Gravity Casting and Die Casting: Which is Better?
In the manufacturing industry, there are two popular methods for casting metal parts: gravity casting and die casting. Each has unique characteristics and advantages and is suitable for different applications. This article will provide a comprehensive comparison and analysis of gravity casting and die casting.
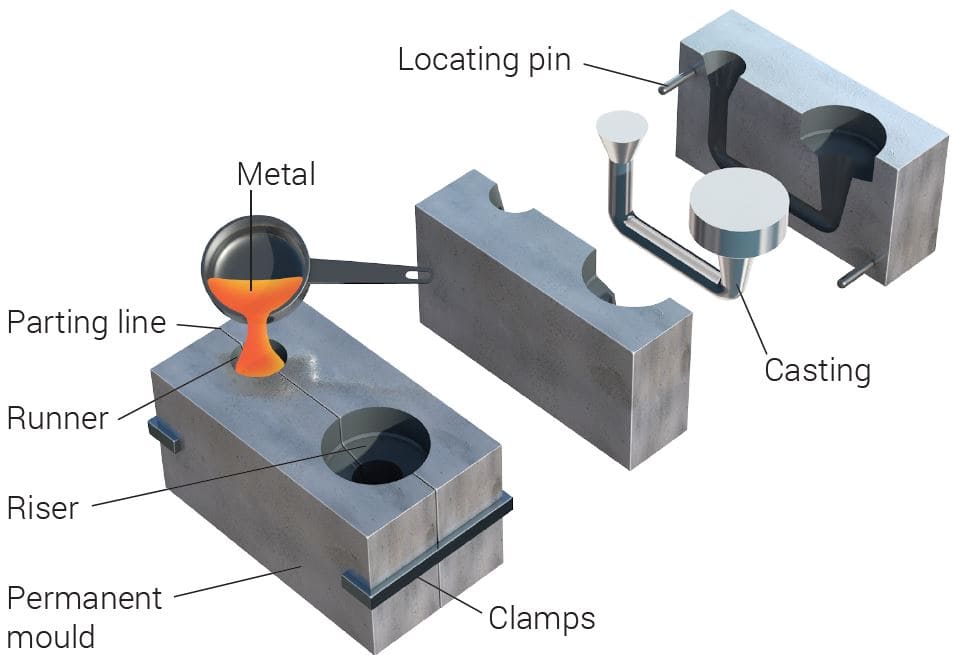
1.Gravity Casting Process
Gravity casting is a casting method that uses gravity to guide molten metal into a mold. The process mainly includes the following steps:
(1) Mold preparation:
Design, clean, treat and heat the mold to shape it to fit the final product.
(2) Metal Pouring:
Heat the metal to the appropriate temperature and pour it into the mold.
(3) Cooling:
The metal solidifies evenly through the cooling channel.
(4) Removing the casting:
Open the mold and remove the casting.
(5) Post-processing:
Post-processing and inspection to ensure product quality.
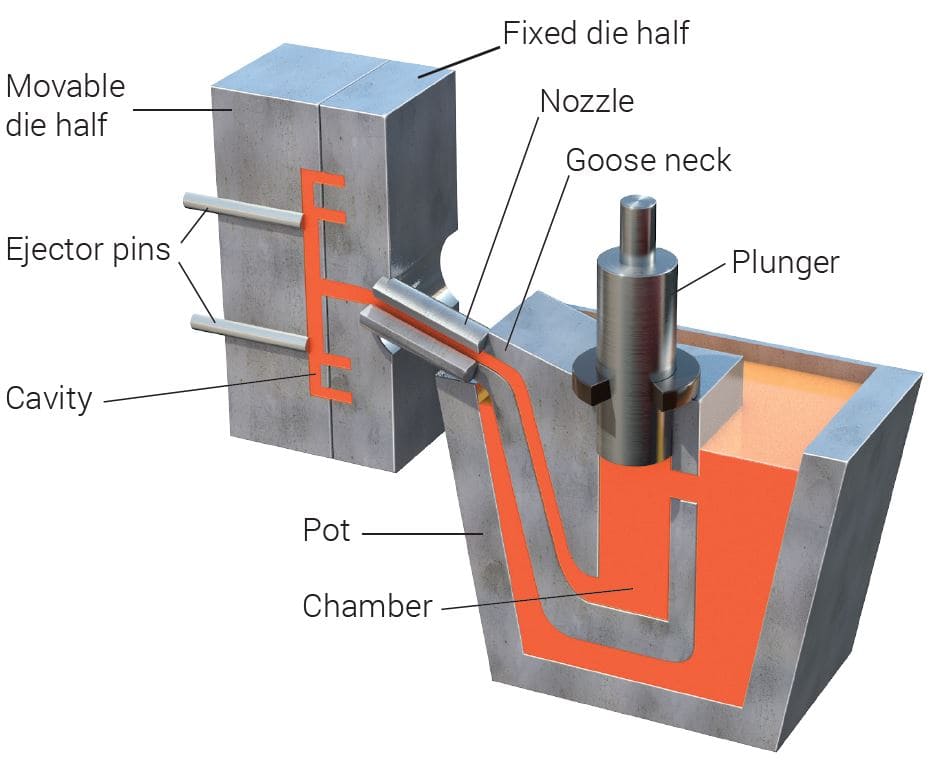
2.Die Casting Process
Die casting uses a reusable two-part mold to shape the metal using pressure. The process is as follows:
(1) Mold preparation:
Mold closing, cleaning, coating, preheating, forming a sealed mold cavity.
(2) Molten metal pouring:
The alloy is melted and poured into the mold under high pressure.
(3)Cooling and solidification:
Cooling channels are used to ensure uniform cooling.
(4)Casting ejection:
Separate the mold and eject the casting.
(5)Final processing:
Remove excess material and finish to final size.
3.Difference between gravity casting and die casting
(1) Finished product
Gravity casting: The parts produced have high surface finish and excellent dimensional accuracy, but the complexity is relatively low.
Die casting: Highly complex parts with excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish can be produced, allowing for more complex designs.
(2) Production process
Gravity casting: In gravity casting, the metal cools naturally and solidifies at its own rate, which is suitable for parts that do not require rapid cooling.
Die casting: In contrast, die casting enables the metal to cool rapidly by using high-pressure channels and rapid cooling.
(3) Production speed
Gravity casting: Gravity casting is slow to produce parts due to low pressure and long cooling time. However, it can produce larger and thicker parts.
Die casting: High efficiency, suitable for large-scale production, can produce more complex parts, and has fast production time.
(4) Performance
Gravity casting: Due to natural cooling and reusable molds, the resulting parts have better ductility and impact resistance
Die casting: High pressure casting and special equipment produce stronger and more durable parts, suitable for industries such as automotive and aerospace that require high-strength parts.
4.How to choose between gravity casting and die casting?
When choosing between gravity casting and die casting, there are several factors to consider:
(1) Scale and complexity
Gravity casting: Suitable for large, simple parts. Natural cooling and reusable molds can handle larger sizes and do not require very tight tolerances.
Die casting: Suitable for complex designs, high pressure and rapid cooling can produce complex shapes and small parts.
(2) Performance
Gravity casting: Suitable for small and medium batch production, high flexibility, and does not require expensive special equipment.
Die casting: Suitable for large-scale production, high efficiency, and short cycle time.
(3) Cost and cycle time
Gravity casting: Low initial cost, suitable for small projects or projects with tight budgets.
Die casting: Although the initial cost of molds and equipment is higher, the high production speed can offset this cost when mass production.
(4) Industrial application
Gravity casting: It can produce delicate and beautiful surfaces and is suitable for decoration or places with high surface requirements.
Die casting: Common in the automotive and aerospace industries, it can produce very fine and precise parts.

Therefore, the choice between gravity casting and die casting depends on the specific requirements of the product, such as size, complexity, output, cost considerations, and intended applications. Careful evaluation of these aspects will help to select the most appropriate casting method.




