Cast Iron vs Stainless Steel Processing Guide: How to Choose the Best Material
In manufacturing and industrial applications, choosing the right material is crucial. Cast iron vs stainless steel are two commonly used metal materials, each with unique properties and advantages. This article will explore the characteristics of cast iron vs stainless steel, processing methods, and how to choose the best material to help you make an informed decision in different application scenarios.
1.Characteristics and Processing of Cast Iron
(1) Characteristics of Cast Iron
Cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy with a high carbon content, usually between 2% and 4%. Its main characteristics include:

1) High strength and hardness:
Cast iron has high compressive strength and hardness and is suitable for heavy loads.
2) Excellent wear resistance:
Due to the presence of graphite, cast iron has good self-lubrication and wear resistance and is suitable for manufacturing friction parts.
3) Good casting performance:
Cast iron has good fluidity, is easy to cast parts of complex shapes, and has a relatively low cost.
4) Poor toughness and plasticity:
Cast iron has poor toughness and is easy to break, so it is not suitable for occasions that require high-intensity impact.
(2) Cast iron processing methods
1) Casting:
The most commonly used processing method for cast iron is casting, including sand casting, die casting and centrifugal casting. Among them, sand casting is the most commonly used method and is suitable for mass production.
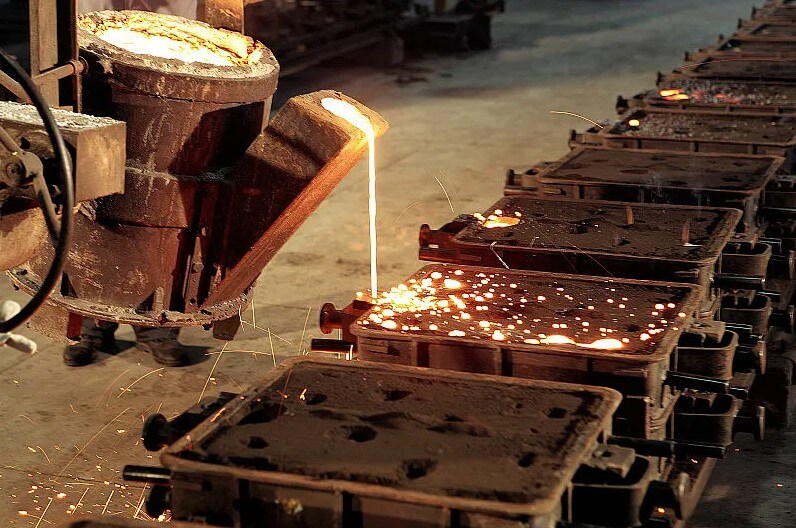

2) Machining:
Cast iron can be machined by turning, milling, drilling and other machining. However, due to its high hardness, it requires the use of tools with good wear resistance, such as carbide tools.
3) Heat treatment:
The mechanical properties of cast iron can be improved by heat treatment, such as increasing hardness and wear resistance. Common heat treatment methods include annealing, normalizing and quenching.
(3) Application areas of cast iron
1) Automotive parts: such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, brake discs, etc.
2) Mechanical equipment: such as machine tool bases, pump housings, valves, etc.
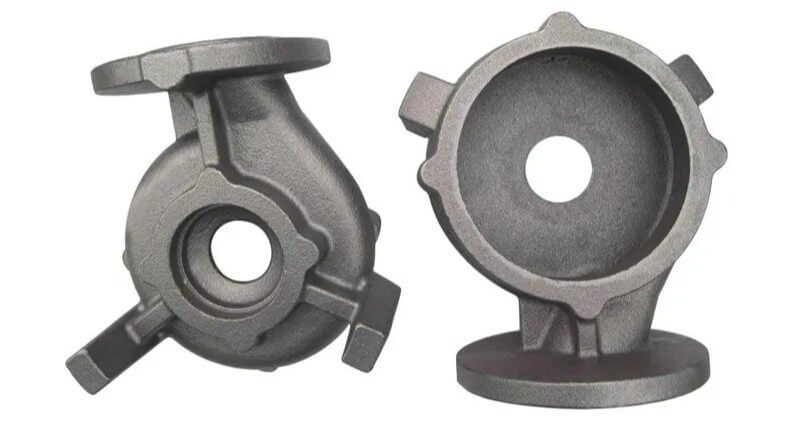

3) Building components: such as cast iron railings, manhole covers, etc.
2.Characteristics and processing of stainless steel
(1) Characteristics of stainless steel
Stainless steel is a kind of alloy steel with a high chromium content, usually above 10.5%. Its main characteristics include:
1) Excellent corrosion resistance:
The chromium element in stainless steel can form a dense oxide film on the surface, which has good corrosion resistance.
2) High strength and toughness:
Stainless steel has high strength and toughness and is suitable for occasions with high-intensity impact.

3) Good processing performance:
Stainless steel can be subjected to various mechanical processing and welding, and has good processing performance.
4) Beautiful appearance:
The surface of stainless steel is smooth and beautiful, and has good decorative effect.
(2) Processing methods of stainless steel
1) Mechanical processing:
The mechanical processing of stainless steel includes turning, milling, drilling, etc. Due to the high hardness and poor thermal conductivity of stainless steel, high-speed steel or carbide tools are required, and appropriate coolant is used.
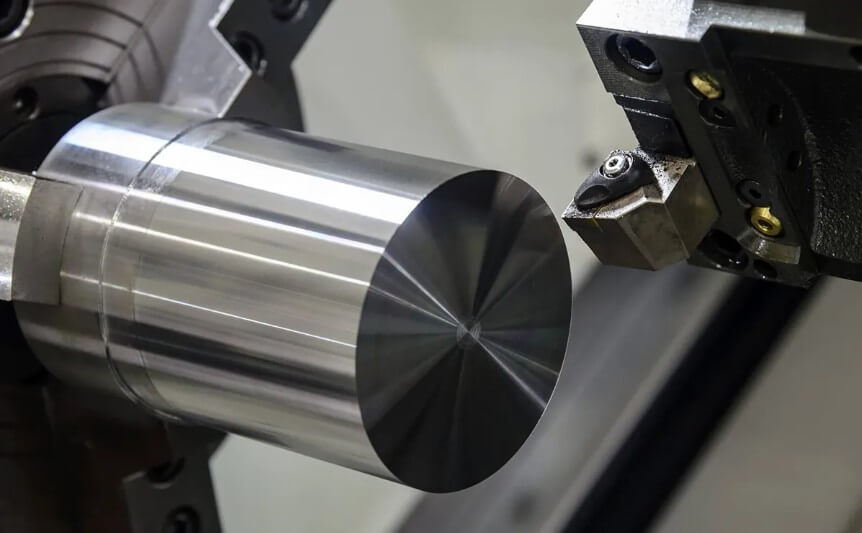

2) Welding:
Stainless steel has good welding properties. Common welding methods include argon arc welding, resistance welding and laser welding.
3) Surface treatment:
Stainless steel can be polished, sandblasted, electroplated and other surface treatments to improve its aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
(3) Application areas of stainless steel
1) Food processing equipment:
Due to its good corrosion resistance and hygiene, stainless steel is widely used in food processing equipment, such as kitchen utensils, tableware, etc.
2) Medical equipment:
The high strength and corrosion resistance of stainless steel make it an ideal material for medical equipment, such as surgical instruments and implants.
3) Chemical equipment:
In the chemical industry, stainless steel is often used to manufacture corrosion-resistant containers, pipelines and other equipment.
4) Architectural decoration:
The aesthetics and corrosion resistance of stainless steel make it widely used in architectural decoration, such as stainless steel doors and windows, handrails, etc.
3.Cast iron vs stainless steel: How to choose the best material
When choosing between cast iron vs stainless steel, the following factors need to be considered:
(1) Operating environment
1) Corrosive environment:
If the equipment needs to be used in a corrosive environment, such as the chemical industry, marine environment, etc., stainless steel is a better choice because of its good corrosion resistance.
2) High temperature environment:
In high temperature environments, cast iron has better thermal stability, while some stainless steels may suffer from intergranular corrosion. Therefore, cast iron may be more suitable in high temperature environments.
3) Heavy load environment:
If the equipment needs to withstand heavy loads, the high strength and hardness of cast iron make it an ideal choice.
(2) Mechanical performance requirements
1) Strength and hardness:
If high strength and high hardness materials are required, cast iron is a better choice. However, if high strength and high toughness materials are required, stainless steel is more suitable.

2) Impact load:
In situations where high-intensity impact is required, the high toughness of stainless steel makes it better than cast iron.
(3) Processing performance
1) Casting performance:
If you need to manufacture parts with complex shapes, cast iron has better casting performance and relatively lower cost.
2) Machining performance:
Stainless steel has better machinability, but it requires the use of tools with better wear resistance and appropriate coolant.
3) Welding performance:
If welding is required, stainless steel has better welding performance than cast iron.
(4) Cost considerations
1) Material cost:
The material cost of cast iron is relatively low, while the cost of stainless steel is higher.
2) Processing cost:
The casting cost of cast iron is lower, but the machining cost is higher. The machining and welding costs of stainless steel are higher, but the overall cost may be lower than cast iron.
(5) Aesthetics and decoration
Appearance requirements:
If you have high requirements for the appearance of the equipment, the aesthetics and decorativeness of stainless steel make it an ideal choice.
4.Cast iron vs stainless steel: the best choice for different processing scenarios
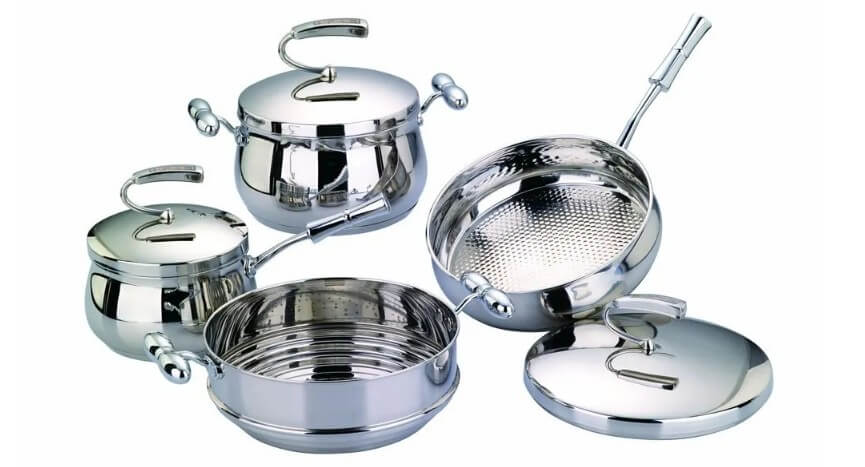
(1) Cookware manufacturing
○ Cast iron pot: good thermal insulation performance, suitable for a variety of cooking methods, but heavy and requires special maintenance. Suitable for home cooking, especially for dishes that require long stewing.
○ Stainless steel pot: good thermal conductivity, beautiful appearance and easy to clean, but expensive and food easily sticks to the pot. Suitable for fast cooking and scenarios with high cooking efficiency requirements.

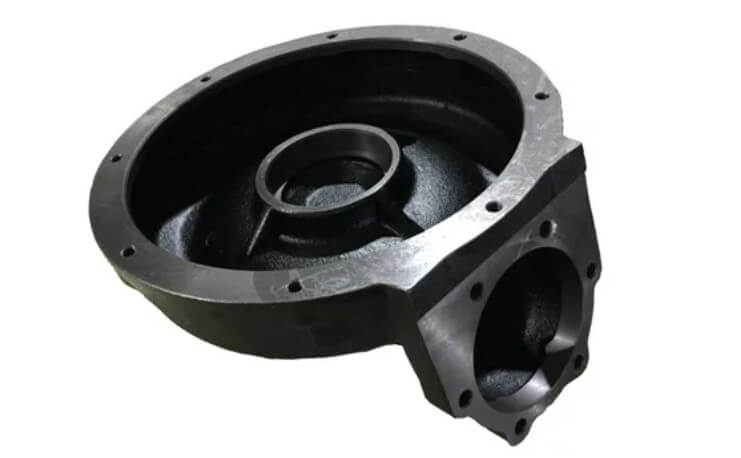
(2) Machinery manufacturing
○ Cast iron: good shock absorption performance, good wear resistance and low cost, suitable for manufacturing parts that require shock absorption and wear resistance, such as machine tool beds and gear boxes.
○ Stainless steel: good mechanical properties, good corrosion resistance and beautiful appearance, but high cost and heavy weight. Suitable for manufacturing parts with high requirements for corrosion resistance and appearance.
(3) Construction field
○ Cast iron: good corrosion resistance, good heat resistance and good sound insulation, suitable for manufacturing drainage pipes, fire protection pipes, etc.
○ Stainless steel: good corrosion resistance, good hygiene and beautiful appearance, suitable for handrails, doors and windows, etc.
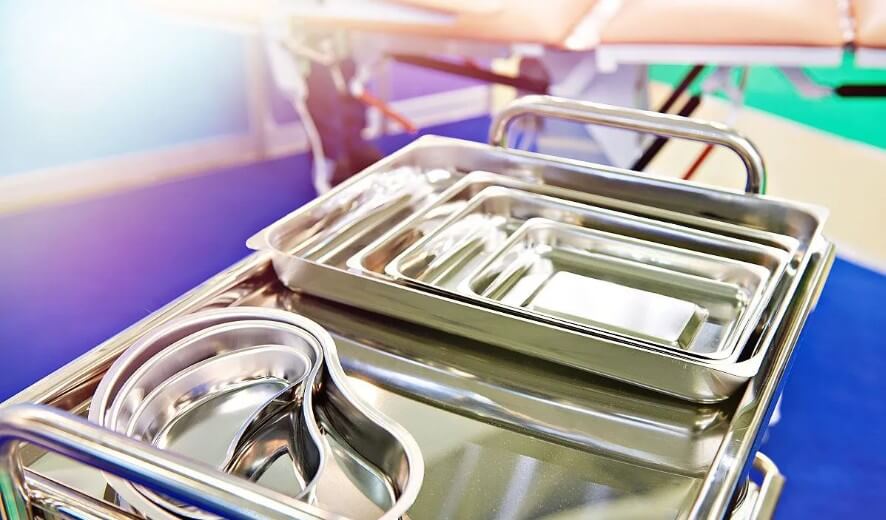
(4) Medical equipment
○ Stainless steel: good corrosion resistance, good hygiene and beautiful appearance, is the preferred material for manufacturing medical equipment.

(5) Chemical equipment
○ Stainless steel: good corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties and beautiful appearance, suitable for manufacturing chemical equipment such as reactors and pipelines.
5.Summary
When choosing between cast iron vs stainless steel, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the use environment, mechanical performance requirements, processing performance, cost, and aesthetics and decoration.
Cast iron is suitable for heavy-load, high-temperature and low-cost applications, while stainless steel is suitable for corrosion-resistant, high-strength and high-decoration applications.
The above provides a variety of reference options for the selection of cast iron vs stainless steel. By reasonably selecting materials, the performance and service life of the equipment can be improved, the production cost can be reduced, and the best economic benefits can be achieved.




