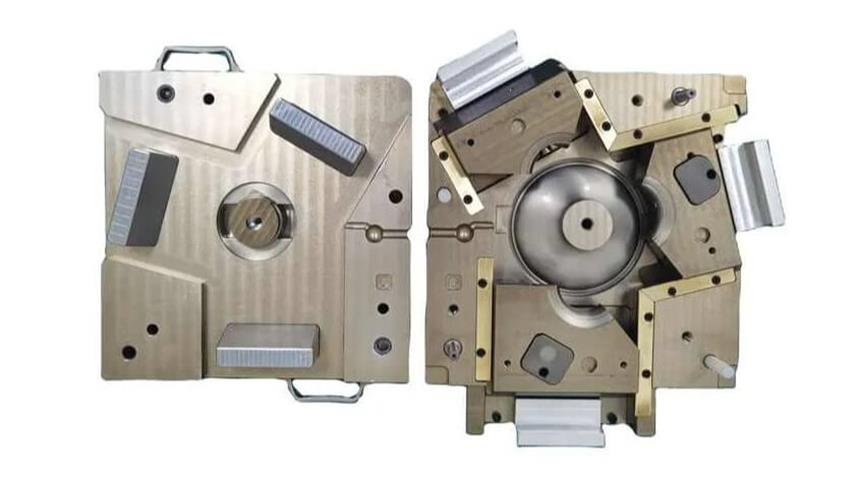
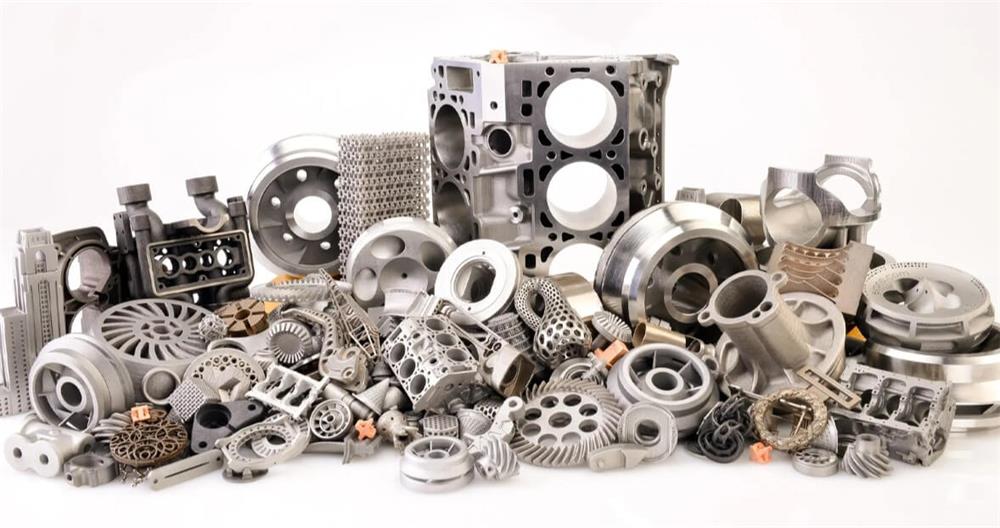
How to make a mold: an integrated guide to material selection, design and processing
How to make a mold? Casting molds play an important role in the metal forming process. This article will comprehensively analyze how to make molds from three aspects: material selection, design and processing.
1.How to make a mold: Part I Material selection
The selection of casting mold materials is crucial. It not only affects the service life of the mold and the precision of the casting, but also directly affects the production cost. The following are several commonly used casting mold materials and their performance characteristics:
(1) Gray cast iron
Advantages: high compressive strength, good wear resistance, and low cost.
Disadvantages: easy to deform and low precision.
Scope of application: small and medium-sized castings.
(2) Ductile iron
Advantages: high strength and yield strength, good wear resistance.
Disadvantages: slightly higher cost than gray cast iron.
Scope of application: large and complex castings.
(3) Alloy steel
Advantages: high strength, high hardness, and good wear resistance.
Disadvantages: high cost.
Scope of application: high-strength, wear-resistant castings.
(4) Carbon steel
Advantages: low strength and hardness, high cost.
Disadvantages: poor wear resistance.
Scope of application: small castings.
(5) Aluminum alloy
Advantages: light weight, good heat dissipation, good oxidation resistance.
Disadvantages: relatively low strength.
Scope of application: precision castings.
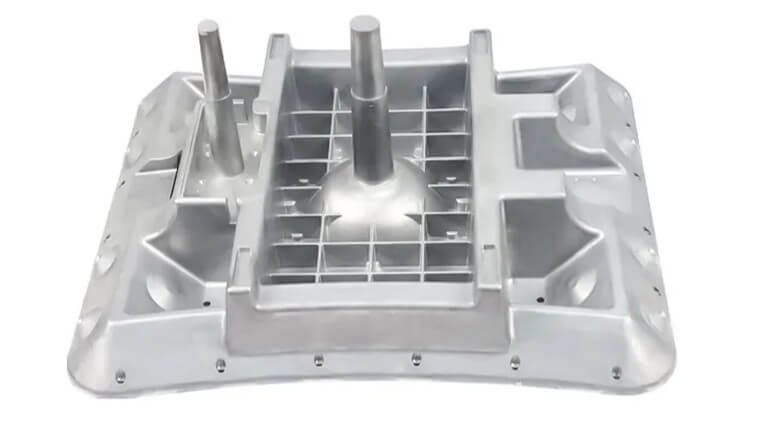

When selecting casting mold materials, the following factors should be considered comprehensively:
- Casting shape, size and weight
- Casting material
- Casting process
- Casting quality requirements
- Mold service life
- Cost
2.How to make molds: Part II Design principles
Casting mold design is the core link in the manufacturing process, and its design quality directly affects the molding effect and production efficiency of the casting. The following are several key principles that should be followed in casting mold design:
(1) Reasonable parting surface
The parting surface should facilitate mold disassembly and casting removal to reduce the difficulty of operation.
(2) Optimization of the pouring system
The pouring system should ensure that the molten metal flows smoothly into the mold, avoid turbulence and eddy currents, and prevent defects such as shrinkage cavities and pores in the casting.
(3) Cooling system design
Reasonably arrange cooling channels to promote solidification, reduce deformation, and improve production efficiency.
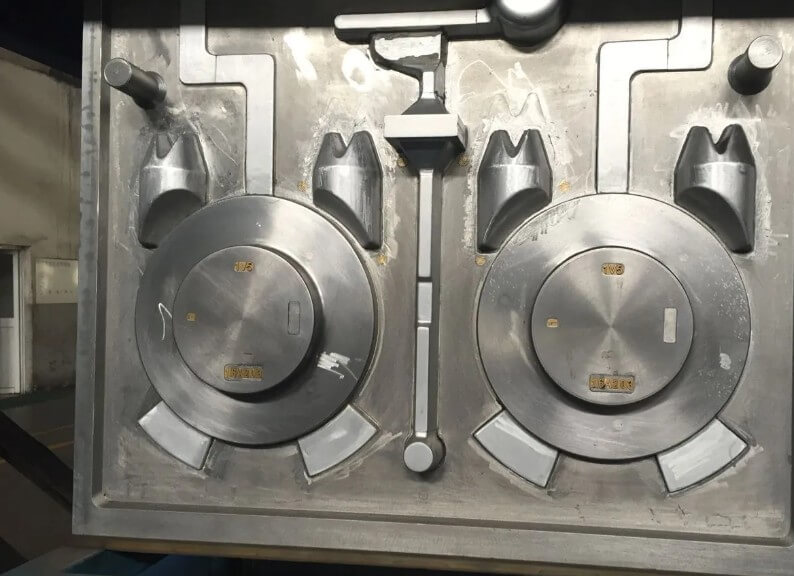

(4) Exhaust system
Set up exhaust channels to remove the gas generated during the pouring process and prevent pores and looseness in the casting.
(5) Strength analysis
Calculate the stress and deformation of the mold to ensure that it can withstand the load during the pouring process and increase the service life of the mold.
(6) Demolding design
Use technologies such as draft angle, lubricant, and vibration demolding to ensure that the casting is smoothly ejected from the mold and avoid defects such as sand sticking and fracture.
(7) Core design
Reasonably design the core according to the structure of the casting to ensure the strength and air permeability of the core and prevent problems such as core breakage and sand flushing during the pouring process.
3.How to make a mold: Part III Specific processing methods
(1) Mechanical processing methods
1) Design preparation:
Use CAD software to design a three-dimensional model of the mold according to the shape and size of the required casting.
2) Material selection:
Select materials suitable for mold processing. Commonly used ones are steel, aluminum alloy, etc. The material type is determined according to the use requirements of the mold.
3) Rough processing:
Use sawing machines, milling machines, lathes and other equipment to perform rough processing on the blank to remove most of the material and approach the basic shape of the mold.
4) Heat treatment:
The mold after rough processing is heat treated, such as annealing or tempering, to eliminate internal stress and improve mechanical properties.
5) Finishing:
Use CNC machining centers, grinders and other precision equipment for finishing to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the mold.
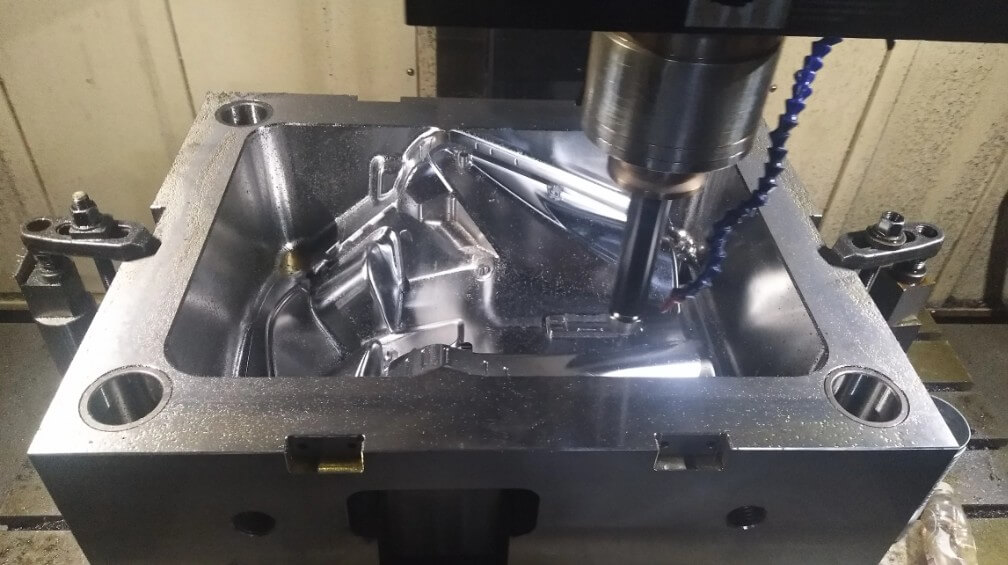

6) Cavity processing:
According to the mold design, process the cavity and core parts, which usually requires high-precision processing equipment such as EDM, wire cutting, etc.
7) Polishing:
Polish the surface of the cavity and core to ensure the smooth surface of the casting.
8) Assembly and debugging:
Assemble the processed parts, and perform mold trials and debugging to ensure that the mold can work properly.
(2) 3D printing technology
1) Design model:
As with mechanical processing, first use CAD software to design the three-dimensional model of the mold.
2) Select materials:
Select suitable 3D printing materials, such as metal powder, according to the use requirements of the mold.
3) Print mold parts:
Use a 3D printer to print each component of the mold layer by layer.
4) Post-processing:
Post-process the printed parts, including removing support structures, surface grinding, heat treatment, etc., to improve their mechanical properties and surface quality.
5) Assembly and debugging:
Assemble the printed and post-processed parts, and perform mold trials and debugging to ensure that the mold can work properly.
The above explains the specific methods and processes of “how to make a mold”. Through these two methods, a casting mold that meets the requirements can be made, thereby achieving efficient and accurate casting production.
4.How to make a mold: an integrated guide
In order to achieve efficient production of casting molds, material selection, design and processing (CNC processing) should be considered as a whole. The following are some suggestions:
(1) Matching of material selection and design
According to the use requirements and expected life of the mold, select suitable materials, and fully consider the performance characteristics of the materials in the design to optimize the mold structure.
(2) Collaboration between design and CNC processing
The feasibility of CNC processing should be considered in the design stage, and the mold structure should be reasonably designed to reduce the difficulty and time of processing.
(3) Process optimization
Through numerical simulation technology, the performance of the mold in the casting process can be predicted, the design parameters can be optimized, and the overall performance of the mold can be improved.
(4) Cost control
In the process of material selection, design and processing, cost factors should be comprehensively considered, and production costs can be reduced by optimizing process flow and material utilization.
(5) Continuous improvement
Continuously summarize experience, continuously improve mold design and manufacturing processes, and improve product quality and production efficiency.
5.Summary
In short, how to make a mold? This is a complex and systematic process involving multiple links such as material selection, design and processing. Only by comprehensively considering the factors of each link can high-quality casting molds be manufactured to provide strong support for the metal forming process.




