Bulk metallic manufacturing process: a combination of tradition and modernity
Bulk metallic manufacturing process, a sophisticated process that combines traditional skills with modern technology, plays an increasingly important role in today’s manufacturing industry with its unique advantages and wide application fields.
This article will explore in depth the definition, importance, traditional processes, modern processes, selection and optimization of bulk metallic manufacturing processes, application fields, and the key technical points and advantages of bulk metal glass manufacturing processes.
1.Overview of prerequisite knowledge of bulk metallic manufacturing process
(1) Definition and importance of bulk metallic manufacturing process
Bulk metallic manufacturing process involves the conversion of metal raw materials into metal materials with specific shapes, sizes and properties through different processing technologies. These processes play a core role in modern industry and are the cornerstone of manufacturing mechanical parts, components and other metal products. Through a variety of bulk metallic manufacturing processes, the utilization efficiency of metal materials can be greatly improved to meet various complex application requirements.
(2) Application fields and their impact on modern industry
Bulk metallic manufacturing process is widely used in aerospace, automobile manufacturing, construction engineering and other fields. In the aerospace field, high-performance metal parts are key to ensuring the safety and efficiency of aircraft and engines; in the automotive industry, lightweight and high-strength metal materials help improve fuel efficiency and vehicle safety. The development of bulk metallic manufacturing processes has not only promoted the advancement of industrial technology, but also had a profound impact on the research and application of new materials.

2.Bulk metallic manufacturing processes – traditional processes
(1) Bulk metallic manufacturing processes: casting processes
Casting is the process of pouring liquid metal into a mold and cooling and solidifying it to form the desired shape. Depending on the mold material and process, casting can be divided into many types.
1) Sand casting
Sand casting is one of the most common casting methods, using sand as the mold material. It is suitable for producing large or complex-shaped castings and is widely used in mechanical manufacturing and construction engineering.
2) Metal mold casting
Metal mold casting uses metal molds, which can be reused and is suitable for mass production. The castings produced by this method have high dimensional accuracy and good surface quality.
3) Pressure casting
Pressure casting is the process of injecting liquid metal into a mold under high pressure, with a fast cooling rate, and is suitable for producing thin-walled, complex metal parts. Commonly used in the manufacture of automobiles and electronic products.

(2) Bulk metallic manufacturing process: forging process
Forging is the process of deforming metal by applying external force to improve its internal structure and mechanical properties. Common forging processes include:
1) Hot forging
Hot forging is to heat the metal to a certain temperature to increase its plasticity and then forge it. Suitable for the production of large and complex parts.
2) Cold forging
Cold forging is carried out at room temperature and can improve the strength and hardness of the metal, but the deformation is limited. Commonly used in the manufacture of precision parts.
3) Isothermal forging
Isothermal forging is carried out at a constant temperature and can reduce the internal stress of the material and improve the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the parts.

(3) Bulk metallic manufacturing process: welding process
Welding is a process of connecting two or more metal parts into one by heating or pressurizing, or both. Common welding methods include:
1) Arc welding
Arc welding uses an electric arc as a heat source to melt the base material and welding wire to form a strong joint. Widely used in construction, manufacturing and maintenance.
2) Resistance welding
Resistance welding melts metal by the resistance heat generated by the current passing through the contact points. It is suitable for mass production, such as automobile body manufacturing.
3) Laser welding
Laser welding uses a high-energy-density laser beam as a heat source. It has a fast welding speed and small deformation. It is suitable for the manufacture of precision instruments.

3.Bulk metallic manufacturing process – modern process
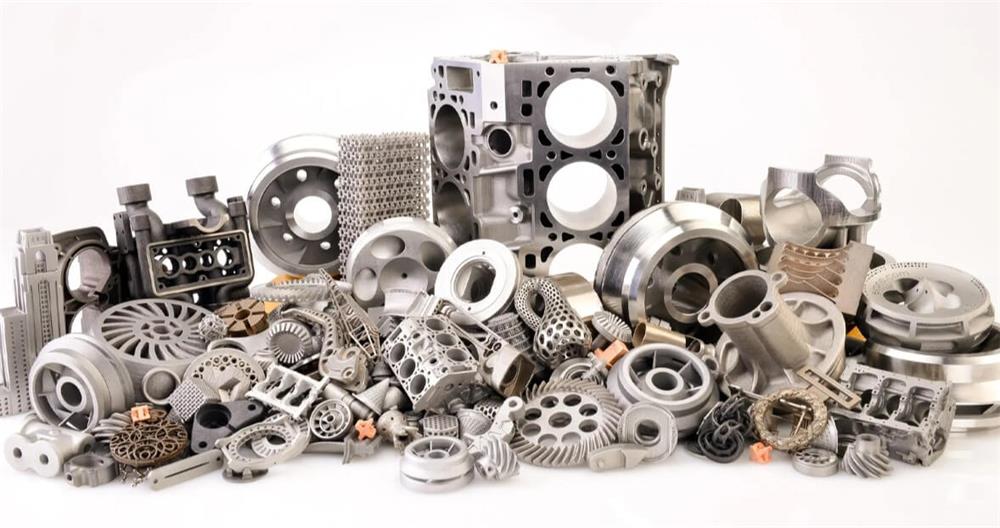
(1) Bulk metallic manufacturing process: additive manufacturing technology (3D printing)
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a technology that builds objects by stacking materials layer by layer. In bulk metal manufacturing, additive manufacturing technology can significantly improve material utilization, reduce waste, and can produce complex structures that are difficult to achieve with traditional processes.
1) Selective laser melting (SLM)
Selective laser melting uses a high-power laser to melt metal powder layer by layer to form dense metal parts. This technology is suitable for manufacturing high-precision and high-complexity parts.
2) Electron beam melting (EBM)
Electron beam melting uses an electron beam as a heat source in a vacuum environment to melt metal powder. This method can reduce oxidation of the material and is suitable for manufacturing parts with high purity requirements.
3) Fused deposition modeling (FDM)
Fused deposition modeling melts thermoplastic material or metal wire by heating the nozzle and then deposits it layer by layer to form parts. Although the accuracy is low, the cost is relatively low and it is suitable for prototyping and small batch production.
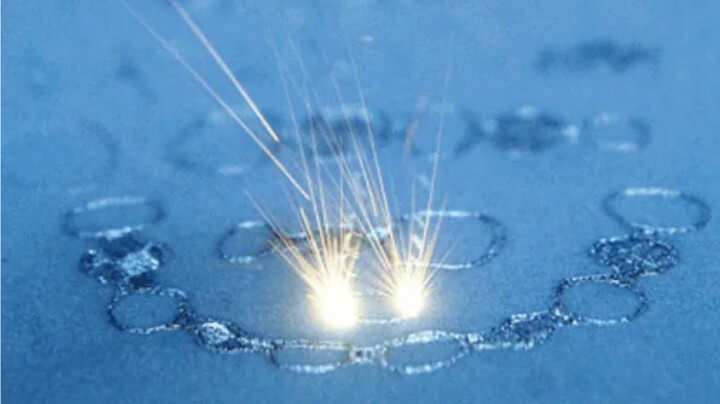
(2) Bulk metallic manufacturing process: powder metallurgy technology
Powder metallurgy is a process technology that manufactures metal materials, composite materials and various types of products by molding and sintering metal powder or a mixture of metal and non-metal powder.
1) Metal injection molding (MIM)
Metal injection molding combines the process of plastic injection molding and the advantages of powder metallurgy to produce metal parts with complex shapes and high precision.
2) Sintering
Sintering is the process of heating metal powder at high temperature to make the particles bond to each other and form a solid structure. Sintering can improve the density and mechanical properties of the material.
3) Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot isostatic pressing is the process of treating materials under high temperature and high pressure, which can eliminate the pores inside the material and improve its density and mechanical properties.

(3) Bulk metallic manufacturing process: production of amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys
Amorphous alloys (also known as metallic glass) and nanocrystalline alloys have been increasingly used in modern industry due to their unique properties.
1) Rapid solidification technology
Rapid solidification technology is to cool liquid metal at an extremely fast speed to form an amorphous or nanocrystalline structure. This technology can significantly improve the hardness and corrosion resistance of the material.
2) Application of bulk amorphous alloys
Bulk amorphous alloys are widely used in electronics, aerospace and other fields due to their excellent mechanical and physical properties.
4.Key technical points and advantages of bulk metallic glass manufacturing process
Bulk metallic glass (BMG), also known as amorphous alloy, is a new type of material with unique structure and excellent properties. Let’s talk about the key technologies and advantages of amorphous alloys mentioned above.
(1) Key technical points
1) High-temperature melting and rapid cooling:
Metal alloy raw materials are melted at high temperature to form a uniform liquid metal. Then, they are cooled at an extremely fast speed, usually up to tens of thousands of degrees per second, so that the liquid metal does not have time to crystallize and directly forms an amorphous structure. This process requires precise control of temperature and cooling rate to ensure the formation of high-quality BMG.
2) Pure raw materials and precise ratios:
Selecting high-purity metal raw materials and mixing them according to precise chemical ratios is the key to ensuring the performance of bulk metallic glass. Different combinations of metal elements will give BMG different properties, such as high strength, high hardness, and corrosion resistance.
3) High-pressure casting and vacuum environment:
During the manufacturing process, high-pressure casting technology is usually used to inject liquid metal into the mold for molding. At the same time, the entire process needs to be carried out under vacuum or inert gas protection to prevent the metal from oxidizing at high temperatures and ensure the purity and performance of the product.
4) Subsequent heat treatment:
Although rapid cooling is a key step in forming an amorphous structure, the subsequent heat treatment process is equally important. By precisely controlling the temperature and time, the microstructure of BMG can be adjusted to further optimize its mechanical and physical properties.

(2) Advantages of bulk metallic glass manufacturing process
1) Excellent mechanical properties:
Bulk metallic glass has excellent mechanical properties such as high strength, high hardness, and high elastic limit, and its strength is much higher than that of traditional crystalline metal materials.
2) Good corrosion resistance:
Due to the uniformity of the amorphous structure, BMG has excellent corrosion resistance and can work stably for a long time in harsh environments.
3) High magnetic permeability and low loss:
Some bulk metallic glasses have the characteristics of high magnetic permeability and low magnetic loss, and have broad application prospects in electronic transformers, sensors and other fields.
4) Unique processing characteristics:
The amorphous structure enables bulk metallic glass to exhibit good plastic deformation ability during processing, and can be processed and formed with high precision.
5.Selection and optimization of bulk metallic manufacturing process
(1) Basis for process selection
When selecting a bulk metallic manufacturing process, the main considerations include material performance requirements, cost and efficiency, etc.
1) Material performance requirements
Different application fields have different performance requirements for metal materials. For example, the aerospace field requires high-strength and high-durability materials, while electronic products may pay more attention to the conductivity and thermal properties of the materials.
2) Cost and efficiency considerations
The selection of bulk metallic manufacturing processes also needs to take into account production costs and production efficiency. High-efficiency processes can reduce production costs, but may require higher initial investments.

(2) Process optimization strategies
In order to improve production efficiency and product quality, the manufacturing process needs to be optimized.
1) Optimization of process parameters
By adjusting process parameters such as temperature, pressure, speed, etc., the quality and production efficiency of the product can be improved.
2) Application of new technologies
The introduction of new technologies and equipment, such as additive manufacturing and automated production lines, can significantly improve production efficiency and product quality.
6.Practical application of bulk metallic manufacturing processes
(1) Application of bulk metallic manufacturing processes in the aerospace field
In the aerospace field, additive manufacturing technology has been widely used to manufacture complex aircraft engine components. For example, titanium alloy turbine blades manufactured using selective laser melting technology are not only light in weight, but also have excellent strength and heat resistance.

(2) Lightweight component production in the automotive industry
Aluminum alloy casting technology is increasingly used in the manufacture of automotive parts. Aluminum alloy engine parts manufactured using casting technology not only reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency, but also enhance vehicle safety and handling.
(3) Manufacturing of metal structural parts in electronic products
The application of precision welding technology in the manufacture of smartphone housings has greatly improved the product’s aesthetics and structural strength. For example, stainless steel or aluminum alloy housings can be precisely connected using laser welding technology, ensuring the durability and waterproof performance of the phone.
7.Conclusion
(1) Current status of bulk metallic manufacturing processes
At present, bulk metallic manufacturing processes has developed to a fairly mature level and can meet the needs of various industrial applications. Traditional processes such as casting, forging and welding still occupy an important position, while modern processes such as additive manufacturing and powder metallurgy technology show greater potential in continuous innovation.
(2) Future development trends
With the advancement of technology and changes in market demand, bulk metallic manufacturing processes are developing towards high efficiency, high precision and environmental protection. Additive manufacturing technology is expected to play a more important role in the future, especially in the manufacture of high-performance materials.




