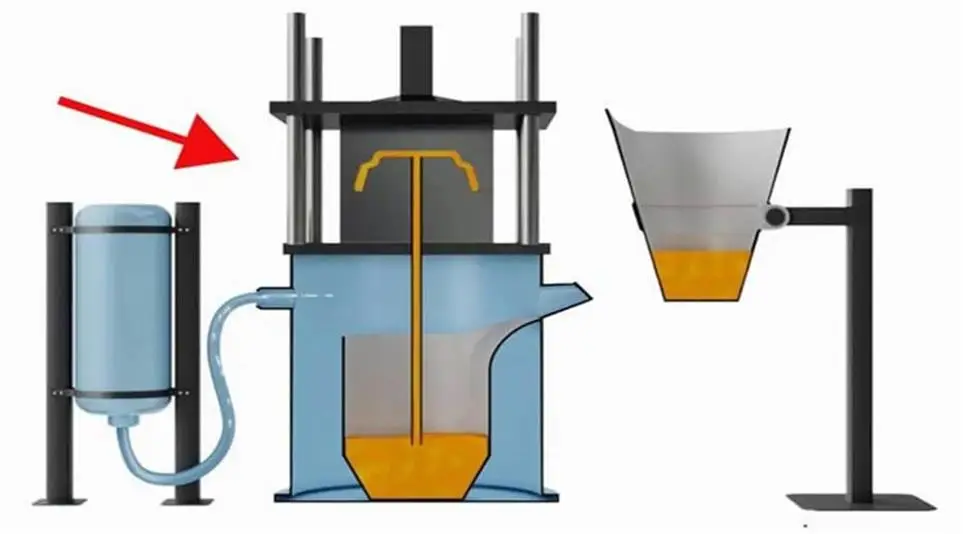
Cast aluminum is brittle: exploring and solving for this problem
Cast aluminum, with its excellent strength, good electrical and thermal conductivity, and relatively light weight, plays an indispensable role in modern industry.
However, the problem of cast aluminum is brittle has always been a major challenge in engineering applications. Especially in low temperature environments or when subjected to high stress, the brittleness of cast aluminum is particularly evident, which greatly limits its application in key areas.
Therefore, in-depth research on the problem of cast aluminum is brittle and its improvement methods is of great significance for improving the application safety of aluminum alloy castings and expanding their application range.
Table of Contents
1.The meaning and manifestation of cast aluminum is brittle
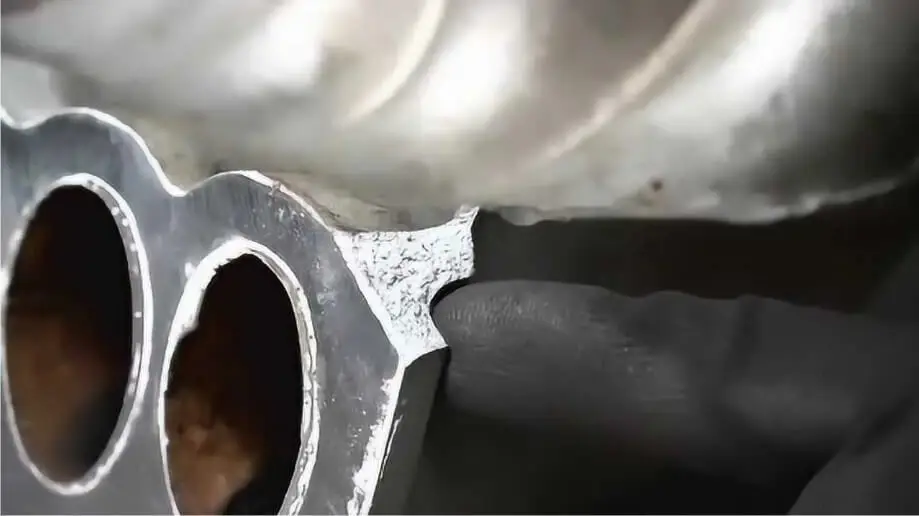
Cast aluminum is brittle, which usually refers to the property that the material breaks when it is subjected to stress without obvious plastic deformation. This phenomenon is manifested in practical applications as cast aluminum components is prone to sudden fracture under external loads without obvious signs. Brittle fractures usually occur along the grain boundaries or internal defects of the material, which may include pores, inclusions, and coarse grains. Brittle fractures often occur very quickly, bringing great safety hazards to engineering applications.
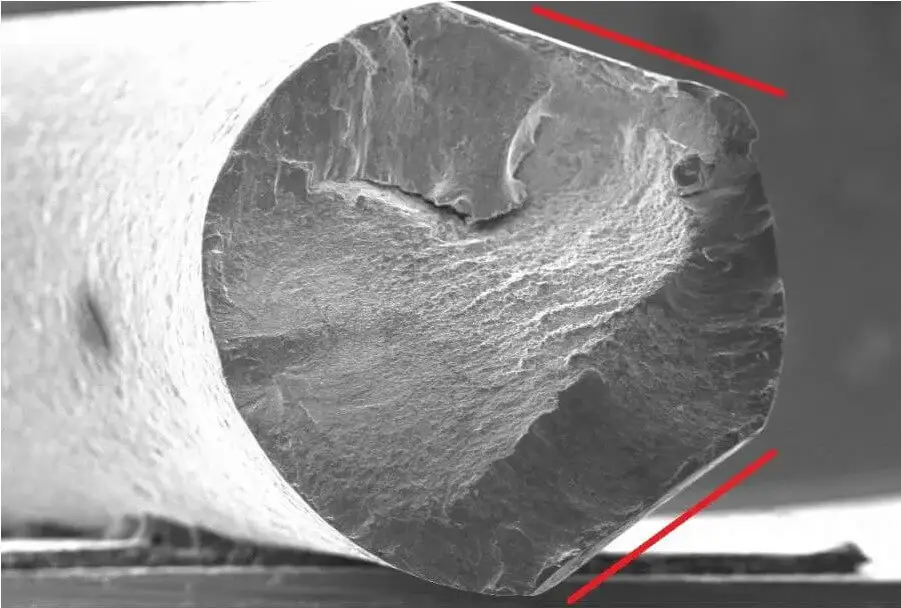
2.Why do we need to solve the problem of cast aluminum is brittle?
(1) Wide application of aluminum alloys
Aluminum alloys have been widely used in aviation, aerospace, automobiles, construction and other fields since the early 20th century due to their light weight, high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. With the development of modern industrial technology, the application scope of aluminum alloys has been continuously expanded, and they play an increasingly important role in high-performance application fields such as aerospace and high-speed rail transportation.
(2) The problem of cast aluminum is brittle has hindered the expansion of aluminum alloy applications
Although aluminum alloys have many advantages, their brittleness has always been a major challenge in engineering applications. Especially in low temperature environments or high stress conditions, the brittleness of cast aluminum is more obvious, which directly affects the safety and reliability of the material. The brittleness of cast aluminum not only affects its service life, but may also cause sudden fractures and cause serious safety accidents.For example, in the field of aerospace, the brittle fracture of cast aluminum parts may lead to catastrophic consequences.
3.Analysis of the reasons why cast aluminum is brittle
(1) The influence of material composition on brittleness
The brittleness of cast aluminum is closely related to the type and proportion of alloying elements. For example, iron and silicon are common impurity elements that form hard and brittle compounds in the aluminum matrix, increasing the brittleness of the material. In addition, although the addition of alloying elements can improve certain properties of aluminum, such as strength, improper proportions may also introduce new brittle phases. For example, the addition of copper and magnesium can improve the strength of aluminum alloys, but excessive copper and magnesium may lead to the formation of coarse intermetallic compounds, thereby reducing the toughness of the alloy.
(2) Effect of manufacturing process on brittleness
The cooling rate, solidification conditions and subsequent heat treatment process during the casting process have a significant effect on the brittleness of cast aluminum. Rapid cooling may cause internal stress and grain refinement, while improper heat treatment may form unfavorable microstructures, such as coarse grains or brittle phases. These factors will cause cast aluminum to be brittle. For example, during the casting process, if the cooling rate is too fast, a large number of microscopic defects such as dislocations and vacancies will form inside the material. These defects may become crack sources under the action of external stress, leading to brittle fracture of the material.
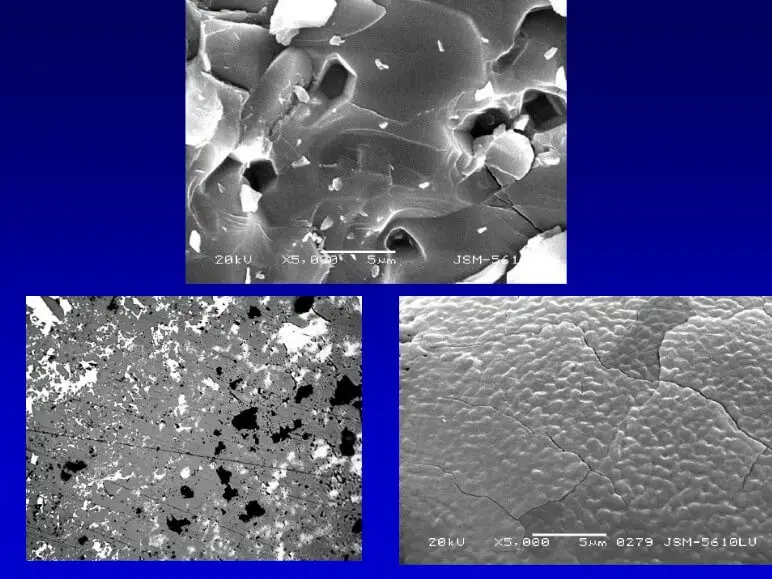
(3) Heat treatment process problems
Heat treatment is an important method to improve the performance of cast aluminum, but if it is not handled properly, it will increase brittleness. For example, quenching cooling speed is too fast may cause internal stress to increase and form quenching cracks. At the same time, overburning or overheating will also cause coarse grains, reducing the plasticity and toughness of cast aluminum.
(4) Machining and stress concentration
During the machining process, if the processing parameters are not properly selected, stress concentration may occur on the surface or inside of the casting, thereby increasing the risk of brittleness. In addition, unreasonable casting structure design, such as sharp corners or large changes in wall thickness, will also cause stress concentration during use and cracks.

(5) Environmental factors
Cast aluminum may corrode and oxidize in certain environments, such as high temperature or corrosive media, resulting in reduced surface performance and increased brittleness. Especially under high temperature conditions, the strength of aluminum will be significantly reduced and the brittle tendency will increase.
4.Methods to improve the problem of cast aluminum is brittle
(1) Composition optimization
The brittleness of cast aluminum can be effectively reduced by precisely controlling the types and proportions of alloying elements. For example, adding an appropriate amount of manganese and chromium can refine the grains and improve toughness. At the same time, reducing the content of harmful impurities such as iron and silicon is also an important measure to reduce brittleness. For example, the addition of manganese can refine the grains by forming fine intermetallic compounds, thereby improving the toughness of the alloy; while the addition of chromium can reduce the brittle phase at the grain boundary by forming stable carbides.
(2) Process improvement
Improving the casting and heat treatment process is another effective way to improve the difficulty of cast aluminum is brittle. For example, slow cooling and homogenization can help reduce internal stress and optimize the microstructure, thereby improving the toughness of cast aluminum and reducing brittleness. In addition, the use of advanced casting techniques such as pressure casting and semi-solid casting can effectively control the grain size and morphology, further improving the brittleness of the material.
For example, pressure casting can reduce internal defects by increasing the density of the casting, thereby improving the toughness of the material; while semi-solid casting can refine the grains and improve the mechanical properties of the material by controlling the temperature of the solid-liquid two-phase region.
(3) Heat treatment strengthening
Heat treatment is one of the important means to improve the performance of cast aluminum. Through solution treatment and aging treatment, the strengthening phase can be effectively precipitated to improve the strength and toughness of cast aluminum. For example, the T6 heat treatment process can significantly improve the mechanical properties of cast aluminum, so that it has good plasticity and toughness while maintaining high strength.
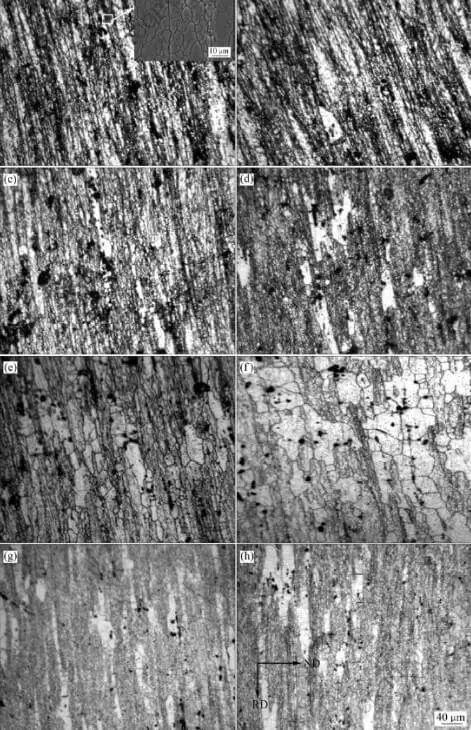
(4) Adding reinforcing materials
Adding reinforcing materials such as ceramic particles, carbon fibers or intermetallic compounds to the cast aluminum matrix can effectively improve its mechanical properties and brittleness resistance. Reinforcing materials improve the fracture toughness and fatigue resistance of cast aluminum by bearing part of the load and hindering crack propagation.
(5) Surface treatment technology
Surface treatment technologies such as laser surface modification, electron beam surface modification and ion implantation can effectively improve the surface properties of cast aluminum. Through these technologies, a modified layer with high hardness, high wear resistance and good brittleness resistance can be formed on the surface of cast aluminum, significantly improving its service life and reliability.
(6) Structural optimization design
In the product design stage, by optimizing the structure of cast aluminum parts, such as increasing fillets, reducing thickness mutations and optimizing rib design, stress concentration can be effectively reduced and its brittleness resistance can be improved. In addition, the use of simulation technologies such as finite element analysis can predict and optimize the stress distribution of cast aluminum parts, further improving their safety and reliability.

5.Comparison between cast aluminum and cast iron
| Performance Index | Aluminum Casting | Cast Iron |
| Density | Low density, approximately 2.7 g/cm³, beneficial for lightweight design | High density, approximately 7.2 g/cm³, resulting in a heavier overall structure |
| Tensile Strength | Generally low, prone to fracture due to defects | Usually high, especially for ductile iron, which can withstand large tensile forces |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent heat conduction performance, suitable for use as heat dissipation components | Poor thermal conductivity, slow temperature rise |
| Corrosion Resistance | Strong inherent corrosion resistance, particularly suitable for humid or outdoor environments | Prone to rusting, usually requiring surface coating protection |
| Weight Characteristics | Extremely lightweight, suitable for weight-reduction designs (such as in automobiles and aviation) | Heavy mass, suitable for occasions requiring high stability or seismic resistance |
Cast aluminum is widely used in aviation, automobile engine housing, electronic radiators and other occasions with high lightweight requirements due to its low density, good thermal conductivity and strong corrosion resistance. However, its brittleness becomes a limiting factor in structural parts with high stress or impact resistance requirements.
Cast iron is widely used in machine tool beds, pipes, brake discs and other parts with high load-bearing capacity due to its higher compressive strength and cost advantages. Ductile iron, in particular, has both strength and toughness.
6.Performance comparison between cast aluminum and wrought aluminum
| Comparison Item | Aluminum Casting | Forged Aluminum |
| Strength | Lower strength, prone to internal defects | High strength, dense structure |
| Durability | Moderate toughness, poor impact resistance | Good toughness, strong impact resistance |
| Manufacturing Process | Molten aluminum casting, suitable for complex structures | High-pressure forming, more uniform microstructure |
| Cost | Low cost, suitable for mass production | High cost, longer processing cycle |
| Typical Applications | Enclosures, casings, general structural parts | High-strength components |
| Structural Complexity | Suitable for complex or thin-walled structures | Mostly used for regular shapes |
Wrought aluminum is generally less brittle than cast aluminum. The production process of wrought aluminum enhances its ductility and toughness, making it more suitable for applications that require high strength and impact resistance. However, in specific application areas, cast aluminum has irreplaceable application advantages.
7.How does die-cast aluminum improve the brittleness of metals?
Die casting is an efficient aluminum alloy forming process that not only improves production efficiency, but also improves the brittleness of materials to a certain extent. Through high-pressure injection and rapid cooling, the die casting process enables aluminum castings to have better organizational structure and performance, which is specifically reflected in the following aspects:

(1) Refined grain effect brought by rapid cooling
During the die casting process, molten aluminum liquid can quickly fill the mold and cool and solidify under high pressure. This process can promote the formation of a finer grain structure. These fine and uniform grain structures help to disperse external stress, thereby improving the strength and fracture resistance of the material, making it less prone to brittle failure when subjected to stress.
(2) Effectively reduce porosity and shrinkage defects
Compared with traditional sand casting, die casting has obvious advantages in terms of density. High-pressure injection reduces the retention of gas in molten aluminum, thereby significantly reducing porosity. The fewer internal defects in the material, the higher its overall mechanical properties and impact resistance, which helps to reduce the probability of cracks.
(3) Better surface quality suppresses stress concentration
The surface of the die-casting mold is smooth, and the formed aluminum parts usually have a high surface finish. This feature helps to reduce surface micro-defects and sharp corners, reducing the probability of stress concentration. Stress concentration is a common cause of brittle fracture of materials, so die-casting improves the durability and crack resistance of aluminum alloy castings to a certain extent.
8.Where is cast aluminum still widely used?
Despite its limitations, cast aluminum excels in many low-stress or corrosion-resistant applications:
(1) Benefits of cast aluminum:
Lightweight properties – critical for improving efficiency in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Corrosion resistance – its protective oxide layer prevents rust, especially in marine or outdoor environments.
Cost-effectiveness – when casting large or complex-shaped parts, cast aluminum can reduce production costs and minimize secondary operations.
(2) Application advantages are obvious in the following areas:
Heatsinks for electronic products, where thermal performance is more important than mechanical strength.
Non-load-bearing housings for household appliances.
Decorative components in architectural design.
Manufacturers can balance performance and affordability by using cast aluminum in the right areas.
9.Summary
In summary, the reasons why cast aluminum is brittle involve many aspects such as material composition, casting process, heat treatment, machining and environment. These factors can be controlled and improved through composition optimization, process improvement, heat treatment strengthening, surface treatment technology, structural optimization design, etc. When you do the above, you can effectively improve the problem of cast aluminum is brittle, improve its comprehensive performance and expand its application range.