Casting defects: appearance, causes, solutions
Casting technology is a vital part of the manufacturing industry and is widely used in many fields such as automobiles, machinery, and aerospace. However, due to the complexity of the casting process, there are many factors that affect the quality of castings, which often lead to various casting defects. These defects not only affect the appearance of the castings, but may also have a significant impact on their key properties such as mechanical properties and durability. This article will discuss in detail the common types of casting defects, appearance, causes and corresponding solutions.
1.Common casting defects: pores
Porosity is a hole of varying sizes inside or on the surface of a casting, mainly due to the release of gas from the molten metal during solidification or the inability of gas in the molding sand to escape.

(1) Appearance
Its appearance is the presence of round, oval or needle-shaped holes on the surface or inside of the casting, of varying sizes and numbers.
(2) Causes
1) Too high gas content in the molten metal:
The molten metal easily absorbs gases, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, during the smelting process. These gases do not have time to escape during the solidification of the molten metal, forming pores.
2) Poor permeability of the mold:
Poor permeability of the mold will cause the gas in the molten metal to be unable to be discharged smoothly, thus forming pores.
3) Unreasonable design of the pouring system:
Unreasonable design of the pouring system will cause poor flow of the molten metal, easily generate eddy currents, entrain gas, and form pores.
(3) Solutions
1) Reduce the gas content in the molten metal:
Take measures to reduce the air absorption of the molten metal during the smelting process, such as vacuum smelting, inert gas protection smelting, etc. .
2) Improve the permeability of the mold:
Add permeable materials such as perlite and diatomaceous earth during the mold making process to improve the permeability of the mold.
3) Optimize the design of the pouring system:
Rationally design the pouring system to avoid poor flow of the molten metal and reduce eddy currents and entrainment.
2.Common casting defects: shrinkage cavities and shrinkage porosity
Shrinkage cavities and shrinkage porosity are holes caused by the volume shrinkage of the molten metal during solidification and the failure to be replenished in time.
(1) Appearance
The appearance of shrinkage cavities is the presence of holes on the surface or inside of the casting, with irregular shapes and clear contours. Shrinkage porosity is the presence of tiny pores inside the casting, which is sponge-like.
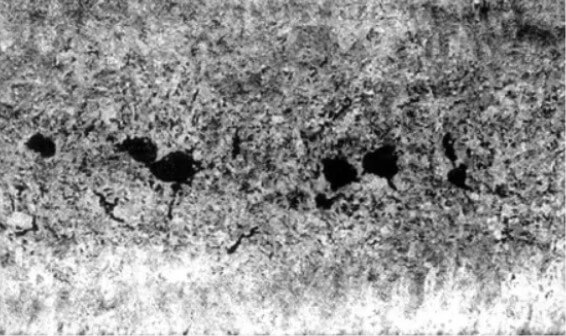
(2) Causes
1) Unreasonable casting structure design:
The casting structure is too complex, the thickness is uneven, and it is easy to produce heat nodes, resulting in shrinkage cavities and shrinkage porosity.
2) Unreasonable gating system design:
Unreasonable gating system design leads to unreasonable metal liquid filling sequence and poor shrinkage compensation channels, which are easy to produce shrinkage cavities and shrinkage porosity.
3) Too fast cooling speed:
Too fast cooling speed will increase the internal stress of the casting and easily produce shrinkage porosity.
(3) Solutions
1) Optimize casting structure design:
Rationally design the casting structure to avoid uneven thickness and reduce heat nodes.
2) Optimize gating system design:
Rationally design the gating system to ensure that the metal liquid filling sequence is reasonable and the shrinkage compensation channel is smooth.
3) Control the cooling rate:
Reasonably control the cooling rate to avoid too fast cooling rate
3.Common casting defects: slag holes
Slag holes are holes formed inside or on the surface of the casting due to the failure to effectively remove the slag in the molten metal.
(1) Appearance
The appearance of slag holes is the presence of irregular holes on the surface or inside of the casting, with a shallow depth and a smooth, shiny and colorful surface inside the hole.
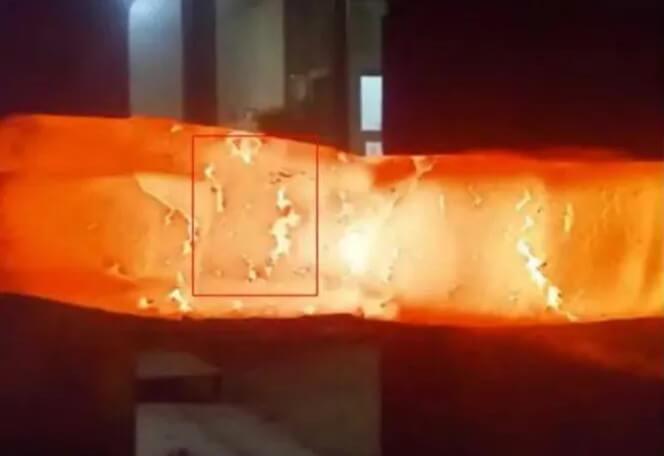

(2) Causes
1) Poor quality of molding sand and core sand:
If the strength, air permeability and other properties of the molding sand and core sand are poor, slag holes are easily formed in the casting.
2) Unreasonable design of the pouring system:
If the pouring system is improperly designed, it will lead to unstable flow of molten metal, which is easy to be involved in gas and inclusions, forming slag holes.
3) Improper smelting and pouring process:
If the smelting temperature is too high or the pouring speed is too fast, the inclusions in the molten metal cannot be fully floated and removed, thus forming slag holes in the casting.
(3) Solutions
1) Improve the quality of molding sand and core sand:
Select high-quality molding sand and core sand, and strictly control their ratio and performance.
2) Optimize the design of the pouring system:
Rationally design the pouring system to avoid excessive turbulence of the molten metal and ensure that inclusions can fully float and be removed.
3) Improve the smelting and pouring process:
Control the smelting temperature to avoid it being too high; control the pouring speed to ensure that the molten metal flows smoothly into the mold cavity.
4.Common casting defects: sticking sand
Sand sticking refers to a layer of molding sand adhering to the surface of the casting, resulting in a rough surface.
(1) Appearance
The appearance of sticking sand is usually a layer of sand particles that are difficult to remove adhere to the surface of the casting. This layer of sand particles forms a mechanically mixed adhesion layer with the surface of the casting, sometimes also called “iron-coated sand”.
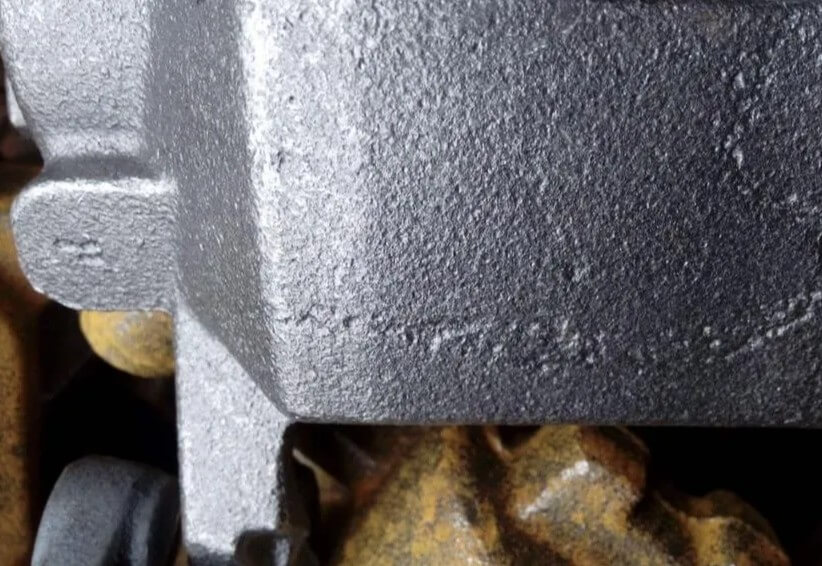

(2) Causes
1) Low refractoriness of the molding sand:
Low refractoriness of the molding sand is easy to melt under the action of high-temperature molten metal, and chemically reacts with the molten metal to form sticking sand.
2) Pouring temperature is too high:
Pouring temperature is too high will aggravate the erosion of molten metal on the molding sand and increase the possibility of sand sticking.
3) Poor coating quality:
Poor coating quality cannot effectively isolate molten metal and molding sand, which will also cause sand sticking.
(3) Solutions:
1) Improve the refractoriness of molding sand:
Select molding sand with high refractoriness, such as zircon sand, olivine sand, etc.
2) Control pouring temperature:
Reasonably control the pouring temperature to avoid excessive temperature.
3) Select high-quality coating:
Select high-quality coating to improve the refractoriness and isolation effect of the coating.
5.Common casting defects: cold shut
Cold shut is an incompletely fused gap or depression on the surface of the casting, usually caused by poor fluidity of the molten metal or interrupted pouring.
(1) Appearance
The appearance of cold shut is the presence of incompletely fused gaps on the surface of the casting, with irregular shapes and smooth edges.
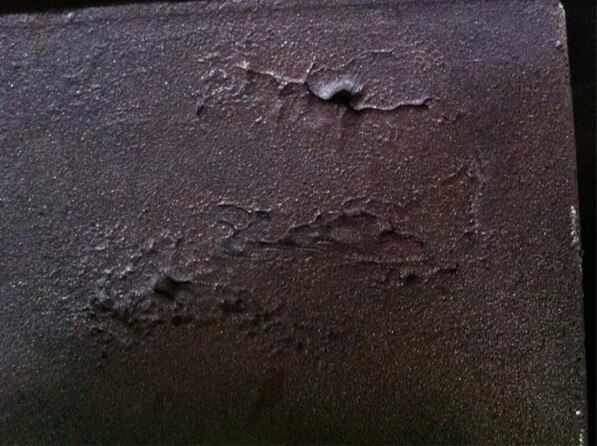
(2) Causes
1) Pouring temperature is too low:
Pouring temperature is too low will lead to poor fluidity of molten metal and easy to produce cold shut.
2) Pouring speed is too slow:
Pouring speed is too slow will cause molten metal to solidify prematurely during the filling process, resulting in cold shut.
3) Mold temperature is too low:
Mold temperature is too low will reduce the fluidity of molten metal and increase the possibility of cold shut and insufficient pouring.
(3) Solutions:
1) Increase the pouring temperature:
Reasonably increase the pouring temperature to ensure that the molten metal has good fluidity.
2) Speed up the pouring speed:
Reasonably speed up the pouring speed to ensure that the molten metal fills the mold cavity before solidification.
3) Increase the mold temperature:
Preheat the mold before pouring to increase the mold temperature.
6.Common casting defects: cracks
Cracks are cracks caused by stress concentration during the cooling process of the casting.
(1) Appearance
The appearance is the presence of cracks on the surface or inside of the casting, with irregular shapes, lengths and widths.
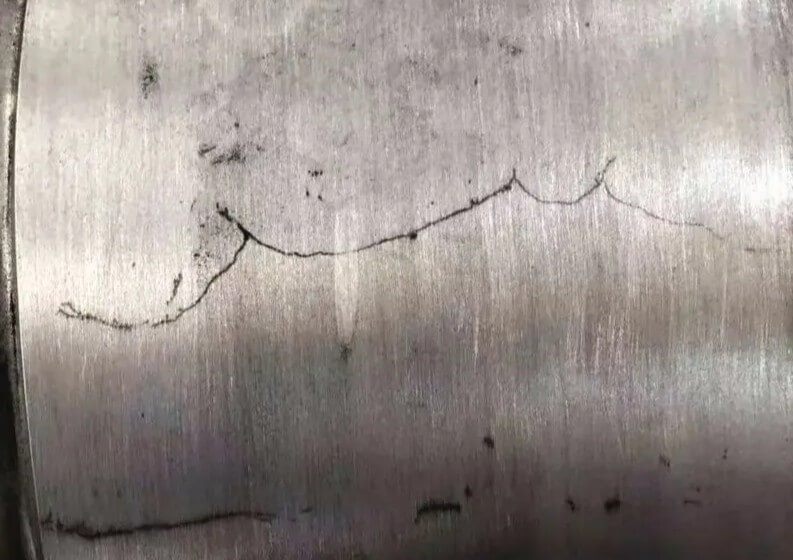

(2) Causes
1) Improper alloy composition:
Improper alloy composition: Too high iron content or too low silicon content, or too high harmful impurity content in the alloy will reduce the plasticity of the alloy and increase the risk of casting defects and cracks.
2) Too low mold temperature:
Too low mold temperature will cause the casting to cool too quickly, thereby generating thermal stress and causing cracks.
3) Unreasonable casting design:
There are places where the casting wall has drastic changes, shrinkage is hindered, and stress is formed at the sharp corners, which is easy to cause cracks.
4) Improper mold retention time and ejection method:
Too long mold retention time or uneven force during ejection will increase the internal stress of the casting, thereby causing cracks.
(3) Solutions
1) Control alloy composition:
Strictly control the alloy composition according to the standard, and add pure aluminum ingots or aluminum-silicon intermediate alloys to adjust the composition ratio when necessary.
2) Improve casting structure:
Increase the fillet, increase the mold taper, reduce the wall thickness difference, and avoid stress concentration.
3) Adjust mold temperature:
Keep the mold temperature stable and avoid too low a temperature.
4) Optimize the ejection process:
change or increase the ejection position to make the ejection force uniform and shorten the mold opening and core pulling time.
7.Common casting defects: sand inclusion
Sand inclusion is a metal flake protrusion on the surface of the casting, with a layer of molding sand between the protrusion and the casting.
(1) Appearance
The appearance of sand inclusion usually includes scar-like metal protrusions on the surface of the casting. These protrusions have a rough surface and sharp edges. A small part of the metal is connected to the casting body, and a sand layer is sandwiched between the scar-like protrusion and the casting.

(2) Causes
1) Insufficient strength of the molding sand:
Insufficient strength of the molding sand is easy to deform or collapse under the pressure of the molten metal, resulting in sand inclusion.
2) Too fast pouring speed:
Too fast pouring speed will cause the erosion of the molding sand by the molten metal to increase, increasing the possibility of sand inclusion.
3) Unreasonable mold design:
Unreasonable mold design, such as improper selection of parting surface, is easy to cause sand inclusion.
(3) Solutions:
1) Improve the strength of the molding sand:
Add an appropriate amount of binder, such as clay, water glass, etc., to the molding sand to improve the strength of the molding sand.
2) Control the pouring speed:
Reasonably control the pouring speed to avoid excessive speed.
3) Optimize the mold design:
Reasonably select the parting surface to avoid setting the parting surface in important parts of the casting.
8.Conclusion
The generation of casting defects is the result of the combined effect of many factors. Solving these problems requires starting from multiple aspects such as design, process, and materials. Only by continuously optimizing and improving the casting process and strictly controlling the quality of each link can we effectively reduce casting defects and improve the quality and performance of castings.
If you are looking for an experienced casting manufacturer, Lvxun is your ideal choice. The Lvxun team is well-equipped, has rich experience and technical talents in solving casting defects, and can provide high-quality perfect castings. If you need more information or discuss your needs with us, please feel free to contact us.




