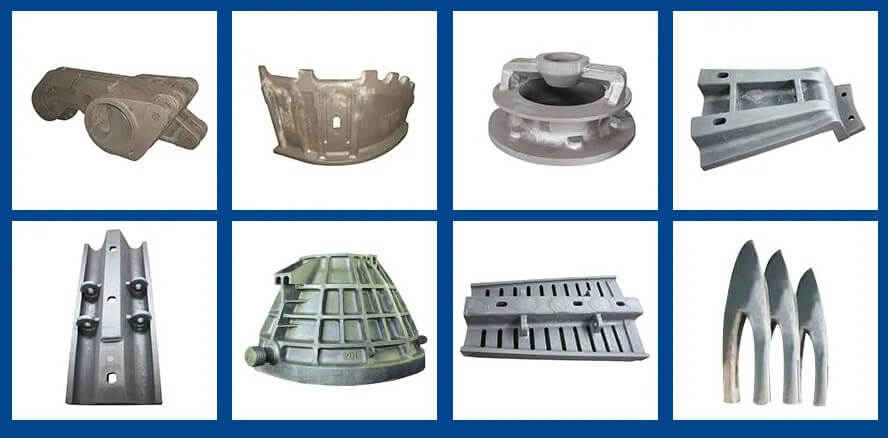
How to distinguish castings and forgings from appearance only
Castings and forgings are two common forms of metal processing. They have their own characteristics and are suitable for different application scenarios. I believe everyone is also very curious, how can we distinguish castings and forgings from appearance alone? Then this article will systematically and comprehensively answer your questions.
1.Basic concepts of castings and forgings
(1) Definition and manufacturing process of castings
Castings are made by pouring melted metal into a mold and cooling it into shape. In this process, the metal is first melted into a liquid state, then poured into a pre-prepared mold, and then removed from the mold after it cools and solidifies, thus forming the desired shape. Castings can form complex shapes and large structures, but their dimensional accuracy and surface quality are usually not as good as forgings.
(2) Definition and manufacturing process of forgings
Forgings are formed by using a forging machine to apply pressure to a metal blank to cause it to undergo plastic deformation. During the manufacturing process, the metal billet is first heated to an appropriate temperature, and then deformed and finally formed through forging or other forging processes. Forgings usually have higher mechanical properties and better internal structure density.
2.Distinguish between castings and forgings by obvious differences in appearance
There are obvious differences in the appearance of castings and forgings, which can help us preliminarily judge their manufacturing processes.
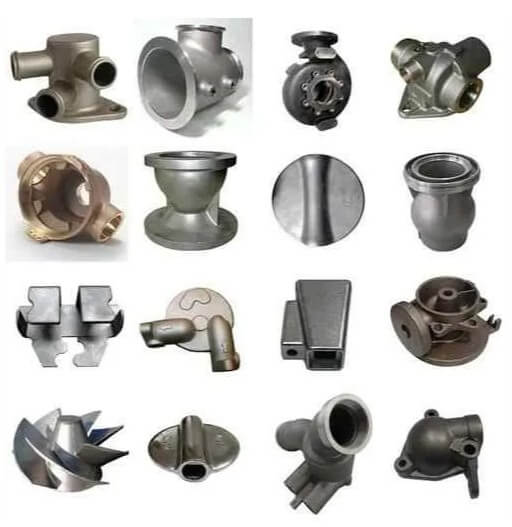
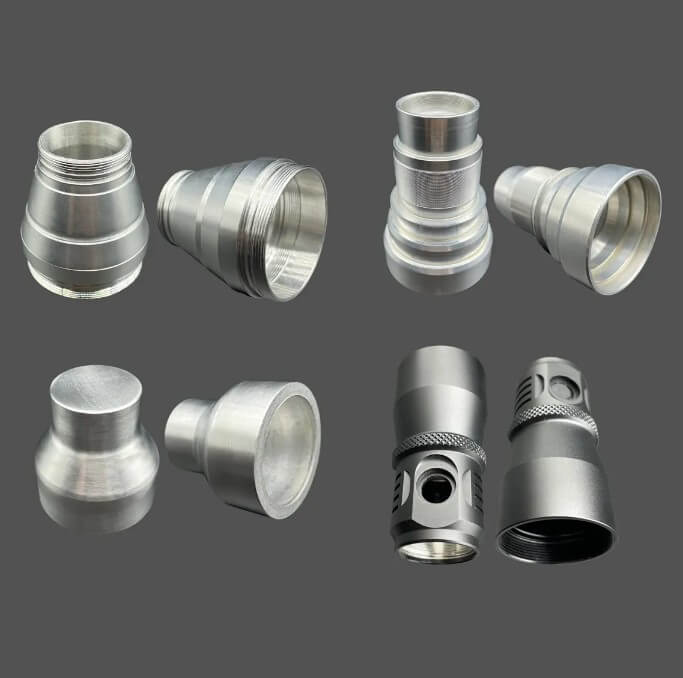


The upper part is a casting, the lower part is a forging
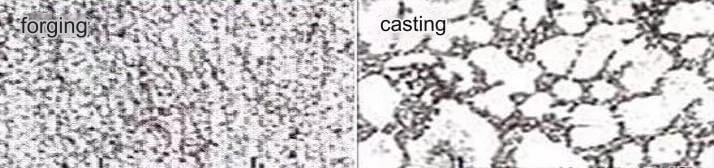
Comparison of crystal structures of castings and forgings
(1) Look at the surface quality
The surface of a casting is usually rough and may be accompanied by defects such as sand holes and pores. These defects are caused by the cooling and solidification of the metal liquid in the mold during the casting process. The surface of a forged part is relatively smooth, with a fine structure and usually no obvious defects. This is because during the forging process, the metal undergoes plastic flow under high temperature and pressure, making its internal structure more dense.
(2) Look at the external dimensions
Castings are suitable for manufacturing complex shapes and large parts, but due to their manufacturing characteristics, their dimensional accuracy is relatively low. On the contrary, although forgings are relatively simple in shape and more suitable for the manufacture of small and medium-sized parts, their dimensional accuracy is higher. This is mainly because the metal deformation during the forging process is more controllable.
(3) Look at the fracture characteristics
The fracture of a casting is usually granular and dark in color. The fracture of a forged part is fibrous and bright in color. This is because the grain structure of the metal is elongated under the action of force during the forging process, forming a fibrous structure.
(4) Look at the corners and transition areas
The corners of a casting may be smoother and the transition area more natural. This is because during the casting process, the liquid metal flows in the mold and naturally forms a smooth transition.
The corners of a forged part may be sharper and the transition area more obvious. During the forging process, the metal billet deforms under pressure, and a clearer fold line may be formed at the corners.
3.Distinguish between castings and forgings by checking specific marks and traces
(1) Check for pouring and riser marks
During the manufacturing process, castings will leave traces of pouring and riser marks. These marks are the points where the liquid metal enters the mold and are usually visible on the surface or edge of the casting. Forgings do not have these marks because they are formed by forging rather than pouring liquid metal.
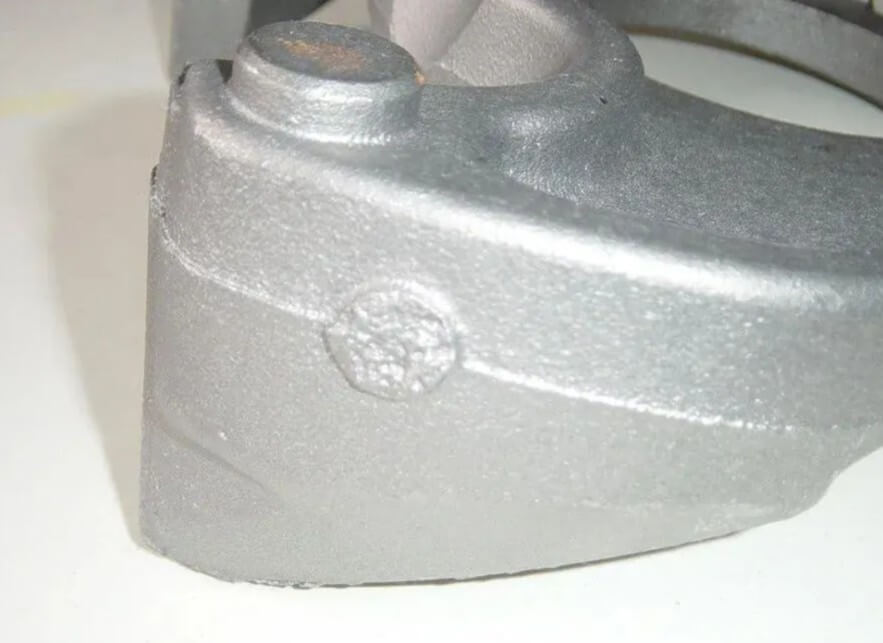

The traces of the casting riser
(2) Check for specific forging marks
During the manufacturing process, forgings may leave forging marks on the surface, such as forging lines or textures. These marks are formed when the metal is subjected to force and deformation during the forging process, while castings do not have these forging-specific marks.
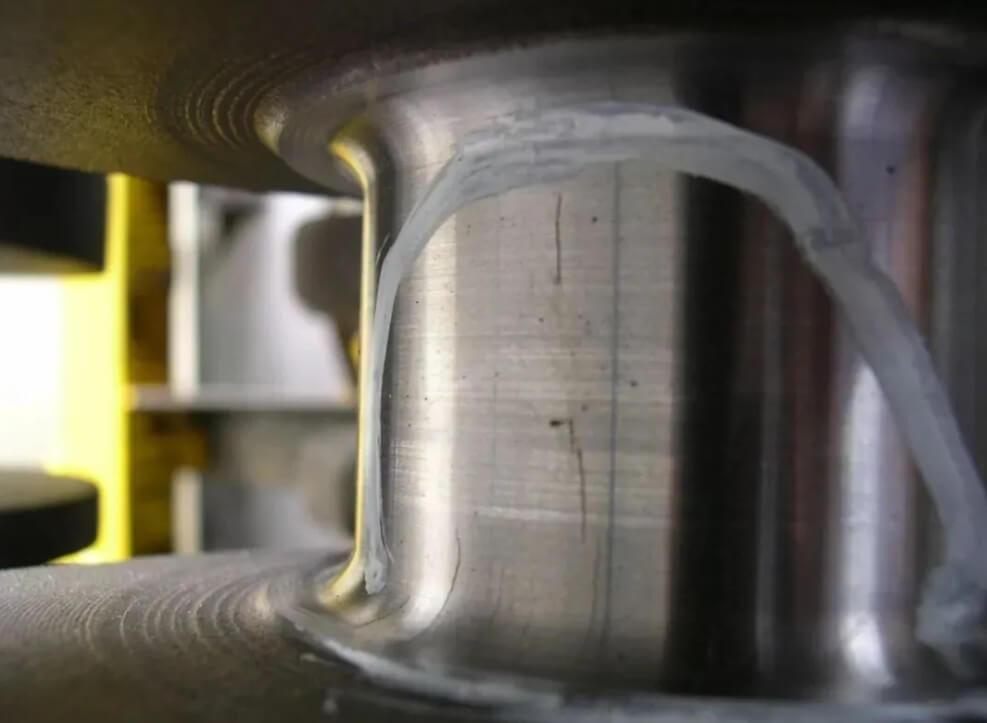
Forging lines or texture marks
4.Distinguish between castings and forgings by material structure and mechanical properties
(1) Determine material structure
The crystal structure of castings is usually coarse and the structure is uneven, which affects its overall performance. During the forging process, the crystal structure of the metal is refined and the structure is more uniform, which makes forgings generally better than castings in terms of performance.
(2) Determine mechanical properties
Due to the difference in structure, the mechanical properties of castings are usually lower, especially in terms of impact toughness and ductility. Due to their fine crystal structure and uniform material structure, forgings have higher strength and toughness, better ductility, and are therefore more suitable for applications that bear heavy loads and dynamic loads.
5.Differentiate between castings and forgings by usage scenarios and typical applications
Castings and forgings have their own characteristics and performance differences, and they have their own advantages in different fields and applications.
(1) Application of castings
Castings are often used to manufacture parts with complex shapes and large sizes, such as valve housings, machine tool beds, etc. These applications usually do not require high mechanical properties, but focus more on the shape complexity and cost-effectiveness of the parts.
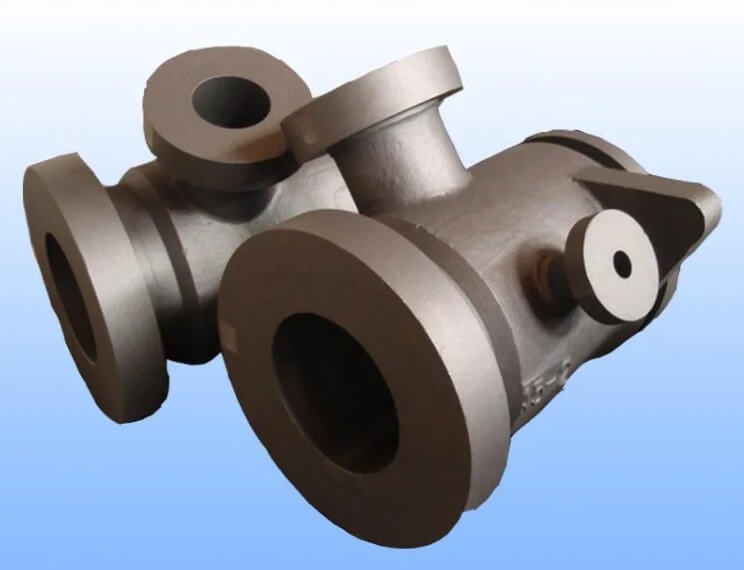

Casting: valve housing
(2) Application of forgings
Due to their excellent mechanical properties, forgings are often used to manufacture parts that withstand large stresses and require high reliability, such as automobile connecting rods and gears. These parts need to withstand large mechanical stresses during operation, so they have high requirements for the strength and toughness of the material.
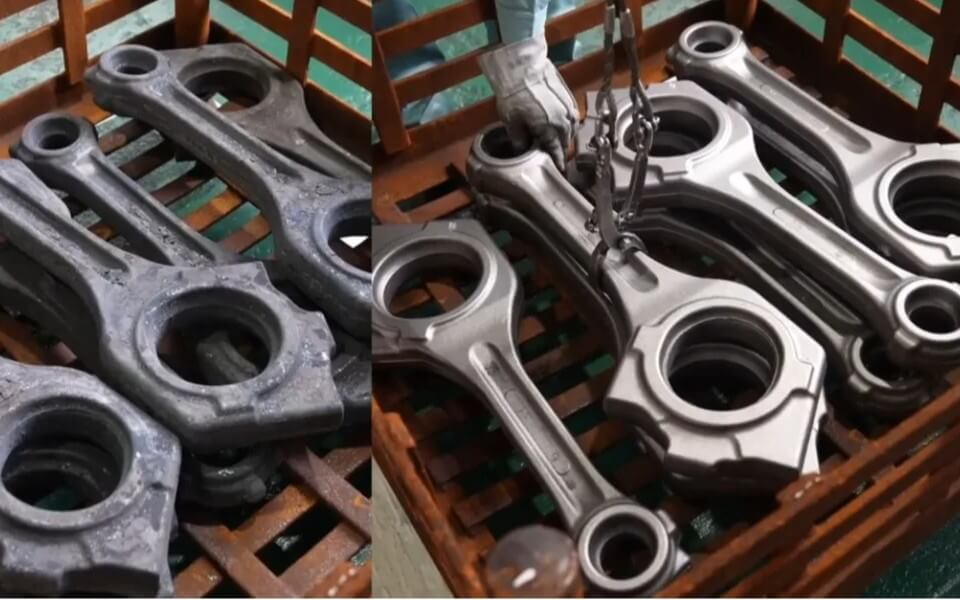

Forging: automobile connecting rod
6.Differentiate between castings and forgings by comprehensive judgment methods
Although castings and forgings have obvious differences in appearance, in actual applications, comprehensive judgments must be made based on the material, performance, and usage scenarios. The following are some commonly used comprehensive judgment methods:
(1) Spark identification method
Judge the material by observing the spark characteristics of the metal on the grinding wheel. The sparks produced by different materials during high-speed grinding have different colors, shapes and densities, which can be used as a preliminary identification method.
(2) Magnetic identification method
Use a magnet to detect the magnetism of the material. Cast iron is usually more magnetic than steel, so this method can be used to distinguish between cast iron and steel forgings.
(3) Hardness test
Use a hardness tester to test the hardness of the material. Forgings are usually harder due to their fine crystal structure. Hardness testing can further verify the manufacturing process of the material. Through these methods, it is possible to more accurately determine whether the metal product is a casting or a forging, thereby ensuring that the selected material is suitable for specific application requirements.
7.Summary
Through the above methods, we can more accurately distinguish between castings and forgings based on appearance alone. These appearance features not only reflect the essential difference between the two processes, but also provide us with a simple and effective means of identification.




