Aluminium Grades for Casting: A Guide to Properties, Applications and Selection
Aluminum and its alloys are used in a wide range of applications in modern industry, especially in the foundry sector.
There is a wide variety of aluminium grades for casting, each with its own unique properties and application scenarios. This article will discuss in detail the different divisions and characteristics of aluminium grades for casting to help readers better understand and select the appropriate aluminum alloy materials.
1.Definition and characteristics of casting aluminium alloy
Casting aluminium alloy refers to aluminum alloy materials made by casting process, they usually contain elements such as silicon, copper, magnesium, zinc and so on, in order to improve their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Casting aluminum alloy not only has good casting performance, but also can further improve its mechanical properties through heat treatment and other means to meet the needs of different fields. According to the different chemical compositions and processing methods, casting aluminum grades can be divided into many categories, each grade has its specific application scenarios and performance requirements.

2.Nomenclature and standards for aluminium grades for casting
(1) Aluminium grades for casting: international naming rules (AA standard)
The naming rules formulated by the International Aluminum Association (AA) are widely adopted. The rules are mainly based on a four-digit code system, which can be followed by a status code. The specifics are as follows:
1) The first digit: indicates the main alloying element, and its significance is as follows:
1: Pure aluminum (aluminum content of at least 99.00%)
2: Copper as the main alloying element
3: Manganese is the main alloying element
4: silicon is the main alloying element
5: Magnesium is the main alloying element
6: Magnesium and silicon as the main alloying elements
7: Zinc is the main alloying element
8: Other elements
9: Alternate group
(2) The second digit: indicates the control of alloying elements or impurity limit content:
0: indicates no special control of impurity limit content
1-9: indicates that one or more impurities or alloying elements limit content of special control

3) Third and fourth digits:
For pure aluminum, the minimum aluminum percentage content of the two decimal points; for other alloys, these two figures have no special significance, only used to identify different alloys in the same group.
4) Status code:
F: free processing state, applicable in the molding process of processed products without mechanical properties required products
O: annealed state, applicable to the processed products by the complete annealing to obtain the minimum strength
H: work-hardening state, applicable to products with increased strength through work-hardening
W: solid solution heat treatment state, applicable only to solid solution heat treatment at room temperature after natural aging of the alloy
T: heat treatment state, applicable to heat treatment to achieve a stable state of the product
For example, 6061-T651 indicates that the main alloying elements are magnesium and silicon, after T651 heat treatment state of aluminum alloy.

(2) Aluminium grades for casting: Chinese naming rules
China’s aluminum alloy naming rules have been revised several times, and now mainly based on the national standard GB/T 16475-1996, the following is the specific casting aluminum grade naming rules:
1) Alloy system code:
L: Aluminum
LF: rust-proof aluminum alloy (Al-Mg, Al-Mn)
LY: hard aluminum alloy (Al-Cu-Mg)
LC: super-hard aluminum alloy (Al-Cu-Mg-Zn)
LD: Wrought aluminum alloy (Al-Mg-Si, Cu-Mg-Si)
LT: special aluminum alloy

2) State code:
F: Free machining state
O: annealed condition
H: work-hardening condition
W: solution heat treatment state
T:Heat treatment state
3) Subdivided state code:
HX1: tensile strength limit of O and HX2 state of the intermediate values
HX2: tensile strength limit of O and HX4 state of the intermediate value
HX3: tensile strength limit of HX2 and HX4 state of the intermediate values
HX4: the limit of tensile strength is the highest value.
For example, LD30-CZ means aluminum-magnesium-silicon-copper alloy with quenching and natural aging treatment.
3.Commonly Used Aluminum Grades for Casting
(1) Aluminium-silicon alloy (Al-Si)
Aluminum-silicon alloy, also known as “silicon-aluminum Ming”, is one of the most common and largest amount of casting aluminium alloy. Their silicon content is usually between 4% and 22%. These alloys have excellent casting properties, such as good fluidity, good airtightness, low shrinkage and low tendency to thermal cracking. After densification and heat treatment, aluminum-silicon alloys exhibit good mechanical properties, physical properties, corrosion resistance and moderate machinability.

1) Performance characteristics:
Good casting properties: good fluidity, good airtightness, small shrinkage and small tendency to thermal cracking.
Mechanical properties: good strength and toughness, especially after densification and heat treatment.
Corrosion resistance: shows good corrosion resistance.
Coefficient of thermal expansion: low, suitable for application scenarios requiring high dimensional stability.
2) Typical applications:
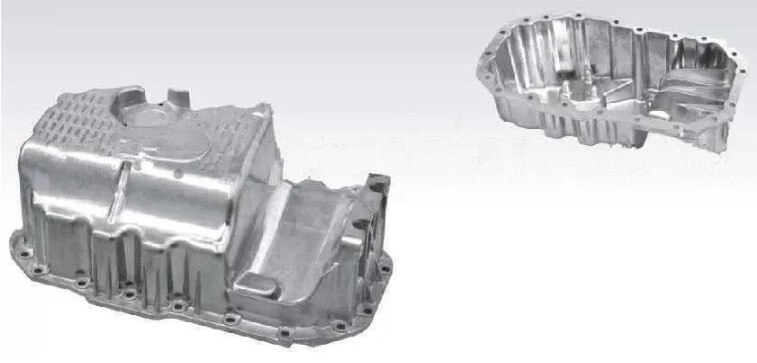
Pistons, engine blocks, cylinder heads and other automotive parts.
Various mechanical parts and housings.
Aerospace components such as frames and structural parts.
3) Common grades:
ZL102: Silicon content 10.0-13.0%, used for castings with general requirements.
ZL104: Silicon content 6.5-7.5%, with the addition of magnesium and titanium to improve mechanical properties and heat resistance.
ZL107: Silicon content of 6.5-7.5%, adding copper and magnesium, for high strength requirements of the castings.
(2) Aluminium-copper alloy (Al-Cu)
Aluminum-copper alloys have been used earlier in industry, and their copper content is usually between 3% and 11%. By adding other elements such as manganese and titanium, aluminum-copper alloy room temperature and high temperature mechanical properties can be significantly improved.
1) Performance characteristics:
Mechanical properties: excellent strength and hardness, especially at high temperatures.
Casting properties: relatively poor, high density, poor corrosion resistance.
Cutting and welding properties: showing good cutting and welding properties.

2) Typical applications:
Aerospace components such as engine parts and frames.
Structural and heat-resistant parts subject to large loads.
3) Common grades:
ZL201: Contains 4.5-5.3% copper, with manganese and titanium added to improve room and high temperature strength.
ZL205A: 4.8-5.5% copper content, is currently one of the world’s highest strength casting aluminum alloy.
ZL207: copper content of 4.0-5.0%, adding mixed rare earths, improving high-temperature strength and thermal stability.

(3) Aluminium-magnesium alloy (Al-Mg)
Aluminium-magnesium alloys with magnesium content between 4% and 11% are characterized by low density and high strength. These alloys have excellent corrosion resistance in the atmosphere and seawater, and good comprehensive mechanical properties and machinability at room temperature.
1) Performance characteristics:
Mechanical properties: high strength and toughness, especially at room temperature.
Corrosion resistance: excellent corrosion resistance, especially in the marine environment.
Cutting and machining performance: the processing surface is bright and beautiful.
Melting and casting process: relatively complex, requiring strict control of process parameters.

2) Typical applications:
Radar base, aircraft engine magazine, propeller, landing gear and other aerospace parts.
Ship structural parts and marine engineering equipment.
High strength requirements of mechanical parts and shell.
3) Common grades:
ZL301: Containing 9.0-11.0% magnesium, with a small amount of zinc and manganese added to improve the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
ZL303: magnesium content of 10.0-13.0%, adding a small amount of silicon and manganese, suitable for high-strength requirements of the castings.
(4) Aluminum-zinc alloy (Al-Zn)
Aluminum and zinc alloy usually add silicon and magnesium elements, known as “zinc silicon aluminum Ming”. In casting conditions, the alloy has a quenching effect, can be used without heat treatment, metamorphic heat treatment casting strength, stabilization treatment after the dimensional stability.
1) Performance characteristics:
Mechanical properties: has high strength and hardness, especially after metamorphic heat treatment.
Casting properties: showing good fluidity, but prone to thermal cracking.
Corrosion resistance: relatively poor, requires surface treatment to improve corrosion resistance.

2) Typical applications:
Models, type plates and equipment supports, etc.
Instrument housing type parts.
3) Common grades:
ZL401: Containing 7.5-9.5% zinc, adding silicon and magnesium, suitable for castings with general requirements.
ZL402: Zinc content 8.0-10.0%, add silicon and magnesium, improve the mechanical properties and dimensional stability.
4.How to choose the right aluminium alloy material according to the aluminium grades for casting?
First of all, according to the aluminium grades for casting classification table, and then according to their own needs to consider the following factors:
1) Performance requirements:
According to the mechanical properties of castings, corrosion resistance, casting performance and other requirements to choose the appropriate grade of aluminum alloy.

2) Application scenarios:
Different grades of aluminum alloys are suitable for different application scenarios, such as automotive, aerospace, marine, machinery manufacturing and so on.
3) Production cost:
Different aluminum alloys have different raw material costs, processing costs and production efficiencies, which require comprehensive consideration of economic results.
4) Process requirements:
Different aluminum alloys have different melting, casting and heat treatment process requirements, which need to be selected according to the existing equipment and process capabilities.
Through the above analysis, you can choose the appropriate casting aluminum alloy according to the aluminium grades for casting and then combined with the specific needs to ensure that the quality and performance of castings to meet the requirements of practical applications.
5.Summary
Different aluminium grades for casting have unique performance characteristics, from strength to corrosion resistance, each characteristic directly affects the quality and reliability of the final product. Therefore, the precise selection of the appropriate aluminum material according to the application requirements can not only optimize the performance of the product, but also effectively reduce production costs and extend the service life of the product.