Cast Iron Engine Block: Advantages and Disadvantages, Manufacturing Process and Application Guide
Cast iron engine blocks are widely used in commercial vehicles, heavy vehicles and high-performance engines due to their high strength, durability and cost advantages. After years of development, their manufacturing process has formed a mature and efficient process.
This article will discuss in detail the advantages and disadvantages, manufacturing process and application scenarios of cast iron engine blocks.
1.Advantages of cast iron engine blocks
(1) High strength and durability:
Cast iron cylinder blocks have excellent pressure resistance and high temperature resistance. They can withstand high pressure and high temperature environments and are not easy to deform, so the failure rate is relatively low.
(2) Excellent modification potential:
For car owners who pursue high performance, cast iron cylinder blocks provide greater modification space and can withstand stronger horsepower and torque output.
(3) Low production cost:
The acquisition and processing technology of cast iron materials is relatively mature and low-cost, which makes cast iron cylinder blocks have significant economic advantages in large-scale production.
(4) Small size and compact structure:
The high strength of cast iron allows for a more compact cylinder structure, which reduces the overall size of the engine and facilitates installation and layout.
2.Disadvantages of cast iron engine blocks
(1) Heavy weight:
Compared with aluminum alloy engine blocks, cast iron engine blocks are significantly heavier, which increases the weight of the vehicle, affects handling flexibility, and may lead to increased fuel consumption.
(2) Poor heat dissipation performance:
The thermal conductivity of cast iron is not as good as that of aluminum alloy, resulting in poor heat dissipation performance of the engine. During intense driving or high-load operation, the engine is prone to overheating.
(3) Insufficient corrosion resistance:
When cast iron is in contact with corrosive substances such as water vapor for a long time, it is easy to rust, affecting its service life and performance stability.

(4) High friction coefficient:
The high friction coefficient between the cast iron engine block and the aluminum alloy piston may affect the performance and efficiency of the engine and increase wear.
Summary:
In general, cast iron engine blocks have advantages in strength, cost and modification potential, but have disadvantages in weight, heat dissipation and corrosion resistance. The choice of cast iron or aluminum alloy cylinder block should be determined according to specific usage requirements and economic conditions.
3.Manufacturing process and complete process of cast iron engine block
(1) Material preparation
1) Raw material selection
Pig iron: The main components are iron, carbon and silicon, which is the basic material of cast iron cylinder block.
Alloy elements: Add alloy elements such as nickel, chromium and molybdenum as needed to improve the strength, wear resistance and heat resistance of cast iron.
2) Melting
Melting furnace: Use a cupola or electric furnace to melt pig iron and alloy elements into molten iron.
Temperature control: Ensure that the temperature of molten iron is between 1400°C and 1500°C to ensure fluidity.
(2) Casting process
1) Mold preparation
Sand casting: Use sand mold as mold, suitable for small batch production.
Metal mold casting: Use metal molds, which are suitable for mass production and have higher precision.
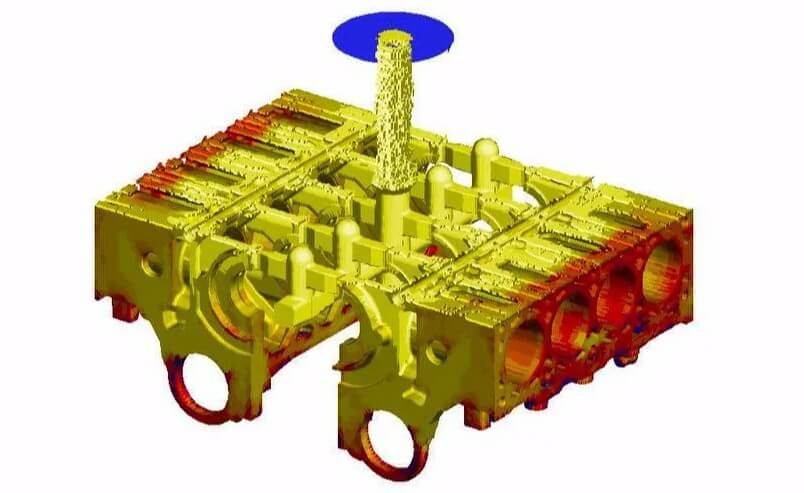
2) Pouring
Poting system: Design a reasonable pouring system to ensure that the molten iron fills the mold evenly.
Pouring speed: Control the pouring speed to avoid defects such as pores and cold shuts.
3) Cooling
Natural cooling: The casting cools naturally to room temperature in the mold.
Control cooling speed: By controlling the cooling speed, the internal structure and performance of the casting are optimized.
(3) Cleaning and trimming
1) Remove the pouring head
Mechanical cutting: Use cutting equipment to remove the pouring head.
Grinding: Grind the cut part to ensure the surface is flat.
2) Surface cleaning
Sandblasting: Use sandblasting equipment to clean the surface of the casting to remove oxide scale and residual sand particles.
Chemical cleaning: Use acid or alkali cleaning to further clean the surface.
(4) Mechanical processing
1) Rough processing
Milling: Mill the main plane of the cylinder to ensure the base surface is flat.
Drilling: Processing bolt holes, water channel holes, etc. of the cylinder body.
2) Finishing
Boring: Precision boring of the cylinder bore to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface roughness.
Grinding: Grinding of key parts to improve surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
(5) Heat treatment
1) Annealing
Stress relief: Annealing is used to eliminate internal stress generated during casting and processing.
Improvement of structure: Optimize the microstructure of cast iron and improve its mechanical properties.
2) Quenching and tempering
Quenching: Improve the hardness and wear resistance of cast iron.
Tempering: Reduce the brittleness after quenching and improve toughness.
(6) Surface treatment
1) Anti-rust treatment
Coating: Chrome or zinc plating is performed on the surface of the cylinder body to improve corrosion resistance.
Painting: Spray anti-rust paint to further protect the surface of the cylinder body.
2) Wear-resistant treatment
Nitriding treatment: Nitriding the cylinder bore surface to improve wear resistance.
Coating: Wear-resistant coating is used to extend the service life of the cylinder block.
(7) Quality inspection
1) Dimension inspection
Three-coordinate measurement: Use a three-coordinate measuring instrument to detect the key dimensions of the cast iron engine block to ensure that it meets the design requirements.
Measuring tool inspection: Use calipers, micrometers and other measuring tools for conventional dimensional inspection.
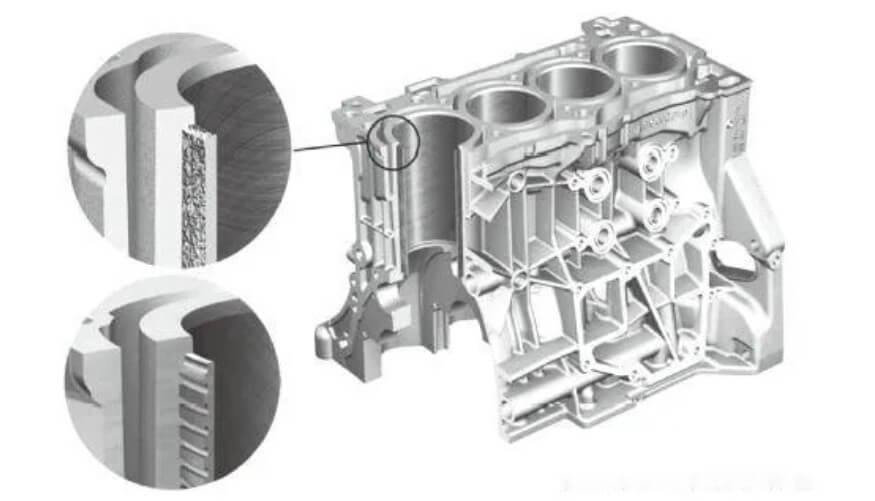
2) Nondestructive testing
Ultrasonic testing: Detect whether there are cracks, pores and other defects inside the cylinder block.
Magnetic particle testing: Detect cracks on the surface and near the surface of the cylinder block.
3) Pressure testing
Hydraulic pressure testing: Perform a hydraulic pressure test on the cylinder block to ensure its sealing and strength.
4.Application scenarios of cast iron engine blocks
Cast iron engine blocks are widely used in many fields due to their high strength, durability and cost advantages. The following are its main application scenarios.
(1) Commercial vehicles
Trucks: high strength and durability suitable for high loads and long-term operation, low cost to control production costs.
Buses: high reliability and low maintenance cost, suitable for long-term use.
(2) Heavy-duty vehicles
Engineering machinery: high strength and wear resistance suitable for high loads and harsh working conditions.
Agricultural machinery: durability and low cost suitable for long-term operation and economic needs.
(3) High-performance vehicles
Racing cars: high strength and heat resistance suitable for high mechanical stress and high performance requirements.
High-performance sports cars: high strength and stability suitable for high-load operation.
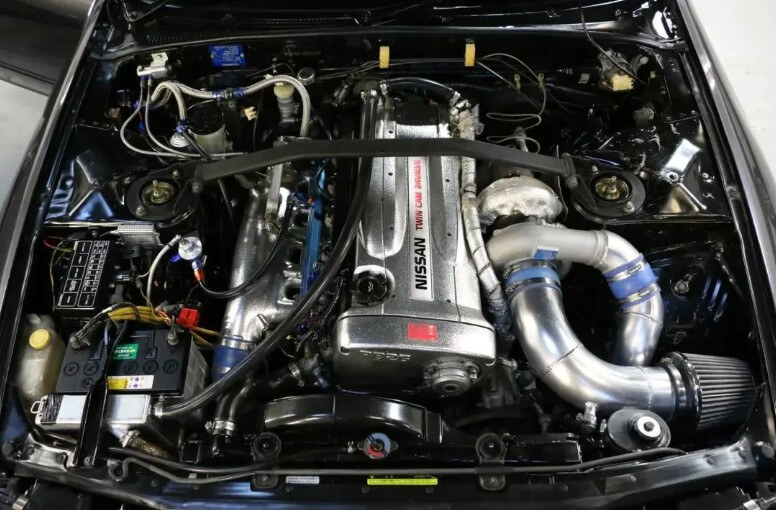

(4) Ships and power generation equipment
Ship engines: high strength and corrosion resistance suitable for high loads and marine environments.
Power generation equipment: durability and low cost suitable for long-term stable operation.
5.Summary
As a traditional engine component, cast iron engine block has limitations in some aspects, but its advantages such as durability and strong load-bearing capacity still make it irreplaceable in many fields.





What do you think?
[…] Cast iron cylinder blocks perform well under high load and high temperature conditions and are suitable for high-performance and heavy-duty engines. […]