Analysis of the difference between High and low pressure casting
High and low pressure casting are two metal forming technologies widely used in the manufacturing industry. Although they both form parts by injecting molten metal into molds, they have significant differences in working principles, processes, costs, economic benefits, application areas, advantages and disadvantages. Let me tell you the difference between high and low pressure casting in detail.
1.The difference between High and low pressure casting in terms of basic concepts and principles
(1) Definition of high pressure casting:
High-pressure casting is a method in which liquid or semi-liquid metal is filled into the die-casting cavity at a high speed under high pressure and solidified under pressure to obtain castings.
(2) Definition of low pressure casting:
Low-pressure casting is a method in which liquid metal fills the mold cavity under low pressure to form a casting.
(3) Principle of high pressure casting:
The molten metal quickly fills the mold cavity under high pressure and solidifies under high pressure to form a high-density, high-strength casting.
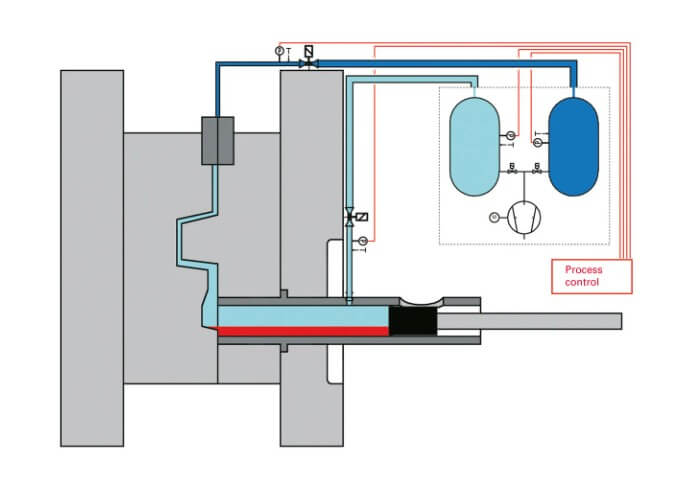
(4) Low pressure casting principle:
The molten metal enters the mold cavity smoothly through the liquid riser tube at a low pressure, and the gas pressure on the liquid surface in the crucible is maintained until the casting is completely solidified.
summary:
To sum up the principle difference between high and low pressure casting in one sentence, high-pressure casting presses molten metal into the mold cavity at high speed through high pressure, while low-pressure casting uses lower pressure to smoothly fill the mold with molten metal.
2.The difference between high and low pressure casting in terms of process flow and technical details
High and low pressure casting are two different metal casting processes, and they have significant differences in process flow and technical details. The following are the main differences between high and low pressure casting:
(1) High pressure casting process
The main steps are: refining aluminum water → insulation → spraying → molding → pouring → injection → pressurization, pressure maintaining → mold opening → picking up and cleaning.
(2) Low pressure casting process
Main steps: Pour dry compressed air into the sealed crucible. Under the action of gas pressure, the metal liquid rises along the liquid riser, enters the mold cavity smoothly through the gate, and maintains the gas pressure on the liquid surface in the crucible. Until the casting is completely solidified.
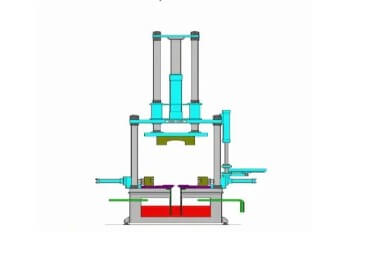
(3) High pressure casting filling speed
High-pressure casting has high-speed characteristics in terms of filling speed, usually 1050 meters/second, sometimes even up to more than 100 meters/second. This high-speed filling allows the molten metal to fill the mold cavity in a very short time, generally 0.010.2 seconds. Although high-speed filling improves production efficiency, it can also easily cause defects such as pores and looseness inside the casting.
(4) Low pressure casting filling speed
In contrast, the filling speed of low-pressure casting is slower, usually controlled at 50150 mm/second, and the pressurization rate is 1.271.75 kPa/second. This slow and steady filling speed helps to discharge the gas in the mold cavity, reduce pores and inclusions in the casting, and improve the density and mechanical properties of the casting.
3.The difference between high and low pressure casting in equipment and molds
(1) High pressure casting equipment:
High-pressure casting equipment mainly includes die-casting machines and molds. The die-casting machine fills liquid or semi-liquid metal into the mold cavity at high speed through high pressure, and solidifies it under high pressure. High-pressure casting machines usually have high clamping force to ensure that the mold is tightly closed under high pressure.
(2) Low pressure casting equipment:
Low-pressure casting equipment consists of a holding furnace, a liquid riser, a mold and a pressurizing device. The working principle is to use a lower pressure (usually lower than the vapor pressure of liquid metal) to inject molten metal into the cavity from the bottom of the mold, gradually rise to fill it, and solidify under pressure.
(3) High pressure casting mold:
The design is complex, and metal flow and exhaust issues during high-speed filling need to be considered. Mold materials usually use high-strength alloy steel to withstand repeated effects of high pressure and high temperature. The mold life is relatively short and requires regular maintenance and replacement.
(4) Low pressure casting mold:
The design is relatively simple and focuses on controlling the smooth filling and solidification sequence of molten metal. There is a wide range of mold materials to choose from, including metal molds, sand molds, etc., because their working conditions are mild and the mold life is long.

4.The difference between high and low pressure casting in terms of cost and economic benefits
There are also differences in cost and economic benefits between high and low pressure casting. These differences are mainly due to their initial costs, production efficiency, part quality, etc.
(1) High pressure casting cost analysis
High-pressure casting requires high-precision equipment and molds, so the initial investment cost is high. However, due to its high production efficiency and suitable for mass production, the cost per unit product can be reduced in the long run. In addition, high-pressure casting has a high degree of automation, which can reduce labor costs.
(2) Low-pressure casting cost analysis
Low-pressure casting has low equipment investment and relatively low mold costs. However, due to the long production cycle, the production efficiency is lower than that of high-pressure casting, and it is suitable for small batch or customized production. Low-pressure casting has lower overall operating costs, especially when producing large and complex castings.
(3) Analysis of economic benefits of high pressure casting
High-pressure casting has high production efficiency and short filling time, which is generally completed within 0.01~0.2 seconds. Therefore, high-pressure casting can quickly produce a large number of castings and is suitable for high-volume production industries such as automobiles and electronics. Although the cost of high-pressure casting equipment and molds is relatively high, due to its production efficiency and high degree of automation, in the long run, the cost per unit product is relatively low and has high economic benefits.
(4) Analysis of economic benefits of low pressure casting
The production cycle of low-pressure casting is longer and the filling speed is slower, usually between a few seconds and a few minutes. Therefore, low-pressure casting has lower production efficiency and is suitable for industries with small batches or customized production. Although low-pressure casting has low equipment investment and mold costs, due to its low production efficiency, the economic benefits per unit product are relatively poor in the long run.
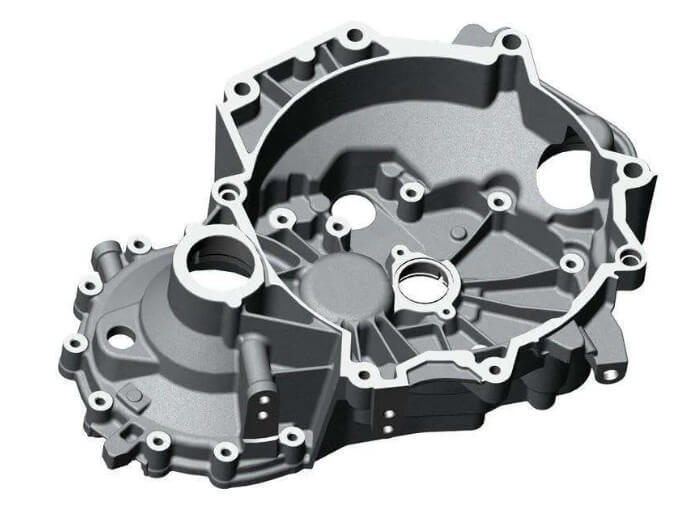

5.Differences in application fields between High and low pressure casting
High and low pressure casting have their own characteristics and advantages in application fields. Here are their main differences:
(1) High pressure casting application fields
1) In the automotive industry, high-pressure casting is widely used to produce complex parts such as engine parts, gearbox casings, and instrument panels. These parts require high precision and surface quality, and also need to withstand high-temperature and high-pressure working environments. High-pressure casting can meet these requirements.
2) In the field of electronic products, high-pressure casting is used to produce parts such as mobile phone casings and laptop computer casings. These parts require high precision and beautiful appearance, and high-pressure casting can achieve these requirements.
3) In the aerospace field, high-pressure casting is used to produce high-precision, high-strength parts, such as aircraft engine parts, satellite parts, etc. These parts have very high requirements on material performance and casting process, and high-pressure casting can meet these requirements. .

(2) Application fields of low pressure casting
1) In the aerospace field, low-pressure casting is widely used to produce high-precision, high-performance key components, such as aircraft engine blades. These parts require excellent high-temperature and mechanical properties, as well as high-precision dimensions and surface quality, and low-pressure casting can meet these requirements.
2) In the field of large mechanical parts, low-pressure casting is used to produce parts such as large turbines and large pump casings. These parts require high strength and good corrosion resistance. Low-pressure casting can achieve these requirements.
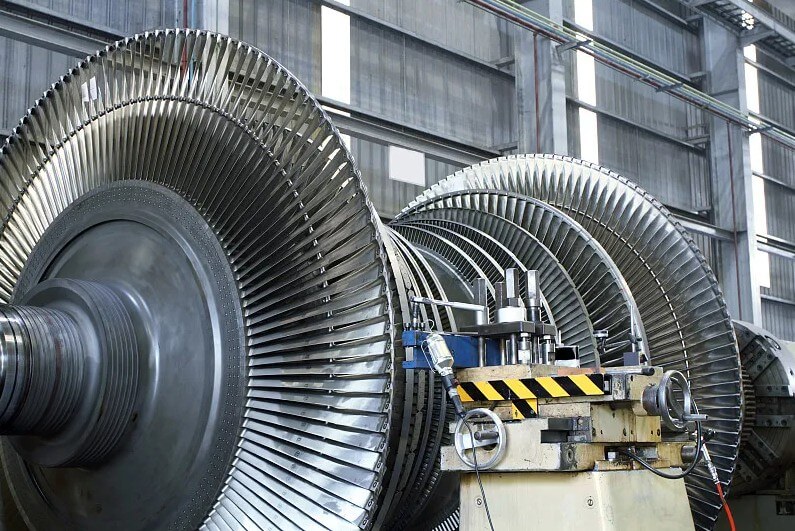

6.Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of high and low pressure casting
High and low pressure casting each have different advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different production needs. The following is a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of high and low pressure casting:
(1) Advantages of high pressure casting:
1) Extremely high production efficiency: High-pressure casting can quickly produce a large number of castings and is suitable for mass production.
2) High dimensional accuracy: The castings have precise dimensions and good surface finish, generally equivalent to grade 5 to 8, and even up to Ra1.6.
3) Higher strength and hardness: The strength and hardness of castings are usually 25~30% higher than those of sand casting.
4) Good interchangeability: Due to high dimensional accuracy, castings have good interchangeability.
5) High metal utilization rate: Die castings generally do not require mechanical processing or the processing amount is very small, which improves the metal utilization rate.
6) Easy to realize automation: The production process is easy to realize mechanization and automation.
(2) Disadvantages of high pressure casting:
1) Porosity is easy to occur inside the casting: Due to the high speed of the molten metal filling the mold cavity and unstable flow state, pores are easy to occur inside the casting, the elongation is not good, and heat treatment cannot be performed.
2) It is difficult to die-cast castings with complex concavities: For castings with complex structures, high-pressure casting may not be able to completely fill the cavity.
3) High equipment and mold costs: High-pressure casting equipment and mold costs are high.
(3) Advantages of low pressure casting:
1) The casting structure is dense: crystallized under pressure, the casting structure is dense, the outline is clear, the surface is smooth, and the mechanical properties are high.
2) Improved metal utilization rate: The feeding riser is omitted, and the metal utilization rate is increased to 90-98%.
3) Easy to realize mechanization and automation: The production process is easy to realize mechanization and automation.
4) Applicable to various casting molds: The pressure and speed during pouring can be adjusted, and it is suitable for various casting molds (such as metal molds, sand molds, etc.).
5) Stable filling: Using bottom-injection filling, the molten metal is filled smoothly without splashing, avoiding gas involvement and erosion of the mold wall and core.
(4) Disadvantages of low-pressure casting:
1) Lower production efficiency: Compared with high-pressure casting, low-pressure casting has lower production efficiency.
2) Equipment costs are higher: Equipment costs for low-pressure casting are higher.
3) The mold cost is low but the service life is short: Although the mold cost is low, the service life is short.
7.Conclusion
In practical applications, the choice between high and low pressure casting mainly depends on the specific requirements of the product, production scale and cost budget. High-pressure casting is suitable for applications requiring high efficiency and mass production, while low-pressure casting is more suitable for areas with strict requirements on the internal quality and performance of castings.
In the future, as market demand changes, both high and low pressure casting will continue to advance technologically. Overall, both casting technologies, high and low pressure casting, will continue to play an important role in their respective fields, providing high-quality casting solutions to different industries.




