Hot chamber die casting: advanced technology for efficient production
As an advanced metal forming technology, hot chamber die casting occupies an important position in modern manufacturing with its unique production method and significant advantages. This article will analyze in depth.The basic principles, characteristics, process steps, optimization of process parameters, applicable materials and related issues in application fields of hot chamber die casting.
1.Basic principles and characteristics of hot chamber die casting technology
(1) Basic principles
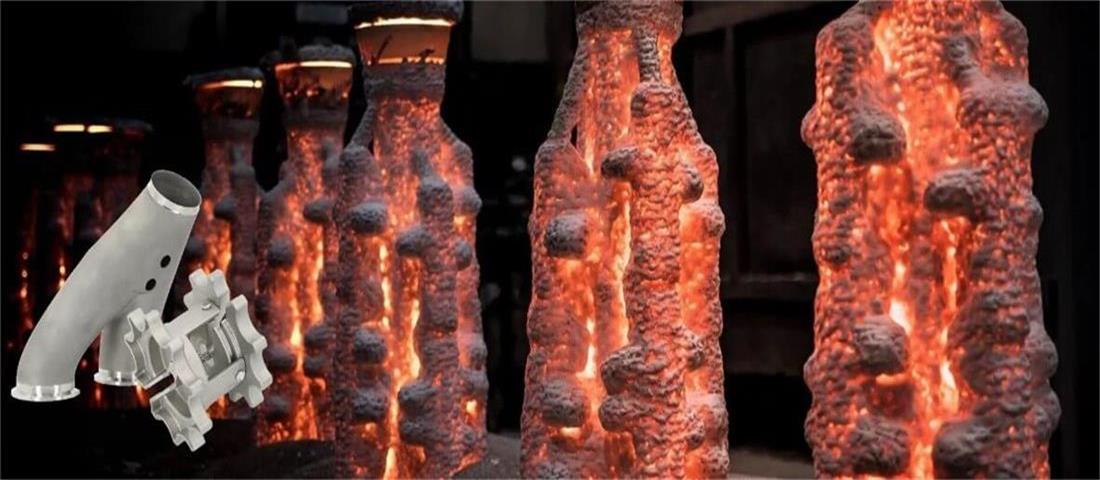
Hot chamber die casting is an efficient metal forming technology, mainly used in the processing of low melting point alloys such as zinc and magnesium. The basic principle is to keep the molten metal in a molten state, quickly inject it into the mold cavity through high pressure, and form a casting of the desired shape after cooling and solidification. The core of this technology is to maintain the temperature and pressure of the molten metal to ensure the smooth progress of the molding process.
(2) Preparation and heating of molten metal
In the hot chamber die casting process, the molten metal is usually heated and maintained at a constant temperature in a special crucible. Crucible design and material selection are critical and need to be able to withstand high temperatures and be effectively insulated to reduce heat loss. The heating method generally uses electric heating to ensure the accuracy of temperature control.
(3) Main features
1) High production efficiency:
Since the molten metal is always in a molten state during the hot chamber die casting process, casting can be performed continuously, greatly improving production efficiency. Especially suitable for mass production.
2) Castings have high dimensional accuracy
This technology can produce castings with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surfaces, reducing the workload of subsequent processing.
3) Fast production cycle
The integrated design of the furnace and injection system of the hot chamber die casting machine allows the molten metal to directly enter the injection chamber, reducing transfer time and heat loss. The entire process is highly automated, greatly shortening the production cycle.
4) Economical and affordable
This process is cheaper than techniques such as cold chamber die casting for several reasons. First, its high productivity directly increases profitability. Additionally, with a built-in furnace, the machine has a smaller footprint, saving manufacturers the cost of equipment and labor responsible for moving molten metal from the furnace to the mold.
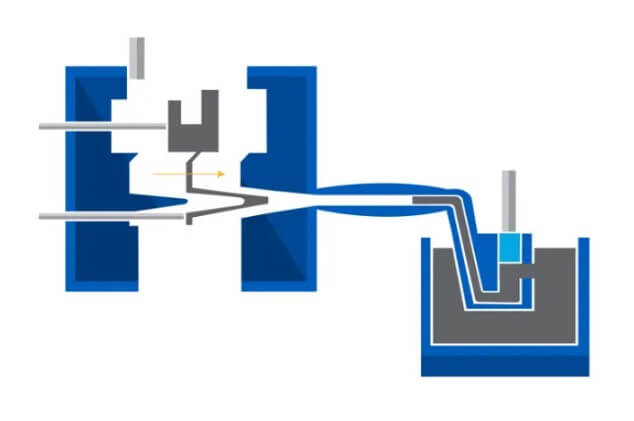
2.Structure and type of hot chamber die casting machine
(1) Structure
1) Injection mechanism
The injection mechanism is the core part of the hot chamber die casting machine, responsible for injecting molten metal into the mold at high speed and high pressure. It usually includes components such as a punch, a pressure chamber, and a gooseneck kettle. Punch design and material selection are critical to the die-casting process and require good wear and heat resistance.
2) Mold clamping mechanism
The mold clamping mechanism is responsible for opening, closing and locking the mold, ensuring that the mold can be tightly closed when high-pressure molten metal is injected to prevent leakage. The accuracy and reliability of this part of the mechanism have a direct impact on the quality of castings.
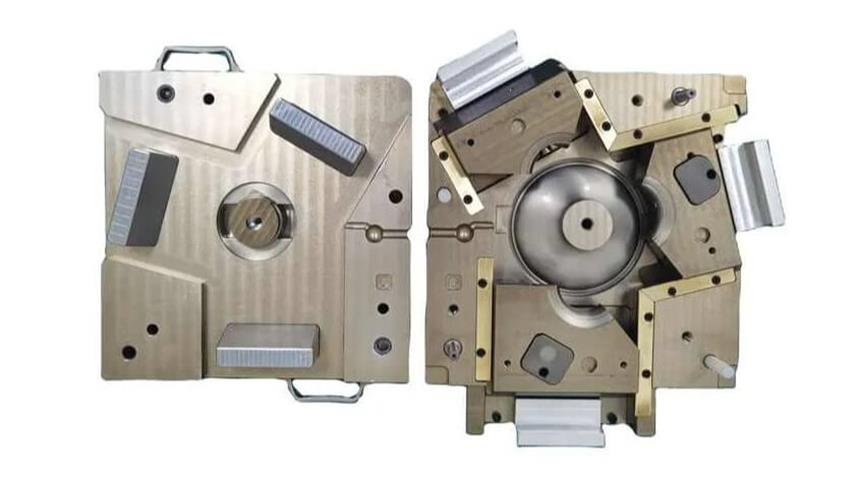
3) Die casting mold
The die-casting mold is the core part of casting molding, and its design and manufacturing accuracy directly affect the quality of castings. Mold materials usually need to have good heat resistance and wear resistance to withstand high temperature and high pressure working environments.
(2) Type
1) Vertical hot chamber die casting machine
The injection mechanism and the mold are arranged vertically, and the molten metal is injected into the mold from above. This layout is beneficial to the flow of molten metal and the discharge of gas, and is suitable for the production of complex-shaped castings.
2) Horizontal hot chamber die casting machine
The injection mechanism and the mold are arranged horizontally, and the molten metal is injected into the mold from the side. This layout is simple to operate and maintain, and is suitable for mass production.

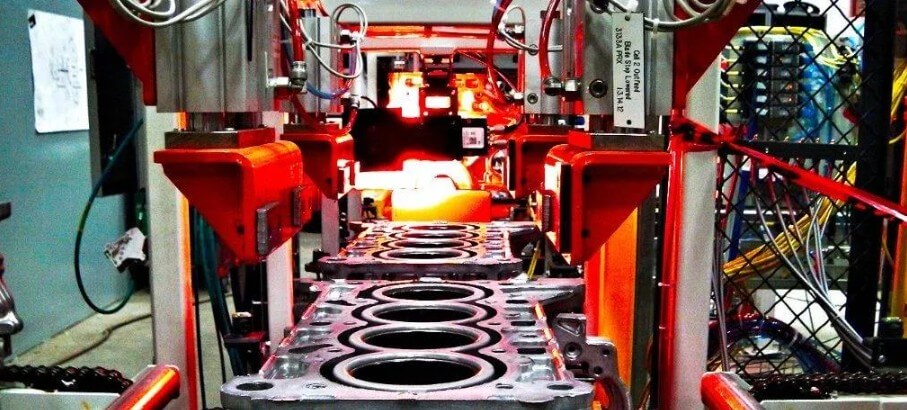
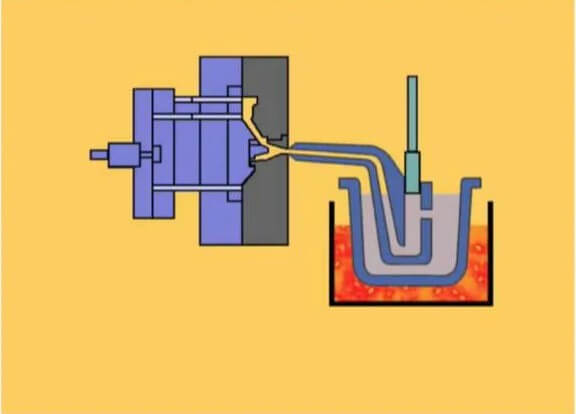
3.Analysis of the main steps of the hot chamber die-casting process
(1) Hot cell filling:
In hot chamber die casting, the injection chamber and injection punch are immersed in molten metal. When the injection hammer head rises, the molten metal in the crucible enters the pressure chamber of the kettle through the entrance of the kettle to prepare for subsequent injection.
(2) Injection:
After the mold is closed, when the hammer head is pressed down, the molten metal is filled from the nozzle head into the die-casting model cavity along the channel. This process requires precise control to ensure that the molten metal fills all parts of the mold evenly and quickly.
(3) High pressure die casting:
After the molten metal is filled, the pressure is maintained until the casting solidifies. This high-pressure stage is crucial to ensure the density and strength of the casting.
(4) Cooling method:
After the casting has cooled and solidified in the mold, the mold is held together under pressure. Once the metal is cool enough, the mold is opened and the casting is ejected through the ejection pin. The cooling process is equally important to prevent deformation of the casting and ensure its dimensional accuracy.
4.Selection and optimization of hot chamber die casting process parameters
(1) Selection of injection force
The choice of injection force has a crucial impact on the quality of castings. If the pressure is too low, the casting may be underfilled and defects may appear; if the pressure is too high, the mold may be damaged. Therefore, the injection force needs to be reasonably selected based on factors such as the material, shape, and size of the casting.
(2) Control of injection speed
Injection speed is another important factor affecting casting quality. Appropriate injection speed can ensure that the molten metal fills the mold evenly and avoids defects such as pores and inclusions. The control of injection speed needs to be combined with the specific conditions of the casting, and the best parameters must be determined through experiments and optimization.
(3) Temperature control
Temperature control is a key link in the hot chamber die casting process. Including the temperature control of the molten metal and the temperature of the mold. The temperature of the molten metal needs to be maintained within an appropriate range to ensure its fluidity and filling capacity; the temperature of the mold needs to be controlled within an appropriate range to avoid castings cooling too fast or too slowly, which affects casting quality and production efficiency.
5.Common hot chamber die casting materials and their applications
(1) Zinc alloy
Zinc alloy is one of the most commonly used materials and has good flowability and formability. Zinc alloy castings are often used in automobiles, electronics, home appliances and other fields because of their low cost and good mechanical properties.
(2) Magnesium alloy
Magnesium alloy is the lightest metal structural material, has good strength and rigidity, and is suitable for manufacturing high-performance lightweight components. Magnesium alloy castings are widely used in automobiles, electronics, aerospace and other fields.

(3) Why not use aluminum alloy as a material?
Because the melting point of aluminum alloy is relatively high, generally above 600°C, the injection chamber and furnace of a hot chamber die casting machine are usually designed in the same heating system and cannot reach such high temperatures. If aluminum alloy is used as the material for hot chamber die casting, the aluminum alloy will not be completely melted, affecting the shape and quality of the die casting. In addition, high temperatures can cause damage to the components of the die-casting machine and reduce the service life of the equipment.
6.Application fields of hot chamber die casting technology
(1) Automobile industry
In the automotive industry, hot chamber die casting technology is mainly used to produce engine parts, transmission parts, body structural parts, etc. These components require high precision and good mechanical properties, and this technology can meet these requirements.
(2) Electronic products
Applications in electronic products are mainly concentrated in structural parts such as housings and frames. These parts often require high dimensional accuracy and surface quality, and this technology provides a high-quality solution.
(3) Aerospace field
This technology can process lightweight materials such as magnesium alloy and zinc alloy to meet the high requirements for weight reduction in the aerospace field. For example, an aerospace engine uses hot chamber die-cast magnesium alloy components, which reduces weight by 30% and improves fuel efficiency by 5% compared with traditional materials.
(4) Household appliances
In the field of household appliances, it is mainly used to produce various structural parts and covers. For example, the casings and internal structural parts of home appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines can be manufactured using this technology.
7.Summary
In short, hot chamber die casting technology is an important metal forming technology with broad application prospects. And with its advantages such as high efficiency and stability, it is playing an increasingly important role in modern manufacturing.




