Treatment and protection of casting surface
The treatment and protection of the casting surface is a key step to ensure its performance and beauty. Surface treatment technologies such as electroplating, painting, metal spraying and anodizing can form a protective layer on the casting surface in different ways, effectively improving the corrosion resistance, wear resistance and decorativeness of the casting. Therefore, understanding and mastering various surface treatment technologies is of great significance to improving the quality of castings and extending their service life.
1.Importance of Casting Surface Treatment
Casting surface treatment is an indispensable part of the casting process. It has a direct and significant impact on the performance, appearance and service life of castings. Surface treatment technology can not only improve the physical and chemical properties of castings, but also improve their aesthetics and market competitiveness.
(1) Effect of surface treatment on casting performance
Surface treatment can significantly improve key properties of castings such as corrosion resistance and wear resistance. For example, through surface treatment technologies such as electroplating and spraying, a protective film can be formed on the surface of the casting to effectively prevent external media from corroding the casting body. This is especially important for castings operating in harsh environments, such as offshore platforms, automotive engine parts, etc. In addition, surface treatment can also improve the mechanical properties of castings, such as hardness, toughness and fatigue strength, thereby extending their service life.
(2) Effect of surface treatment on the appearance of castings

Proper surface treatment technology can significantly improve the appearance quality of castings. For example, through mechanical processing such as grinding and polishing, the surface of the casting can be made smooth and delicate, improving its visual effect and market competitiveness. In some application fields that have high requirements on appearance, such as architectural decoration, household appliances, etc., good surface treatment can make castings more attractive. In addition, surface treatment can also cover defects on the casting surface, such as pores, cracks and inclusions, etc., and improve the overall quality of the casting.
(3) Effect of surface treatment on the service life of castings
Proper surface preparation can significantly extend the service life of your castings. For example, anti-corrosion coating treatment can prevent corrosion of castings in harsh environments and extend their service life. This has important economic significance for some key components, such as bridge structures, oil pipelines, etc. In addition, surface treatment can also reduce the maintenance and repair costs of castings and improve their economic benefits. For example, surface hardening treatment can improve the wear resistance of castings and reduce wear and damage, thereby reducing the frequency and cost of maintenance and repairs.

2.Requirements and standards that the casting surface must meet
The quality of the casting surface directly affects its service life and appearance, so it must meet certain requirements and standards. The following are the main requirements and standards that the casting surface needs to meet:
(1) Surface roughness requirements:
The roughness of the casting surface is usually measured by the arithmetic mean deviation of the profile (Ra), in microns (um). According to different process requirements, surface roughness is divided into different levels, such as Ra 1.6, Ra 3.2, Ra 6.3, etc. The surface of the casting needs to reach the corresponding roughness level according to the usage requirements.

(2) Surface defect requirements:
There shall be no obvious defects on the casting surface, such as pores, cracks, sand inclusions, cold shuts, etc. These defects can seriously affect the strength and appearance of the casting. The surface should be smooth and flat without any penetrating defects.
(3) Cleaning requirements:
The cleaned casting surface should be free of molding sand, core sand, sticky sand and other residues. Succulents, burrs, flying edges, pouring risers, etc. should be shoveled flat and flush with the casting surface to ensure a neat appearance.
(4) Size and shape requirements:
The geometry and dimensions of the castings should comply with the requirements of the product drawings and ordering agreement. For inclined parts on castings, the dimensional tolerances should be arranged symmetrically along the inclined plane. Wrong shapes, casting deviations, etc. should be corrected to achieve a smooth transition.

(5) Surface treatment requirements:
As needed, the non-machined surface of the casting may require shot peening or other surface treatment to meet cleanliness level Sa21/2 or other standard requirements.
(6) Additional technical requirements:
For special-purpose castings, such as surfaces that require coating, polishing or sealing, the corresponding process requirements should be met to ensure that there are no defects on the surface that will affect subsequent processing or use.
(7) Defect acceptance criteria:
For some minor defects that cannot be completely avoided, such as surface bulges or depressions, their degree and quantity should comply with the standards agreed by both the supplier and the buyer. Grading acceptance is usually done based on the height, area percentage, etc. of the defect.

summary:
Through strict implementation of the above requirements and standards, we can ensure that the surface quality of castings meets expectations and provide reliable guarantee for subsequent use.
3.Casting surface treatment measures
Surface treatment of castings is a key step in improving their quality, durability and aesthetics. The following are several main surface treatment measures designed to meet the needs of different application scenarios.
(1) Mechanical treatment:
Mechanical treatment is an important means of preliminary cleaning of the casting surface, including tumbling, sandblasting, polishing and grinding. These methods can effectively remove the oxide scale and rust on the casting surface, providing a clean surface for subsequent treatment. For example, the surface of the casting after sandblasting is more uniform, which is conducive to the adhesion of subsequent coatings.
(2) Cleaning, oil and rust removal:
Cleaning is the basic step of surface treatment, usually using clean water or specific cleaning agents. Cleaning not only removes dust and dirt from the surface, but also prepares it for subsequent chemical treatment. Oil and rust removal is a key link. Commonly used methods include chemical oil removal and pickling and rust removal to ensure that the surface is oil-free and rust-free, exposing a fresh metal matrix.
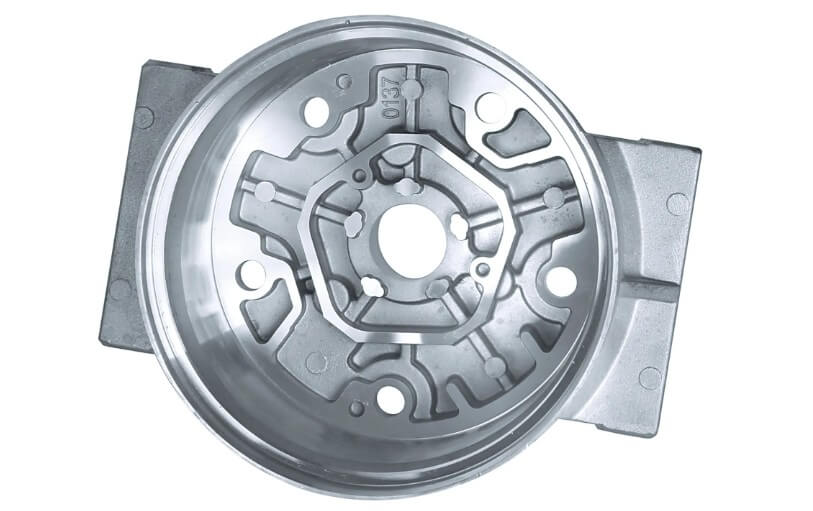

(3) Blackening treatment:
Blackening treatment is a commonly used surface anti-rust measure, especially the normal temperature blackening process, which is widely used because of its low cost and simple operation. Blackening at room temperature can form a uniform black protective film on the surface of the casting to improve rust prevention and aesthetics. After treatment, sealing is required to prevent acidic residual liquid from corroding the surface.
(4) Phosphating treatment:
Phosphating treatment not only improves the rust-proof performance of the casting by forming a phosphate film on the surface of the casting, but also enhances the adhesion of the coating. Phosphating treatment is divided into two types: normal temperature and medium temperature, which can be selected according to specific needs. The surface of the phosphated casting is gray-black and is suitable for pre-treatment in processes such as painting and plastic spraying.
(5) Electroplating and painting:
Electroplating can coat other metal layers on the surface of castings, such as copper, nickel, chromium, etc., to improve its wear resistance, corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Painting involves applying various paints, such as epoxy anti-rust primer and alkyd topcoat, on the surface of the casting to further enhance its protective capabilities. Phosphate or chromate solution treatment is usually required before painting to improve the adhesion of the paint layer.
(6) Metal spraying and anodizing treatment:
Metal spraying is to cover the surface of castings with a thin metal film under high vacuum to simulate different metal appearances. It is widely used in occasions with high decorative requirements. Anodizing treatment forms an oxide film on the surface of zinc alloy castings through electrolysis, which significantly improves its corrosion resistance and hardness.
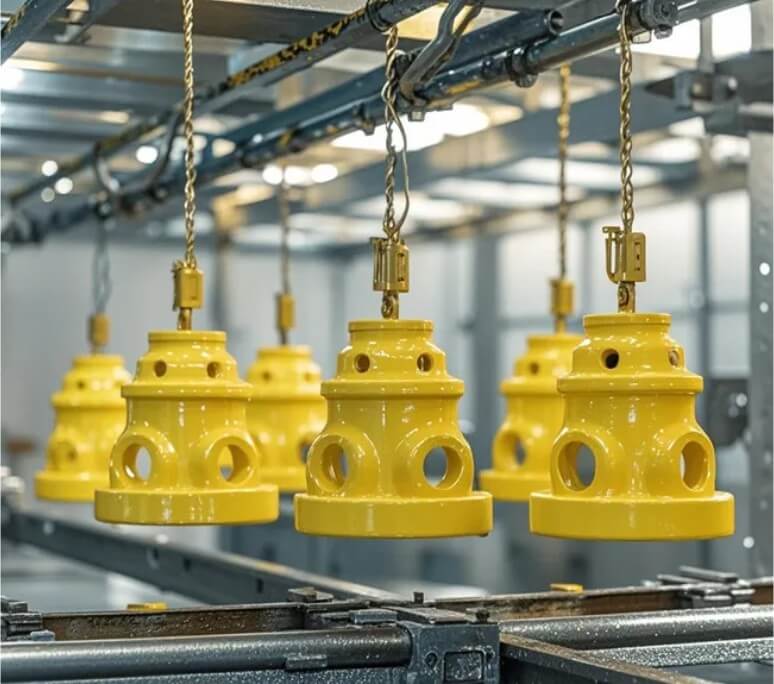

(7) Closed processing:
Sealing treatment is the last step of surface treatment. The purpose is to close the pores on the surface of the casting to prevent the penetration of corrosive media. Commonly used sealants include HH912 chromium-free passivation liquid, water-soluble sealants, etc. The protective capabilities of sealed castings are significantly improved and can meet the requirements for long-term storage and use.
summary:
Through the above surface treatment measures, the corrosion resistance, aesthetics and service life of castings can be effectively improved to meet the needs of different application scenarios.

4.Selection and cost-benefit analysis of casting surface treatment
When choosing a suitable casting surface treatment method, it is necessary to consider not only the material properties of the casting, but also the environment in which it is used to achieve the best cost-effectiveness. Here are some points on how to choose a surface treatment method based on the casting material and use environment, and analyze its cost-effectiveness.
(1) Select the processing method according to the casting material
1) Steel castings
Mechanical grinding: suitable for removing surface scale, rust spots and burrs. The cost is low, but the labor intensity is high and the efficiency is low. Suitable for preliminary processing during mass production.
Chemical treatment: Use acid or alkali washing to remove surface impurities. The efficiency is high, but attention must be paid to controlling the time and solution concentration to prevent excessive corrosion. Suitable for thin plate parts and small castings.
Electroplating: Plating other metals, such as zinc, nickel, etc., on the surface of steel to improve corrosion resistance and decoration. The cost is higher, but the effect is significant.
2) Aluminum castings
Mechanical grinding: also suitable for preliminary cleaning of aluminum castings.
Anodizing: Forming an oxide film on the aluminum surface to improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance. The cost is moderate, the effect is good, and it is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Chemical conversion coating treatment: such as chromate treatment, which forms a protective film and improves corrosion resistance. However, due to environmental issues, it was gradually replaced by chromium-free treatment.
3) Copper castings
Mechanical grinding: remove surface oxide layer and impurities.
Electroless plating: such as electroless nickel plating, which improves surface hardness and wear resistance.
Hot-dip plating: such as hot-dip tin plating, which improves corrosion resistance and conductivity.
(2) Select the treatment method according to the use environment
1) Resistant to corrosive environment
Chemical conversion coating treatment: such as phosphating treatment to form a protective film and improve corrosion resistance.
Electroplating: Plating corrosion-resistant metals, such as zinc, chromium, etc.
Coating: Spray anti-corrosion paint to form a protective layer.
2) Wear-resistant environment
Mechanical grinding: improve surface roughness and enhance friction coefficient.
Thermal spraying: Such as thermal spraying ceramics to improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
Overlay welding: Overlay welding of wear-resistant alloy to improve surface wear resistance.

3) Decorative environment
Electroplating: Plating bright metals, such as chromium, nickel, etc., to improve decoration.
Painting: Spray decorative paint to create a beautiful surface.
Hot Stamping: Hot stamping metal foil to create a decorative pattern.

(3) Cost-effectiveness:
1) Economy:
For large-scale production of castings, priority should be given to lower-cost and more efficient processing methods, such as mechanical grinding, sandblasting, etc. Although these methods are simple, they can effectively remove surface impurities and meet basic needs.
2) Efficiency:
Highly automated processing methods such as electrophoretic coating, electrostatic spraying, etc., although the initial equipment investment is high, can significantly improve production efficiency and are suitable for mass production.

3) Long-term benefits:
Although some casting surface treatment methods have higher initial costs, they can significantly extend the service life of castings and reduce maintenance costs, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), etc.
5.Summary
After years of development, casting surface treatment and protection technology has formed a variety of mature technologies. Correct understanding and application of these technologies will not only bring new vitality to castings, but also provide a solid guarantee for industrial development.