cast aluminum melting point: Discovering the thermal secrets of the king of metals
The cast aluminum melting point is a technical term that hides the mysteries of countless industrial applications. As a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal, cast aluminum plays an important role in modern manufacturing. From automotive parts to aerospace vehicles, cast aluminum is ubiquitous, and understanding the cast aluminum melting point is the key to mastering its processing technology. In this paper, we will discuss the melting point of cast aluminum related knowledge, including the introduction of the melting point of each alloy, factors affecting the cast aluminum melting point, as well as its measurement and control method analysis.
1. Overview of aluminum and cast aluminum
(1) Basic Properties of Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with good electrical and thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. These properties make aluminum the material of choice for many industrial applications. Aluminum has a density of about 2.7 g/cm³, only about 1/3 that of iron and copper, which gives it a significant advantage in reducing the weight of structures. At the same time, the surface of aluminum is easy to form a layer of dense oxide film, this film can effectively prevent further oxidation and corrosion of aluminum, giving aluminum and its alloys excellent weathering and corrosion resistance.
(2) Cast aluminum applications in industry
Cast aluminum is widely used in aerospace, automobile manufacturing and construction industry because of its excellent casting performance and mechanical properties.
In the aerospace field, the lightweight characteristics of cast aluminum help improve fuel efficiency and flight performance;
In automotive manufacturing, the application of cast aluminum parts can reduce the weight of the vehicle body, thus improving fuel economy and vehicle handling performance;
In the construction industry, cast aluminum is commonly used in the manufacture of window and door frames, decorative parts, etc. because of its beauty, corrosion resistance and workability.

2. The basic content of the cast aluminum melting point
(1) the melting point of pure aluminum
The melting point of pure aluminum is 660.4 degrees Celsius. This temperature is the key point of aluminum from solid to liquid, for aluminum processing and casting is of great significance. The relatively low melting point of pure aluminum allows for low energy consumption and high process flexibility in casting and processing.
(2) Changes in the melting point of aluminum alloys
Aluminum alloys change their physical and mechanical properties by adding various elements such as copper, magnesium, and silicon. The addition of these alloying elements significantly affects the cast aluminum melting point.
For example, aluminum-silicon alloys (Al-Si) have lower melting points and are commonly used in casting processes, with melting points ranging from 577°C to 660°C, depending on the silicon content; aluminum-copper alloys (Al-Cu) have higher melting points, ranging from about 548°C to 643°C, which makes them more widely used in high-temperature environments.
(3) Common aluminum alloys and their melting points
Common aluminum alloys include Al-Si, Al-Cu, Al-Mg and other series.
Al-Si series aluminum alloys are widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries due to their good fluidity and resistance to thermal cracking, and their melting points are usually between 577℃ and 660℃;
Al-Cu series aluminum alloys are commonly used in the manufacture of high-strength structural components due to their high strength and heat resistance, with melting points ranging from 548°C to 643°C;
Al-Mg series aluminum alloys are widely used in the shipbuilding and construction industries for their excellent corrosion resistance and medium strength, with melting points ranging from 450℃ to 630℃.
3. Factors affecting the cast aluminum melting point
(1) Alloy composition
Aluminum alloy in different alloying elements on the cast aluminum melting point has a significant impact. Major alloying elements such as copper, magnesium, silicon, etc., affect the melting point of aluminum by changing its crystal structure and phase transition behavior.
(2) Role of major alloying elements
Elements such as copper, magnesium and silicon play important roles in aluminum alloys. Copper can improve the strength and heat resistance of aluminum alloy, commonly used in the manufacture of high-strength structural parts; magnesium can improve the strength and toughness of aluminum alloy, suitable for the manufacture of high-strength and corrosion-resistant structural parts; silicon is mainly used to reduce the melting point of aluminum alloy, improve its casting performance, widely used in automotive and aerospace industries.
(3) The influence of trace elements
Although the amount of trace elements added is not large, the impact on the performance of aluminum alloys should not be ignored. Titanium, vanadium, chromium and other trace elements can refine the grain, improve the mechanical properties and heat resistance of aluminum alloy. The addition of these elements can improve the microstructure of aluminum alloy, thus improving its overall performance.
(4) Heat treatment conditions
Heat treatment can change the microstructure of aluminum alloy, thus affecting its cast aluminum melting point and mechanical properties. Quenching and aging treatments are commonly used heat treatment methods, and the properties of the alloy can be optimized by controlling the heating temperature, holding time and cooling rate. For example, quenching treatment can improve the hardness and strength of aluminum alloy, while aging treatment can further stabilize the structure of the alloy and improve its comprehensive performance.
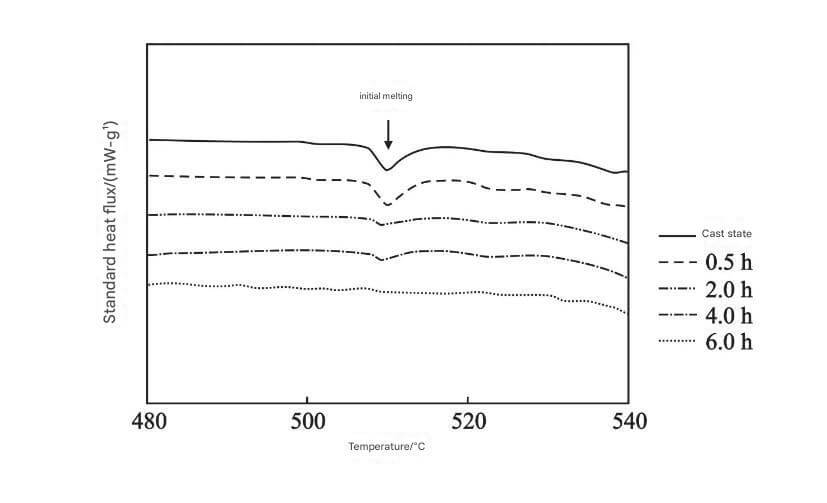
Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Cast Aluminum Alloy
(5) Influence of casting process on melting point of cast aluminum
Different casting processes have different effects on the melting point of aluminum alloy. For example, die-casting process due to fast cooling speed, can get fine grain structure, improve the strength and toughness of the alloy; while sand casting is slower cooling speed, easy to lead to coarse grains, reduce the mechanical properties of the alloy. Therefore, it is crucial to choose the appropriate casting process to optimize the performance of aluminum alloy.
(6) Impurities and defects on the melting point of cast aluminum impact
Impurity elements such as iron, copper, magnesium, etc., although it can improve some mechanical properties, but will significantly increase the cast aluminum melting point. Iron in aluminum to form hard points, increase mobility but reduce the melting point; copper to improve strength and hardness, but also increase the melting point.
Defects such as porosity and shrinkage can disrupt the structural integrity of cast aluminum, resulting in localized melting point changes. Porosity makes the material easy to produce stress concentration during the heating process, thus affecting the stability of the melting point; shrinkage leads to defects in the solidification process of the material, the melting point will also change accordingly.
4. cast aluminum melting point measurement methods and precautions
(1) cast aluminum melting point measurement method
Measurement of the cast aluminum melting point mainly includes differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and optical microscopy. These methods can accurately determine the thermal behavior and structural changes of the material to determine the melting point.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry determines the melting point by measuring the change in heat flow of a material during heating;
Thermogravimetric analysis analyzes the thermal stability of a material by measuring the change in its weight during heating;
Optical microscope method to determine the melting point by observing the changes in the microstructure of the material during the heating process.
(2) Precautions in the measurement process
When measuring the cast aluminum melting point, attention needs to be paid to the preparation of the sample and the choice of measurement conditions. The purity, particle size and shape of the sample have a significant effect on the measurement results, so the sample preparation process needs to be strictly controlled. In addition, the temperature control, heating rate and atmosphere conditions during the measurement process will also affect the measurement results, so it is necessary to choose appropriate measurement conditions and equipment to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results.
5. The importance of controlling the cast aluminum melting point and how to control the cast aluminum melting point
(1) The importance of melting point control
Control of the cast aluminum melting point is essential to ensure the quality and performance of the material.
1) the impact on casting quality
Precise control of the cast aluminum melting point is critical to casting quality. If the melting point is not properly controlled, it may lead to cracks, porosity and other defects in the casting, affecting its mechanical properties and appearance quality. By precisely controlling the cast aluminum melting point, the casting process can be optimized to improve the quality and consistency of castings.
2) the impact on mechanical properties
The control of the cast aluminum melting point not only affects the casting quality, but also has an important impact on the mechanical properties of the material. Appropriate melting point control can improve the strength and ductility of the material, so that it shows good performance in different application environments. For example, by controlling the melting point of aluminum alloy, its microstructure can be optimized to improve its tensile and yield strength, while maintaining good plasticity and toughness.
(2) How to control the cast aluminum melting point
1) Alloy composition adjustment:
The melting point of cast aluminum material can be controlled by adjusting its alloy composition. For example, the addition of silicon, copper, magnesium and other elements can change the melting point of aluminum alloy. Different alloy compositions will have different cast aluminum melting point, so it is very important to choose the right alloy composition according to the actual demand.
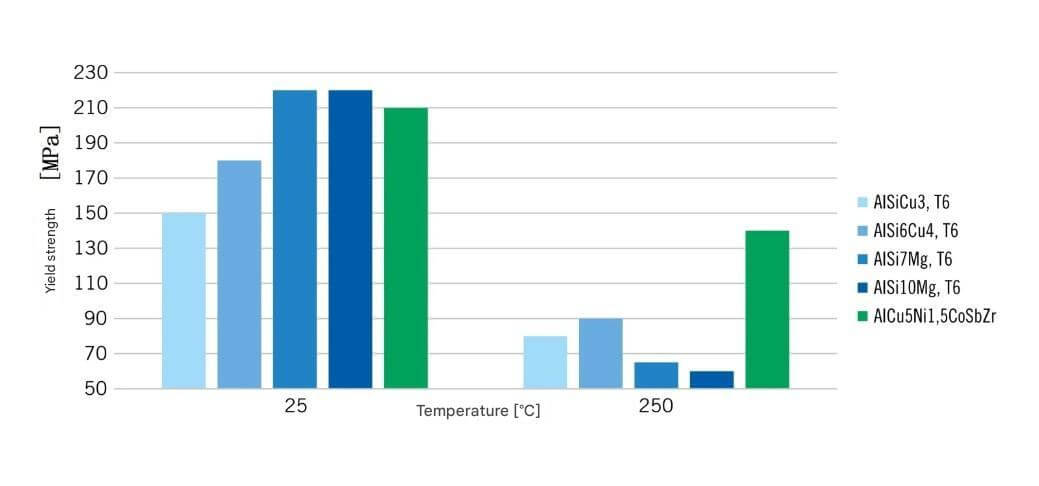
Room temperature strength and hot strength of various cast aluminum alloys
2) Control the melting temperature:
In the melting process, the melting temperature should be strictly controlled to avoid too high or too low temperature. Too high a temperature will lead to material burnout and oxidation, increasing the porosity of the casting and inclusion defects; too low a temperature will affect the fluidity of the material and filling properties, resulting in cold segregation, shrinkage and other defects in the casting.
3) Add metamorphic agent:
In the melting process, you can add some metamorphic agents to change the crystallization process of aluminum liquid, thus affecting its melting point. For example, sodium, strontium and other elements can be used as metamorphic agents to refine the grain and improve the mechanical properties of the material.
4) Use of melting agent:
In the melting process, the use of suitable flux can protect the aluminum liquid from oxidation and reduce the mixing of impurities, thus ensuring the stability of the melting point of the material.
5) Heat treatment process:
Through appropriate heat treatment processes, such as solid solution treatment and aging treatment, the organization and properties of cast aluminum materials can be improved, which indirectly affects their cast aluminum melting point.

6.Conclusion
Accurate control of cast aluminum melting point is important for improving the quality and performance of the material. Through advanced measurement technology and control process, precise control of cast aluminum melting point can be realized, so as to optimize the microstructure and properties of the material.




