directly affects the quality and performance of the final casting. This article will conduct a comprehensive analysis and introduction around the applicable types and performance requirements of these four types of investment casting materials.
1.What are the materials for investment casting? Why is their selection important?
Investment casting materials mainly include casting materials, wax pattern materials, refractory materials and binders
One of the main advantages of investment casting is that it is suitable for a variety of materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Therefore, the final parts can achieve a variety of mechanical property combinations and are suitable for multiple applications.
Among investment casting materials, wax and refractory materials are the most core materials. Wax is used to make the initial pattern, and it is required to have good fluidity, plasticity and dimensional stability to ensure the formation of accurate investment patterns. Commonly used waxes include paraffin wax, Sichuan wax, etc., and sometimes some natural resins and plastics are added to improve their performance.
Refractory materials are used to make mold shells. They need to have excellent high-temperature strength and thermochemical stability to ensure that no deformation or cracks occur during high-temperature pouring. Quartz, zircon, fused corundum and high-alumina vanadium are commonly used refractory materials that can meet the needs of castings of different materials.
In addition to wax and refractory materials, binders are also indispensable materials in the selection of investment casting materials. Commonly used binders include water glass, silica sol and ethyl silicate, which can firmly bond the refractory materials together to form a stable shell. The selection of binders needs to match the refractory materials to ensure that the shell has good strength and permeability.
In short, the selection of investment casting materials is a complex and critical process that requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as casting material, structure, precision requirements and production cost. By rationally selecting and optimizing material ratios, the quality and production efficiency of castings can be significantly improved, and the application and development of investment casting technology in aerospace, automotive, medical and other fields can be promoted.
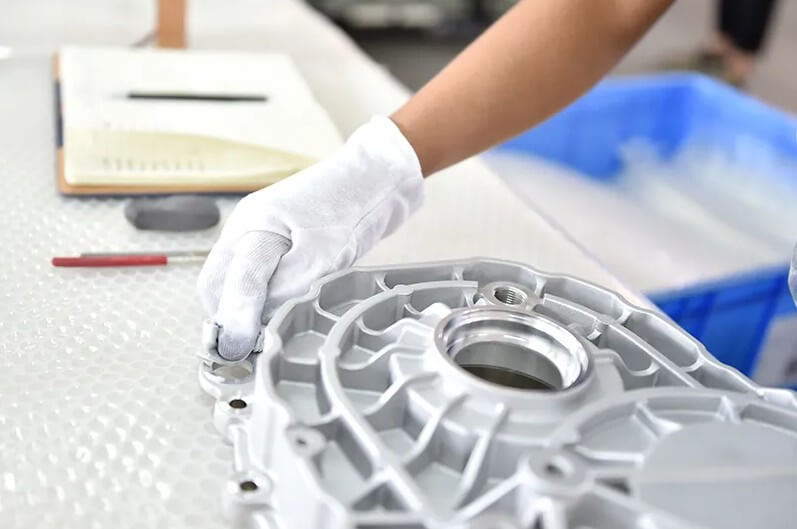

Investment Casting Product Picture
2.Investment casting materials Category 1: Metal casting materials
Commonly used metal materials for investment casting include but are not limited to the following categories:
(1) Stainless steel:
This is one of the most common materials in investment casting. It has good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties and is suitable for food processing, chemical equipment, medical equipment and industrial parts. Common grades include 304, 316, 410 and 17-4PH.
(2) Carbon steel:
High strength and good machinability, while relatively low cost. Suitable for structural parts, industrial machinery, tools and other fields. Common grades include 1020, 1045 and WCB.
(3) Alloy steel:
This material further improves its strength, hardness and wear resistance by adding alloy elements. It is suitable for parts that withstand high loads and high impacts, such as automobiles, construction machinery and heavy industrial equipment. Typical grades include 4140, 4340 and 8620.
(4) Aluminum alloy:
It is lightweight, high-strength and has good corrosion resistance. It is particularly suitable for fields that require weight reduction, such as aerospace, automotive industry and electronic equipment. Common grades include A356, A319 and 356-T6.

(5) Cobalt-based alloy:
This material has excellent wear resistance, corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability. It is suitable for aircraft engine components, medical implants and parts used under high temperature conditions. Common ones include Stellite 6, Stellite 21 and CoCr alloys.
(6) Nickel-based alloy:
It has extremely strong high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance. It is often used in high-end applications in harsh environments, such as gas turbines, aerospace engines and chemical equipment. Typical grades include Inconel 625, Inconel 718 and Hastelloy series.
(7) Copper alloy:
It is known for its good electrical and thermal conductivity. It also has good corrosion resistance and wear resistance. It is often used in electrical components, pumps and valves, decorative parts, etc. Common grades include brass, bronze and beryllium copper.
These metal materials are widely used in investment casting processes due to their respective physical, chemical and mechanical properties. Different application requirements will determine the type of alloy selected.
3.Investment casting materials category 2: wax pattern material
(1) Classification of wax pattern materials
Wax pattern materials are generally divided into three categories: low-temperature wax, medium-temperature wax and high-temperature wax:
1) Low-temperature wax pattern materials:
The melting point is below 60°C, and the commonly used paraffin-stearic acid pattern materials (50% each) belong to this category. Low-temperature wax pattern materials have low cost and simple process, and are suitable for castings of general precision.
2) Medium temperature wax mold material:
The melting point is between 60°C and 120°C. This type of mold material is usually made of rosin, ozokerite, polystyrene, etc. Medium temperature wax mold material has good fluidity and dimensional stability, and is suitable for castings with medium precision and complex shapes.
3) High temperature wax mold material:
The melting point is higher than 120°C, such as rosin-based and wax-based mold materials. High temperature wax mold material has excellent heat resistance and dimensional accuracy, and is suitable for high-precision and high-demand castings, such as aerospace parts.

(2) Performance requirements of wax mold materials
1) Thermophysical properties:
Melting temperature and solidification temperature: Appropriate melting temperature and solidification range ensure the stability of the wax mold during manufacturing and demolding.
Thermal expansion and contraction: Smaller thermal expansion and contraction rates to ensure the dimensional accuracy of the casting.
Heat resistance: Higher softening point to prevent the wax mold from deforming in a high temperature environment.
2) Mechanical properties:
Strength and hardness: Sufficient strength and hardness ensure that the wax model is not easily damaged during the production process and maintains surface finish.
Plasticity and flexibility: Good plasticity and flexibility to meet the casting needs of complex shapes.
3) Process performance:
Viscosity and coating: Appropriate viscosity and good coating ensure that the surface of the wax model is evenly coated with refractory materials.
Ash content: Low ash content (less than 0.05%) reduces surface defects of castings.n 0.05%) reduces surface defects of castings.
(3) Basis for selection of wax model materials
When selecting wax model materials in investment casting materials, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the type of casting material, the dimensional accuracy of the casting, the complexity of the shape, and the production cost. For example, for high-precision, small-sized castings, high-temperature wax model materials can be selected; for large-sized, simple-shaped castings, low-temperature wax model materials are more economical and practical.
4.Investment casting materials category 3: refractory materials
Refractory materials, as the main component of the mold shell, are also the key selection materials for investment casting materials, and play a vital role in the quality of castings. Selecting the right refractory material is the key to ensuring the surface quality, dimensional accuracy and production cost of castings.
(1) Selection criteria for refractory materials
1) Refractory properties:
Refractory materials should have sufficient refractory properties to withstand the impact of high-temperature molten metal without deformation.
2) Thermochemical stability:
At high temperatures, the material should remain chemically stable to avoid reacting with the molten metal and affecting the quality of the casting.
3) Thermal expansion coefficient:
The thermal expansion coefficient of the material should be small and uniform to reduce the risk of cracking of the shell during heating and cooling.
4) Particle size:
The particle size of the refractory material should be moderate to ensure the density and strength of the shell.
5) Cost and non-toxicity:
The cost and health impact on operators should be considered when selecting materials.

(2) Commonly used refractory materials and their properties
1) Quartz:
Quartz sand (powder) is widely used in investment casting and has good high-temperature stability and low cost. However, its thermal expansion coefficient is large, so attention should be paid to temperature control.
2) Fused corundum:
Fused corundum (α-Al₂O₃) has extremely high refractoriness and thermal conductivity, and is suitable for casting high-alloy steel and high-temperature alloys. It is relatively expensive and is usually used for surface materials.
3) Aluminum-silicon materials:
such as bauxite and refractory clay, these materials are low-cost and have good thermal stability, and are suitable for the reinforcement of the back shell.
4) Zircon:
Zircon (ZrSiO₄) has excellent thermal shock stability and high-temperature chemical stability, and is suitable for castings with high surface finish requirements.
Selecting the right refractory material is the key to the success of investment casting. The selection of investment casting materials needs to comprehensively consider factors such as casting material, precision requirements, production cost, and process conditions. Through reasonable material selection and process control, the quality and production efficiency of castings can be significantly improved.
5.Investment Casting Materials Category 4: Binder Materials
(1) Applicable types of binders
1) Ethyl silicate hydrolyzate:
This is an acidic silicate colloid obtained by hydrolysis of ethyl silicate. It is one of the earliest and most commonly used binders in investment casting.
2) Water glass:
Also known as sodium water glass, it is an alkaline silicate colloid, usually used to produce carbon steel castings with high precision requirements and non-ferrous alloy castings with low melting points.
3) Silica sol:
It has good stability and can be stored for a long time. No special hardener is required when making the mold shell, but the mold shell hardening process is a drying process and takes a long time. It is the most widely used binder.
4) Composite binder:
In addition to the above three main binders, composite binders are sometimes used, such as the composite use of water glass and silica sol to improve the performance of the mold shell.

(2) Performance requirements of binders
1) Strength performance:
The binder must have sufficient dry strength and wet strength to ensure that the mold shell is not easily damaged during transportation and pouring.
2) Fluidity:
Good fluidity helps the binder to be evenly coated on the surface of the wax mold, ensuring the compactness and surface finish of the shell.
3) Thermal stability:
Under high temperature conditions, the binder should remain stable to avoid decomposition or the generation of harmful gases that affect the quality of the casting.
4) Collapsibility:
After pouring, the binder should be easy to collapse, easy to clean, and improve the yield of castings.
6.Summary
Investment casting is different from gravity casting and die casting. Compared with these two processes, the process of investment casting is more complicated. Investment casting materials mainly include four basic materials: mold materials, refractory materials, binders and cast metal materials, while gravity casting and die casting only have one metal material, and sand molds are used in a few cases.
In summary, we know the four materials involved in the investment casting process. In addition to the cast metal material, the three materials of profiles, refractory materials and binders are unique to investment casting. Due to the wide variety of materials used and the complex process, investment casting produces higher precision parts than gravity casting and die casting. If you have parts that can be completed by investment casting, then welcome to contact us! Of course, we have a wide variety of casting projects. If you have other considerations, we can also provide you with die casting, gravity casting, low pressure casting and other related services. In this regard, you can fully trust our LVXUN processing technology.
In short, the combination of investment casting materials ensures the smooth progress of the investment casting process and the production of high-quality castings.