Aluminum Metal Casting Molds: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Optimization
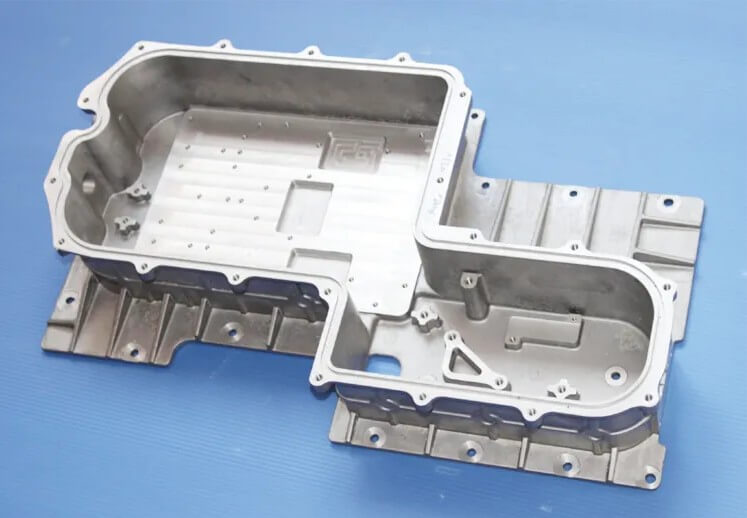
Aluminum metal casting molds, as an indispensable part of modern industrial production, has received great attention from various industries for its unique performance and wide application fields. Aluminum alloy is increasingly used in mold manufacturing due to its low density, high strength, good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Especially in the fields of automobiles, aviation, electronic products, etc., aluminum metal casting molds have become the first choice in the manufacturing process because they can provide precise component forming and efficient production cycle.
This article will introduce in detail the design, manufacturing and processing technology of aluminum metal casting molds, the impact of casting process on aluminum metal casting molds, common problems in its use and its solutions, and methods to extend the life of aluminum metal casting molds.
1.Design of aluminum metal casting molds
The design of aluminum metal casting molds is a key factor in ensuring the quality and production efficiency of aluminum products. The following are some design points of aluminum metal casting molds.
(1) Mold structure design
1) Ejection mechanism design
The ejection mechanism includes push rods, push tubes, ejector pins, push plates, etc., which are used to eject castings after molding. When designing, it is necessary to ensure that the ejection force is evenly distributed to avoid deformation or damage of the castings. The arrangement of the push rod and the ejector pin should take into account the shape and wall thickness of the casting, and the ejection position and number should be reasonably selected.
2) Guide mechanism design
Guide mechanisms such as guide pins and guide sleeves are used to ensure the precise fit between the movable mold and the fixed mold. The number, position and diameter of the guide pins should be considered during the design to ensure the stability and accuracy of the mold opening and closing process.
3) Core pulling mechanism design
For castings with complex structures, it is necessary to design a core pulling mechanism, such as a motorized or manual core pulling mechanism, a slider, etc. The design of the core pulling mechanism should ensure that the core pulling action is smooth and reliable to avoid damage to the casting during the core pulling process.
4) Overflow system design
The overflow system includes an overflow trough and an exhaust trough, which are used to remove excess metal liquid and gas during the casting molding process. A reasonable design of the overflow system can effectively prevent defects such as pores and shrinkage cavities in the casting.
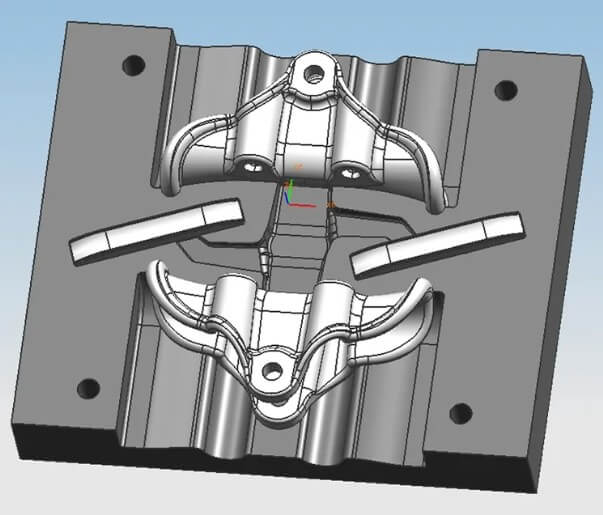
(2) Material selection for aluminum metal casting molds
The material selection for aluminum metal casting molds is a complex process involving multiple factors, which needs to be comprehensively considered based on specific casting processes, casting requirements, and production efficiency. The following are some key material selection and standards:
1) Sand casting molds usually use wood and aluminum as materials.
2) Metal mold gravity casting molds can choose A3 steel, 45# steel, HT200 cast iron, ductile iron 600 and 5CrMoMu.
3) Low pressure casting mold materials are similar to metal mold gravity casting, including HT200, ductile iron 600 and 5CrMoMu.
4) The core of the die casting mold usually uses H13 steel and 45# forged steel.
5) For aluminum alloy die casting molds, mold steel with high heat resistance, high hardness, high toughness and high thermal conductivity should be selected, such as LG mold steel.
6) The mold material should have good cutting processability, thermal stability, polishing performance, and sufficient surface hardness and wear resistance.
(3) Standard requirements for aluminum metal casting molds:
1) The chemical composition of aluminum alloy casting molds should comply with the provisions of GB/T15114-1994.
2) The mechanical properties of the mold should meet the requirements of GB/T15114-1994, including tensile strength, yield strength and elongation.
3) The dimensional tolerance and geometric tolerance of the mold should comply with the provisions of GB/T6414-1999 and be marked on the drawing.
4) The surface roughness of the mold should comply with the provisions of GB/T15114-1994, and defects such as cracks and undercasting are not allowed.
5) The mold design should consider the setting of process parts such as gates, flash, overflow ports, as well as the position of ejector pins and parting lines.
6) The mold temperature should be controlled at about 1/3 of the pouring temperature of aluminum alloy liquid to affect the mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy and mold life of the die casting.
7) The cooling methods of the mold mainly include air cooling, water cooling, oil cooling, etc. The appropriate cooling method should be selected according to the wall thickness of the casting and the mold structure.
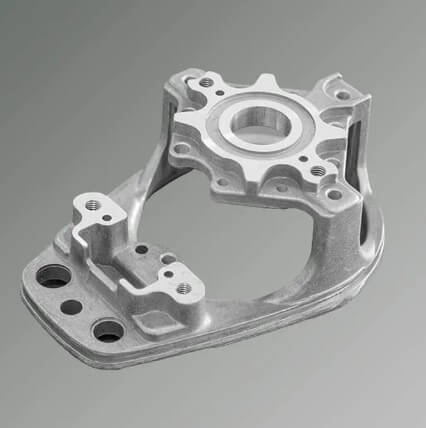

2.Manufacturing and processing technology of aluminum metal casting molds
The manufacturing and processing technology of aluminum metal casting molds is a crucial part of modern manufacturing industry, which mainly includes processing flow and surface treatment. The following will introduce them in detail.
(1) Processing process
1) Drawing review and material decision:
First, the design drawings need to be reviewed in detail to ensure the feasibility and accuracy of the design. Then, the previously pre-selected materials and standards are decided.
2) Mold frame processing:
The mold frame is the basic structure of the mold, and its processing accuracy directly affects the overall quality of the mold. Mold frame processing includes the processing of A/B plates, control panels, ejector fixing plates and other parts. Each part must ensure flatness and flatness, usually within 0.02mm.
3) Mold core processing:
The mold core is the core part of the mold and determines the shape and size of the casting. Mold core processing includes burr treatment, fine grinding, milling machine processing, CNC preliminary processing, tempering treatment, fine polishing, CNC deep processing, EDM wire cutting and other steps. Each step requires strict control of accuracy and surface quality.
4) Mold parts processing:
In addition to the mold frame and mold core, the mold also includes various auxiliary parts, such as guide rail sliders, clamping blocks, etc. The processing of these parts also requires high precision to ensure the overall performance and stability of the mold.
5) Inspection and assembly:
After completing the processing of each part, the mold needs to be fully inspected to ensure that each part meets the design requirements. Subsequently, the parts are assembled to form a complete aluminum metal casting molds.
6) Mold trial and production:
After completing the mold assembly, a mold trial is required to verify the actual production effect of the mold. After making necessary adjustments based on the mold trial results, the mold can be put into formal production.
(2) Surface treatment
1) Polishing:
Polishing is an important part of mold surface treatment, which can improve the smoothness and wear resistance of the mold surface. Common polishing methods include mechanical polishing, chemical polishing and electrochemical polishing.
2) Heat treatment:
The purpose of heat treatment is to improve the mechanical properties of the mold material and increase the service life of the mold. Common heat treatment methods include quenching, tempering, aging treatment, etc.
3) Surface coating:
In order to further improve the performance of the mold, the mold surface can be coated. Commonly used coating materials include cemented carbide, ceramics, etc., which can improve the wear resistance, corrosion resistance and demolding properties of the mold.
4) Anti-oxidation treatment:
Aluminum metal is easily oxidized, which affects the service life of the mold and the quality of the casting. Therefore, the mold needs to be treated with anti-oxidation. Common methods include surface oxidation treatment and painting.
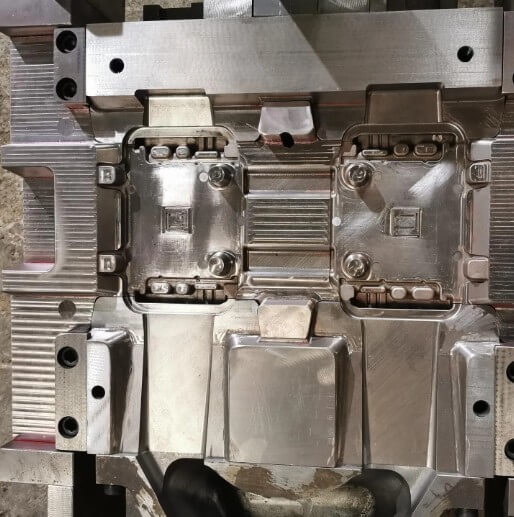
Summary:
The manufacturing and processing of aluminum metal casting molds is a complex and delicate process, which requires strict control of the quality of each link. Through advanced processing technology and effective surface treatment, the performance and service life of aluminum metal casting molds can be improved, providing high-quality casting products for the manufacturing industry.
3.Casting process and its impact on aluminum metal casting molds
(1) Selection of casting method
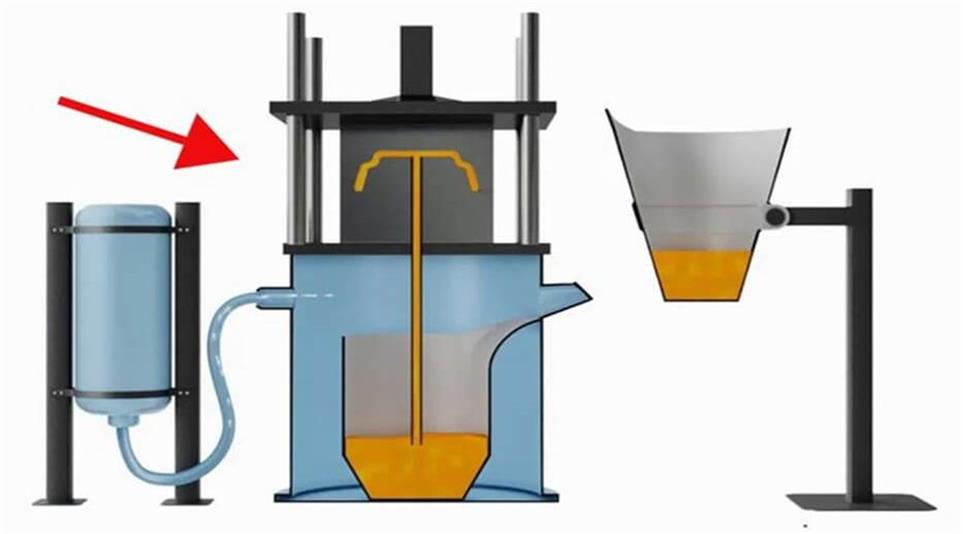
In the production of aluminum metal casting molds, choosing a suitable casting method is crucial to ensuring the quality and performance of the mold. Commonly used casting methods include sand casting and die casting.
1) Comparison between sand casting and die casting
Sand casting is suitable for the production of large or complex-shaped molds. It has the advantages of low cost and strong adaptability, but the production cycle is long and the surface accuracy and dimensional accuracy are relatively low.
Die casting is widely used in mass production due to its efficient production speed and high dimensional accuracy, and is particularly suitable for small and precise aluminum parts. However, the equipment investment for die casting is high, and the manufacturing and maintenance costs of the mold are also relatively high.
2) Advantages and disadvantages of each and applicable scenarios
The advantages of sand casting are its flexibility and low cost, which is suitable for single-piece or small-batch production, as well as large or complex castings.
The advantages of die casting are high production efficiency, high casting dimensional accuracy, good surface finish, and small precision castings produced in large quantities.
(2) Key technologies in the casting process
1) Mold preheating and cooling control
The preheating and cooling control of aluminum metal casting molds is a very critical technology in the casting process. Proper preheating can reduce the temperature difference between the mold and the aluminum liquid, reduce thermal stress, and thus improve the quality of the casting and the life of the mold. Cooling control affects the solidification rate and microstructure of the casting. A properly designed cooling system can effectively control the cooling process of the casting and avoid defects such as shrinkage cavities and cracks.
2) Quality control of aluminum liquid
The quality of aluminum liquid directly affects the quality of the casting. Before casting, the aluminum liquid needs to be refined to remove impurities and gases to ensure the purity of the aluminum liquid. In addition, temperature and flow rate control during the casting process are also key factors to ensure the quality of aluminum liquid.
4.Common problems and solutions of aluminum metal casting molds during use
(1) Metal liquid splashing
1) Reasons:
The mold between the movable mold and the fixed mold is not tight, there is a gap, causing metal liquid leakage; the clamping force is insufficient; the support plate has a large span and the injection force is large, resulting in deformation of the sleeve plate.
2) Solution:
Reinstall the mold to ensure that the movable mold and the fixed mold are tight and have no gap; increase the clamping force; add a support plate to improve the rigidity of the mold.
(2) Cold shut
1) Cause:
The alloy composition is impure, or contains impurities, and the metal liquid has poor fluidity; poor exhaust and low filling speed; low mold temperature and low metal liquid pouring temperature.
2) Solution:
Change the alloy composition and remove impurities; improve exhaust conditions and increase filling speed; control mold temperature and pouring temperature to ensure good metal liquid fluidity.
(3) Mold failure
1) Cause:
Premature failure and scrapping of molds caused by factors such as materials and processing. The manifestations of die-casting molds are thermal cracks, wear, cracking of sharp corners and corners, erosion, and slider jamming.
2) Solution:
Preheat the mold before production to prevent cracking; set up a certain cooling system to prevent periodic thermal expansion and contraction; regularly maintain and inspect the mold and replace severely worn parts in time.
(4) Porosity
1) Cause:
The gas content in the metal liquid is too high or the exhaust is not smooth.
2) Solution:
Optimize the casting process, improve the mold exhaust effect, reduce the temperature of the molten metal, etc.

(5) Shrinkage
1) Cause:
Defects caused by the shrinkage of the molten metal during the cooling process.
2) Solution:
Optimize the casting process, control the molten metal temperature and cooling rate, increase the riser and other measures.
Summary:
Through the above measures, the common problems of aluminum metal casting molds in the use process can be effectively solved, and the service life of the mold and the quality of the casting can be improved.
5.What are the commonly used methods to extend the life of aluminum metal casting molds?
There are many ways to extend the life of aluminum metal casting molds. The following are some commonly used measures:
(1) Mold design and manufacturing:
1) Optimize mold design, reduce sharp corners and corners, use materials reasonably, and standardize processing and heat treatment processes.
2) Select high-quality mold steel, equip with precise mold production equipment, and have an experienced mold manufacturing team.
(2) Surface treatment technology:
1) Chemical heat treatment processes such as carburizing, nitriding, N-C co-diffusion (soft nitriding), surface aluminizing and mold chromizing can improve the hardness, wear resistance and fatigue resistance of the mold surface.
2) Vapor deposition technology (such as CVD and PVD) can form a metal or compound coating with special properties on the mold surface to improve the wear resistance and friction resistance of the mold.
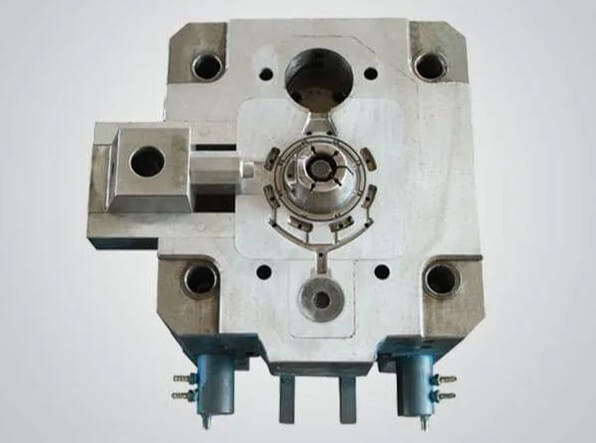

(3) Mold use and maintenance:
1) Reduce the pouring temperature of aluminum liquid to reduce erosion and thermal fatigue of the mold.
2) Strengthen the maintenance of aluminum metal casting molds, perform regular maintenance, and regularly temper the mold cavity to relieve stress and eliminate internal stress.
3) Perform deep cold treatment on the mold to improve wear resistance and dimensional stability.
4) Use reasonable quenching and tempering processes, such as cooling quenching, high temperature quenching and tempering in the first type of temper brittleness zone to improve the performance and life of the mold.
6.Summary
Through the comprehensive application of the above measures, the service life of aluminum metal casting molds can be effectively extended, and production efficiency and economic benefits can be improved.