Casting small metal parts: small parts with big impact
Casting small metal parts may be tiny, but they play a vital role. These parts often require extremely high precision to ensure proper operation and overall performance of the equipment. Therefore, how to ensure the accuracy of casting small metal parts has become the focus of the manufacturing industry.
This article will answer this question for everyone. It is hoped that continued technological innovation and process improvement will promote the continuous improvement of the precision of cast small metal parts and provide solid technical support for the progress of modern industry.
1.The role of casting in metal processing
Casting is a technology in which molten metal is injected into a mold, cooled and solidified to obtain parts of the desired shape and size. This process offers significant advantages in metal processing, making it an indispensable manufacturing method in many industrial sectors.
(1) Efficient production:
Casting can achieve continuous and mass production, and has higher production efficiency than methods such as mechanical processing and forging. Especially when manufacturing parts with complex shapes and large sizes, the advantages of casting are more obvious.
(2) Cost-effectiveness:
Through casting, parts close to the final shape can be obtained directly, reducing the workload of subsequent machining, thereby reducing production costs.
(3) Design flexibility:
Casting technology can produce parts with complex shapes and various sizes to meet different industrial needs. Casting is used in a wide range of applications, from everyday items to high-tech equipment.
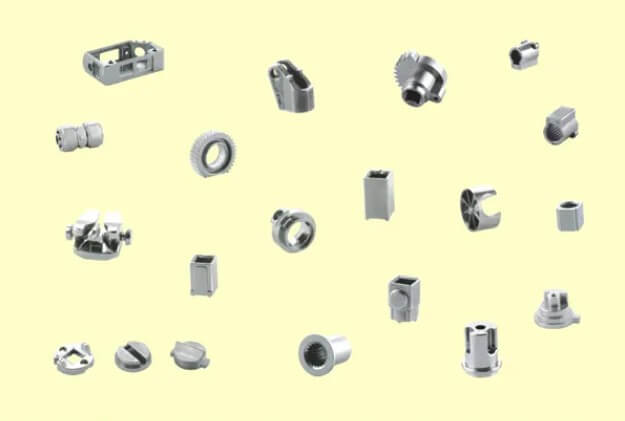

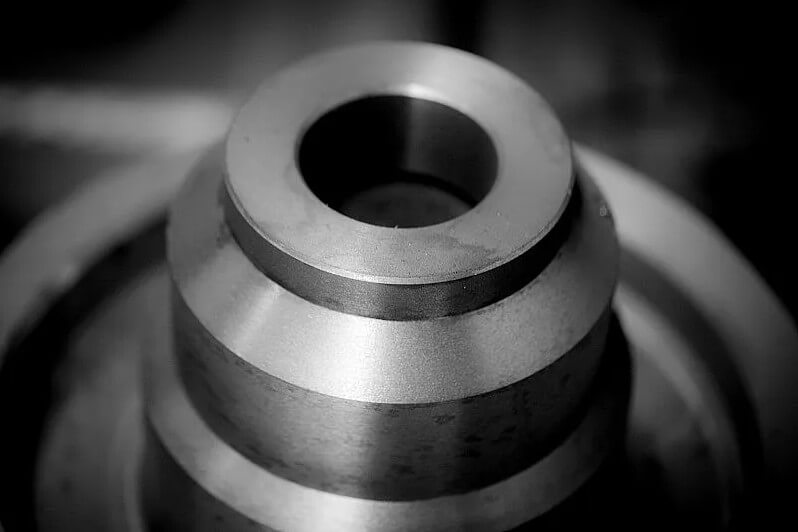
2.The unique charm of casting small metal parts
Although small in size, small metal parts play a key role in many precision equipment and machinery. Casting technology exhibits the following characteristics when producing these small parts:
(1) Accuracy and performance:
Modern casting technologies, such as metal mold casting and pressure casting, can produce small metal parts with high dimensional accuracy and good surface finish. These parts not only look beautiful, but also have excellent mechanical properties.
(2) Material diversity:
A variety of metal materials can be used to cast small metal parts, such as aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, copper alloy, etc. Different materials give the parts different performance characteristics and adapt to different application scenarios.
(3) Process innovation:
With the development of science and technology, casting technology continues to innovate. For example, the emergence of special casting methods such as lost foam casting and centrifugal casting provides more possibilities for the production of small metal parts. These technologies can improve the accuracy and performance of castings while reducing material waste and environmental pollution.

3.Wide application of casting small metal parts
Small metal parts are widely used in modern industry. From automobiles, electronic equipment to medical equipment, aerospace and other fields, casting small metal parts plays an important role.
(1) Automobile industry:
Key components such as engine blocks and gearbox parts are mostly produced using casting processes. These small metal parts are crucial to the performance and reliability of the car.
(2) Electronic equipment:
Structural parts and heat dissipation parts in electronic equipment such as mobile phones and computers are often made of lightweight, high-strength cast alloy materials, which not only ensures the performance of the equipment, but also reduces the weight.
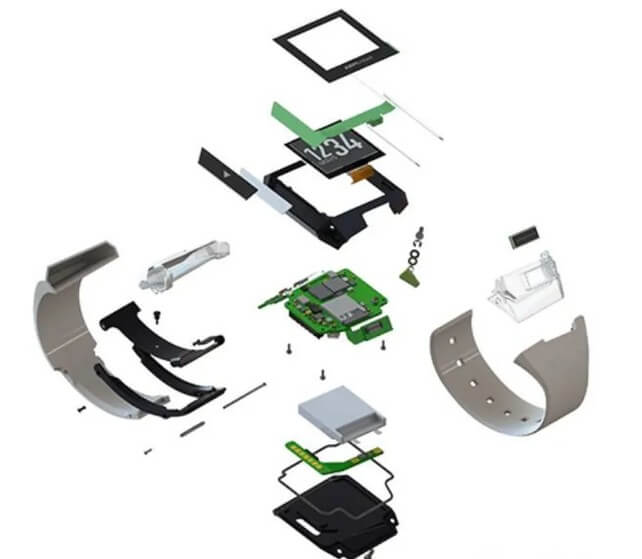

(3) Medical devices:
Small metal parts in precision medical devices require high precision and good biocompatibility. Casting technology can meet these special needs and provide reliable parts for the medical field.
4.How to choose materials for casting small metal parts?
When casting small metal parts, choosing the right material is key to ensuring part performance and cost-effectiveness. Commonly used metal types include aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, copper alloys and steel materials, each with its own unique characteristics.
(1) Common metal types and their characteristics
1) Aluminum alloy
Aluminum alloys have high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, easy processing and welding, low electrical conductivity and low thermal expansion. These properties make it ideal for manufacturing lightweight, high-strength parts.
2) Zinc alloy
Zinc alloys offer excellent castability, corrosion resistance, high strength and low cost. Zinc alloy is easy to shape and has a low melting point, making it suitable for rapid production.
3) Copper alloy
Copper alloys have excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, good machinability and corrosion resistance. Copper alloys also possess high toughness and ductility.
4) Steel materials
Steel materials have high hardness, strength and toughness, are relatively low-priced, and are easy to process and shape. Stainless steel also has excellent corrosion protection properties.
(2) Material selection considerations
1) Part functional requirements:
Depending on the intended use of the part, materials with appropriate properties are selected. For example, parts that require high electrical conductivity should choose copper alloys, while parts that require lightweight and high strength are suitable for aluminum alloys.
2) Production batch:
For high-volume production, zinc alloys and aluminum alloys have advantages due to their fast production speed and lower costs. For low-volume or custom production, steel may be more flexible.
3) Cost:
The cost of different metal materials varies significantly. Zinc alloys and aluminum alloys generally cost less, while copper alloys and some specialty steels cost more.
4) Processing performance:
Consider the machinability of the material, such as casting performance, cutting performance, etc. Zinc alloy and aluminum alloy have excellent casting properties, while steel materials are more suitable for forging and machining.
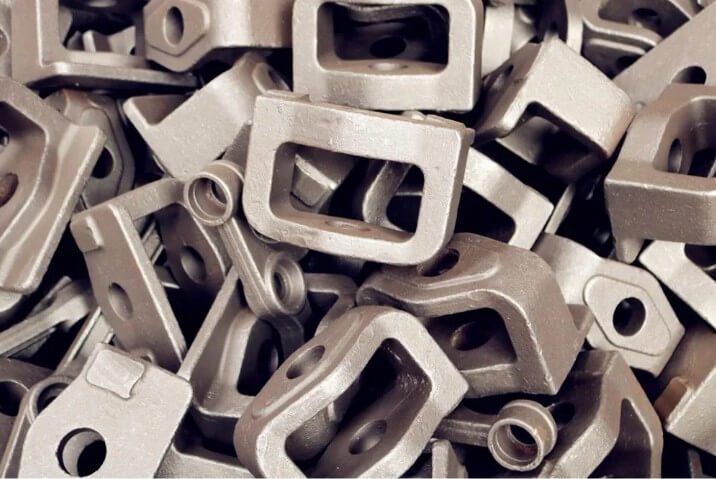

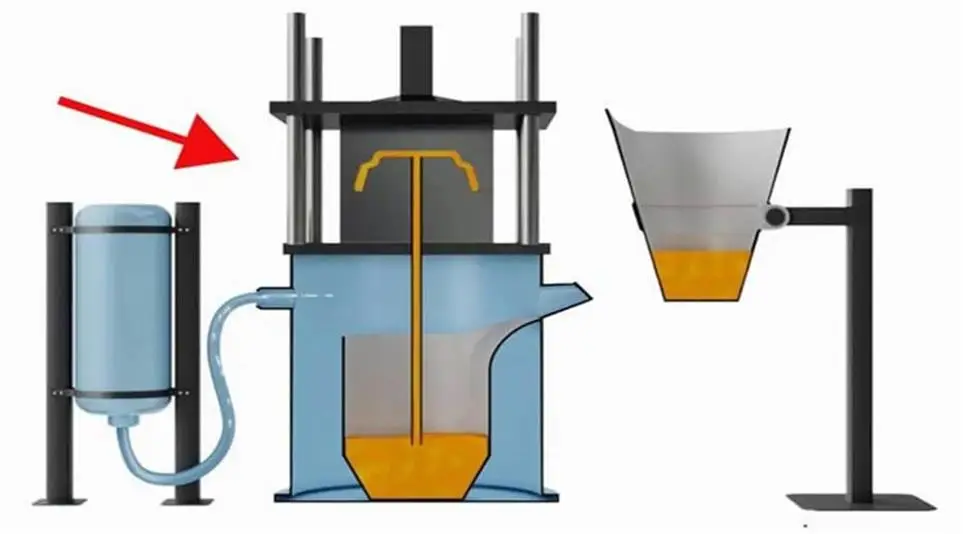
5.How to casting small metal parts?
Casting small metal parts is a complex process involving multiple steps. Here are the general steps for casting small metal parts:
(1) Design model:
First, a model needs to be designed based on the size and shape of the required part. This mold, which can be wooden or metal, is used to create the cavity in the sand mold.
(2) Making sand mold:
A sand mold is created around the model using special molding sand. Molding sand is usually a mixture of sand and clay, with other substances sometimes added to enhance its strength and plasticity. After the sand mold is made, the model needs to be removed, leaving a cavity, which is the mold.
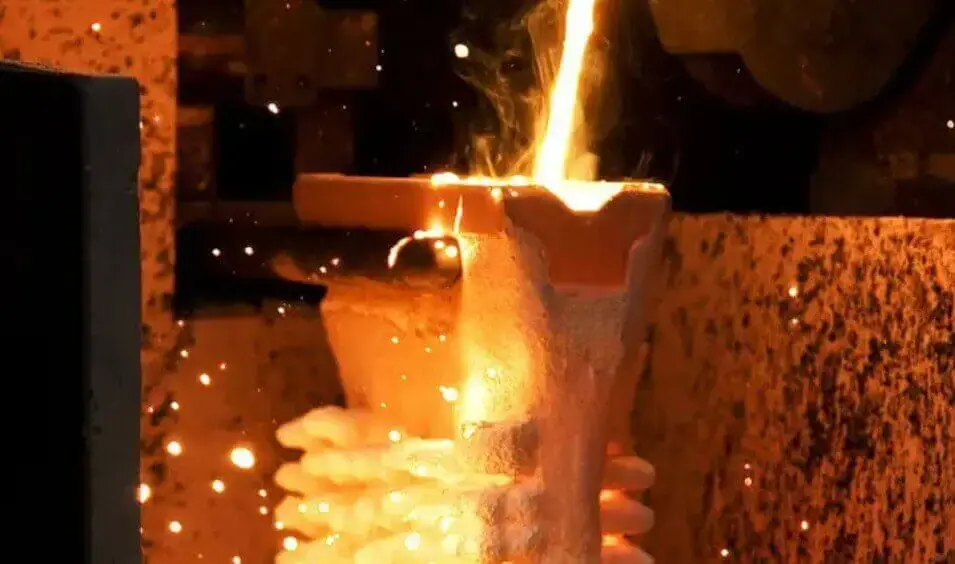
(3) Smelting metal:
The metal raw material is heated to its melting point, turning it into a liquid state. Commonly used metals include aluminum, copper, iron, etc.
(4) Pouring:
Pour molten liquid metal into the mold. This process requires controlling the temperature and pouring speed of the molten metal to ensure that the molten metal can evenly fill every corner of the mold.
(5) Cooling and solidification:
The molten metal cools and solidifies in the mold. This process can take a while, depending on the size of the part and the type of metal.
(6) Take out the casting:
After the metal solidifies, the sand mold is broken and the casting is removed. The resulting casting usually also has a gating system and risers that require further processing.
(7) Post-processing:
After the casting is taken out, it needs to be cleaned to remove sand and impurities on the surface. Heat treatment is then performed as needed to improve the mechanical properties of the casting. Finally, the casting may need to be machined to achieve final dimensional accuracy and surface finish requirements.
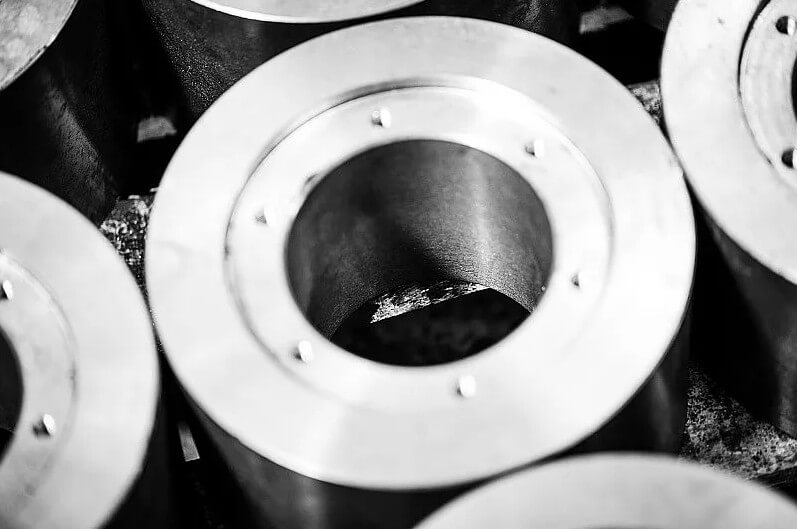

6.Design points for casting small metal parts
(1) Part shape and structure requirements:
1) Avoid internal undercuts and complex core-pulling parts, and simplify the mold structure.
2) Design reasonable ribs (reinforcing ribs) to improve the strength and rigidity of the part. The thickness of the ribs is generally 2/3~3/4 of the wall thickness.
3) Ensure that the wall thickness is uniform and avoid being too thick or too thin. Usually, the reasonable wall thickness of aluminum alloy die castings is determined based on the surface area.
(2) Dimensional accuracy and surface requirements:
1) Reasonably determine the dimensional accuracy of die castings based on usage requirements to avoid unnecessary accuracy requirements that increase costs.
2) Surface requirements include surface finish, fillet design, etc. The fillet radius is generally 1/2 wall thickness ≤ R ≤ wall thickness, which helps metal flow and prevents stress concentration.
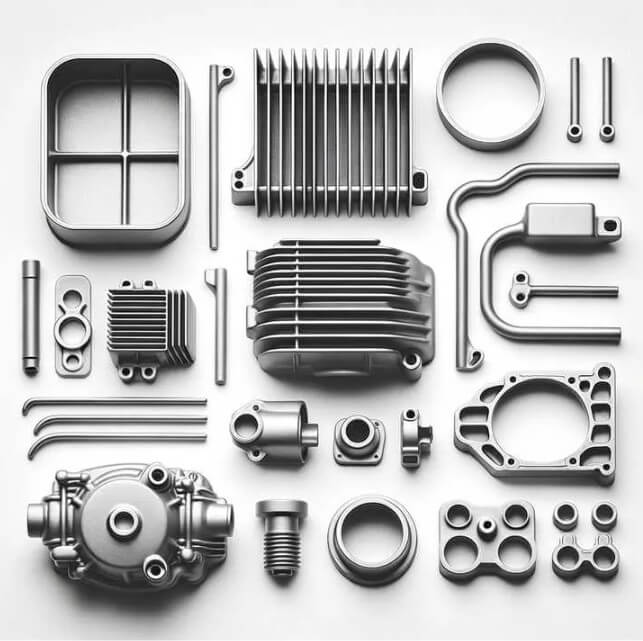

(3) Determination of parting surface:
1) The parting surface is the surface where the mold is separated to take out the casting. Reasonable selection of the parting surface can simplify the mold structure and ensure the quality of the casting.
2) The parting surface should avoid affecting the appearance and function of the part, and the largest cross-section of the part is usually selected.
(4) Casting slope:
1) Design an appropriate casting slope to reduce the friction between the casting and the mold cavity and facilitate the removal of the casting. The general minimum casting slope for aluminum alloy die castings is 1° for the outer surface and 1°30′ for the inner surface.
2) The shrinkage direction of the metal needs to be considered during design, and the slope changes with the shrinkage resistance.
(5) Gate design
1) The gate should be located at the thick wall of the product to reduce pressure loss.
2) Direct impact of plastic on weak parts should be avoided to prevent product deformation.
3) Melt flow and exhaust must be considered to ensure uniform filling of the cavity.
7.Process methods to improve the accuracy of casting small metal parts
Modern manufacturing requires high precision and quality in casting small metal parts. In order to improve the precision of casting small metal parts, the following are some key process methods:
(1) Optimize mold design:
1) The mold is a key factor in the casting process. Precise mold design ensures part size and shape accuracy. High-precision CAD/CAM software is used for mold design, and simulation technology is used to predict potential problems during the casting process, such as shrinkage cavities and pores.
2) Reasonably design the cooling system of the mold to ensure uniform mold temperature and reduce part deformation caused by thermal stress.
(2) Select appropriate materials:
1) Choosing the right metal material is crucial to improving part accuracy. Different metals have different thermal expansion coefficients and shrinkage rates, and these characteristics directly affect the accuracy of casting small metal parts.
2) Use high-quality raw materials and strictly control their chemical composition to reduce casting defects.

(3) Improve casting process parameters:
1) Precisely control parameters such as temperature, pressure and time during the casting process. For example, appropriately increasing the pouring temperature can improve the fluidity of molten metal and reduce defects such as pores and slag inclusions.
2) Use advanced casting technologies, such as high-pressure casting, low-pressure casting, etc., which can fill the mold under higher pressure and improve the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the parts.
(4) Strengthen process control:
1) Implement strict quality control measures and monitor all aspects of the casting process. For example, regularly check the wear of molds and replace or repair them in time.
2) Use advanced testing equipment and technology, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM), X-ray inspection, etc., to conduct comprehensive dimensional and defect inspection of castings.
(5) Post-processing process:
1) Perform appropriate heat treatment on castings, such as annealing, quenching, etc., to eliminate internal stress and improve mechanical properties.
2) Use precision machining methods, such as CNC machining, grinding, etc., to further modify the size and shape of casting small metal parts to improve their accuracy.
8.Summary
To sum up, the precision control of casting small metal parts is a complex and delicate process. By continuously optimizing the casting process, improving the quality of raw materials, improving mold design, adopting post-processing processes, and strengthening quality control measures, the accuracy of casting small metal parts can be effectively improved.