Shell casting: a comprehensive explanation and process comparison
As an important metal casting process, shell casting plays an indispensable role in industrial production. This article will analyze the shell casting process in detail (mainly including basic introduction, applicable materials, process flow, advantages and disadvantages, and application fields), and compare it with two other common casting processes-sand casting and investment casting, so as to better understand its characteristics and application fields.
1.Basic introduction
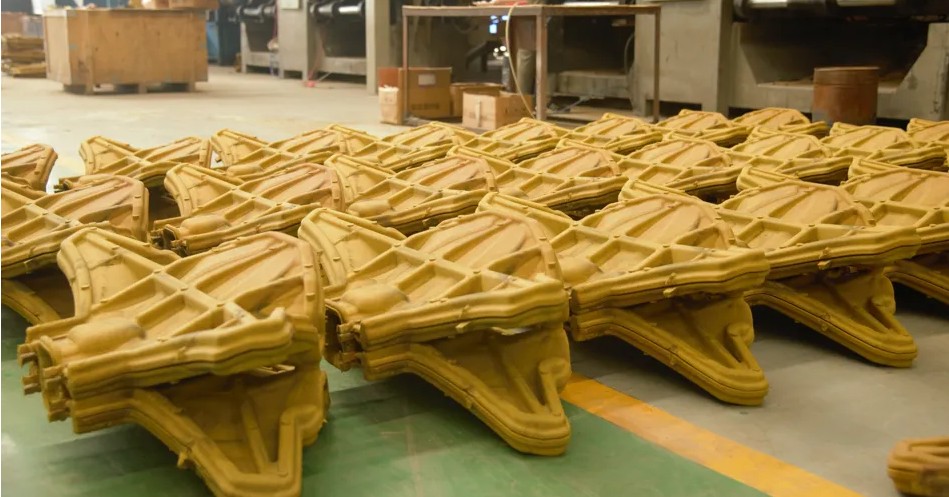
The shell casting process, also known as the Croning process, is a casting method that uses resin sand to heat and solidify on a metal template to form a thin shell mold, and then pours it to obtain high-precision castings. The key to shell casting is that its mold is composed of a thin shell, usually with a thickness of 6 to 12 mm. This thin shell not only improves the accuracy of the casting, but also significantly reduces the use of materials and the workload of subsequent processing.
Shell casting processes are mainly divided into two types: ceramic shell and resin sand shell. Ceramic shell is mainly used for the production of high-temperature alloy castings, while resin sand shell is widely used in the production of cast iron, cast steel and non-ferrous alloy castings. Resin sand shell molds are more common in industrial production because of their easy operation and low cost.
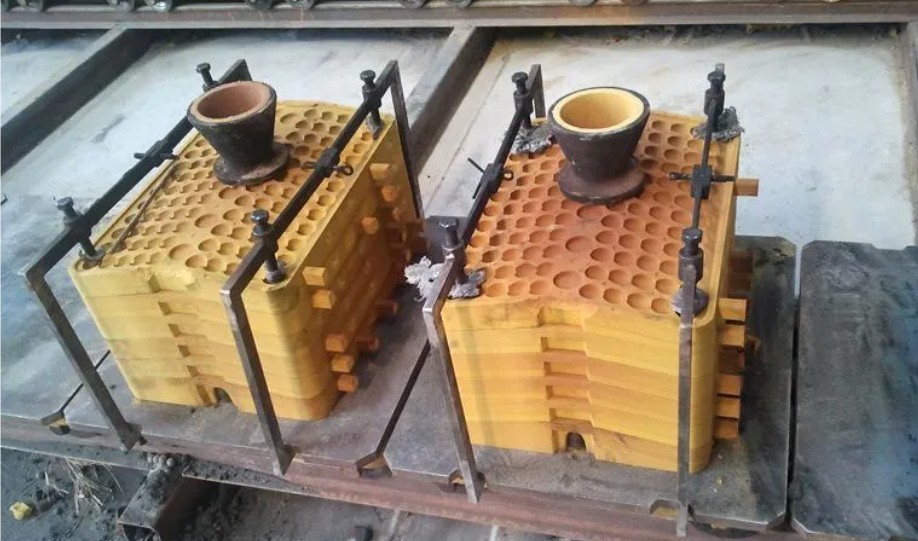

2.Analysis of applicable materials for shell casting
(1) Cast iron:
Shell casting is applicable to various grades of cast iron and can produce castings with clear contours and smooth surfaces. It is particularly suitable for thin-walled complex parts produced in large quantities.
(2) Carbon steel and low alloy steel:
These materials have good fluidity and castability. Through shell casting, high-precision and dimensionally stable parts can be manufactured. They are widely used in the automotive and machinery manufacturing fields.
(3) Stainless steel:
With excellent corrosion resistance and high temperature strength, stainless steel is also suitable for shell casting and is often used to manufacture parts that require high durability and high precision.
(4) Aluminum alloy:
Shell casting is also widely used in aluminum alloy materials. It can produce lightweight and complex parts to meet the needs of aviation, aerospace and other industries.
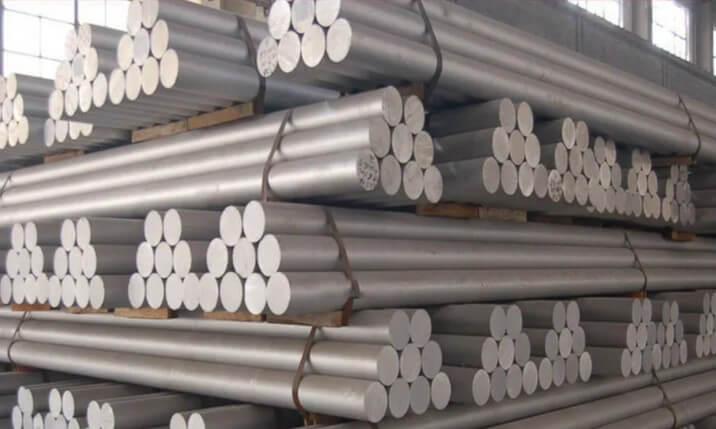

(5) Copper alloy:
Shell casting is also applicable to copper alloy materials. It can produce castings with complex shapes and high dimensional accuracy, which are suitable for the electronics, electrical and other industries.
3.Shell casting process
Shell casting is a high-precision casting process, the core of which is the production of molds and the pouring of metal. The following is a detailed introduction to the process:
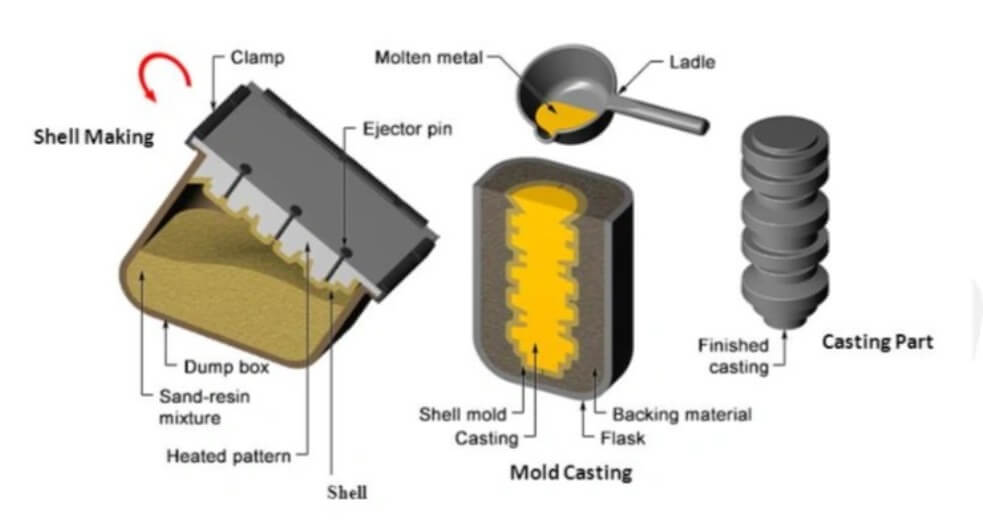
(1) Making metal models
1) Model design:
Design the metal model according to the shape and size of the casting, and fully consider the shrinkage rate and processing allowance after the metal cools.
2) Material selection:
Steel or cast iron are usually used to make the model, but for active metals (such as titanium and aluminum), graphite is a more suitable choice.
3) Split mold design:
Divide the metal model into two halves for subsequent demolding and mold assembly.
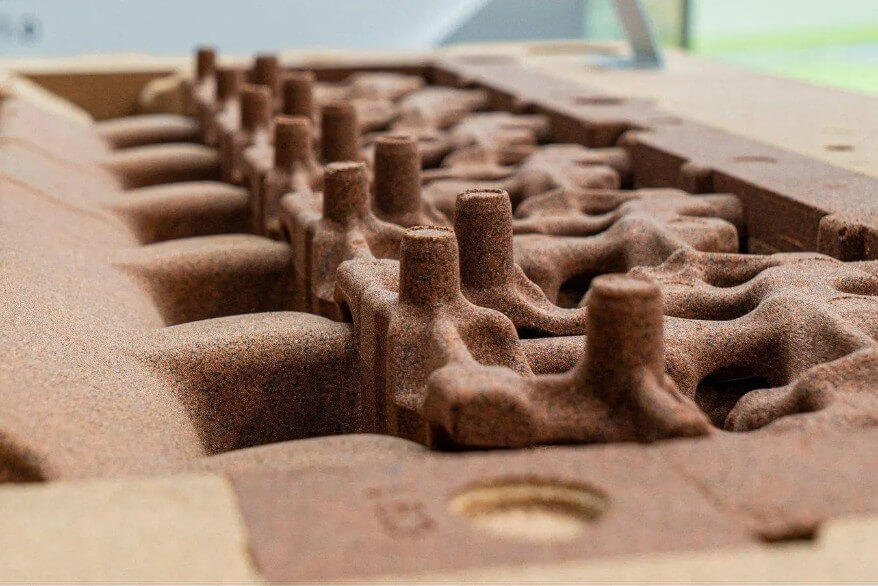
(2) Mold making
1) Heating the metal model:
Heat the metal model to 230–340ºC (450–650ºF) so that the subsequent sand shell can better adhere and solidify.
2) Lubricate the model:
Apply calcium stearate as a lubricant to the model surface to prevent the sand shell from adhering to the model and facilitate demolding.
3) Cover with sand-resin mixture:
Hang the heated model in a dump box filled with a mixture of fine silica sand and thermosetting phenolic resin.
Turn the dump box over so that the sand-resin mixture evenly covers the model surface.
4) Initial curing:
The heat of the model causes the sand-resin mixture to form a 9-20 mm thick cured shell on the surface.
After a few seconds, turn the dump box upside down and the uncured loose sand falls off, leaving only the cured shell attached to the model.
5) Complete curing:
Put the shell in an oven for further curing to give it a tensile strength of 350 to 450 psi.
Repeat the above process to make the other half of the mold.
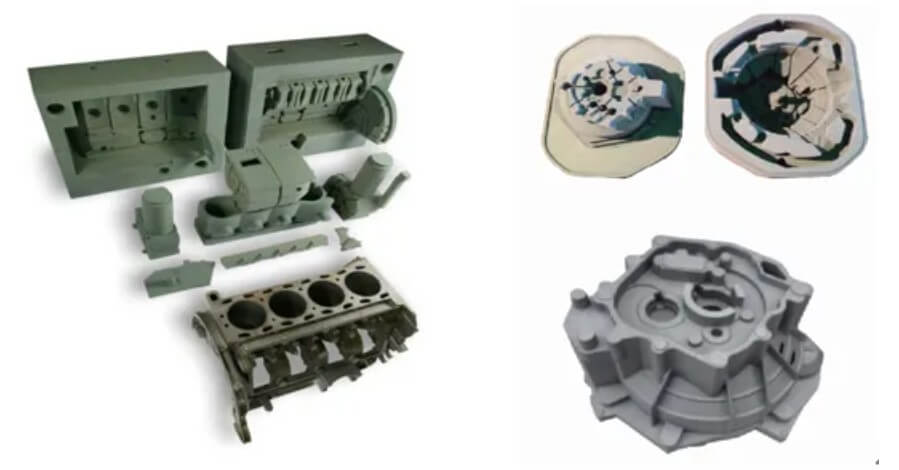

(3) Mold assembly
1) Connection method:
Assemble the two halves of the mold by clamping or bonding to form a complete mold cavity.
2) Check the sealing:
Ensure that the mold joints are tight to prevent metal liquid leakage.
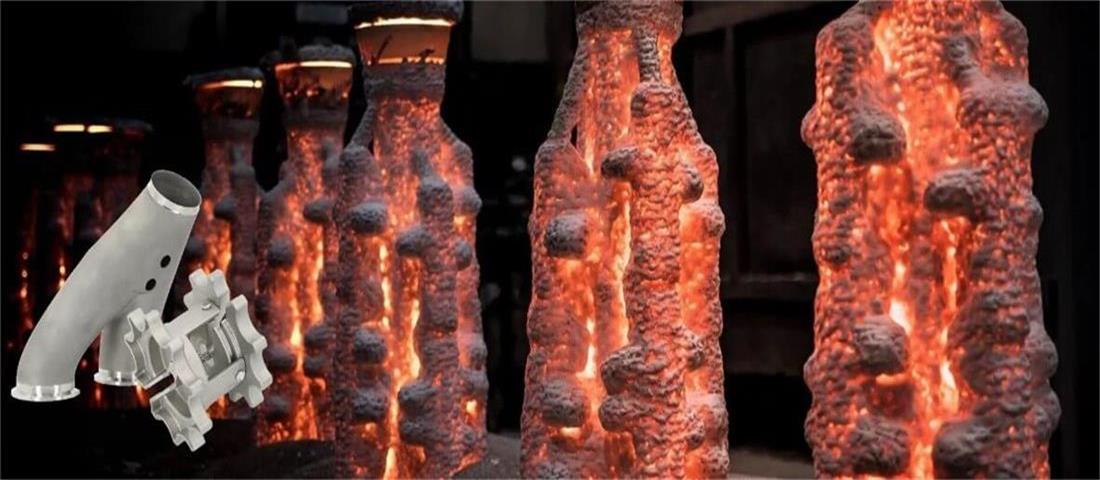
(4) Casting process
1) Strengthen support:
To increase the strength of the mold, technicians can place the mold in a casting sleeve or surround it with materials such as sand, gravel, and metal shots.
2) Pouring metal liquid:
Pour the molten metal into the mold cavity. The pouring process is usually completed by a machine.
3) Control parameters:
Strictly control the pouring temperature and speed to ensure the quality of the casting.
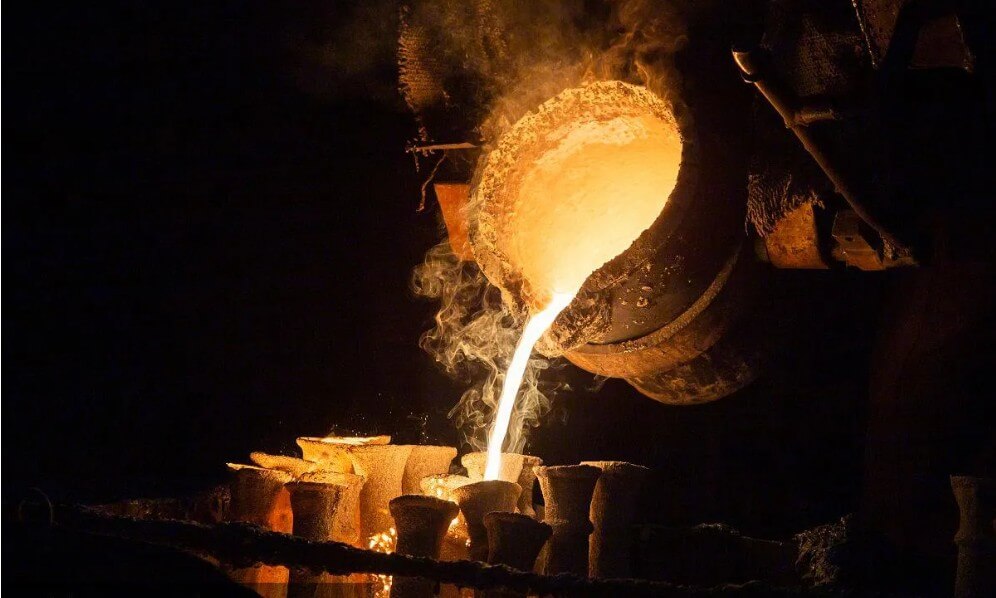

(5) Cooling and demolding
1) Natural cooling:
Let the casting cool naturally in the mold to ensure uniform metal structure.
2) Open the mold and take out the casting:
After the casting is completely solidified, open the mold or break the shell to take out the casting.
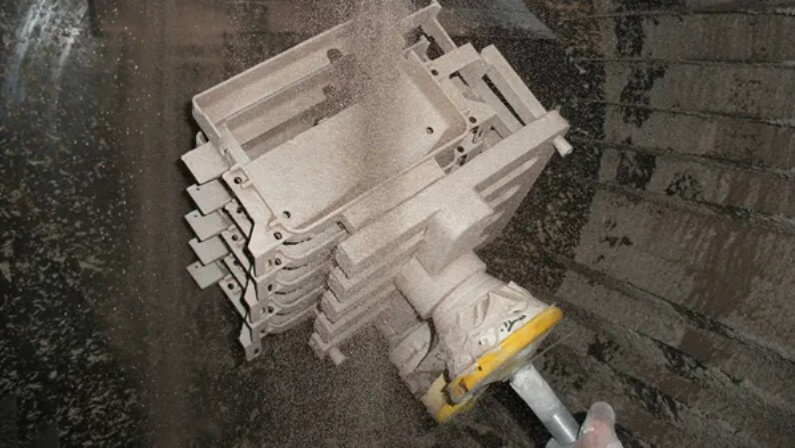
3) Cleaning and processing:
The casting is cleaned to remove excess sand shells and burrs, and subsequent processing is performed as needed.
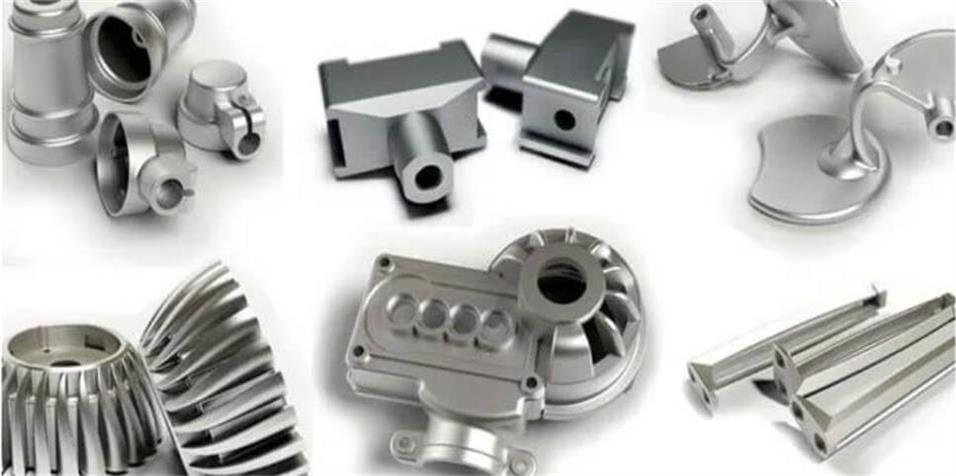
4.Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of shell casting
(1) Advantages
1) High dimensional accuracy:
Resin sand is used to make thin shell castings, which makes the castings clear in outline and accurate in size, usually without or only requiring a small amount of machining.
2) Production efficiency:
This process has high production efficiency and is suitable for mass production, especially for small and medium-sized castings.
3) Good surface finish:
Due to the smooth surface of the casting, the resulting casting has a high surface finish and can meet high requirements for appearance.
4) Reduce the level of gas defects:
During the casting process, the molding sand hardens at high temperature, reducing the possibility of gas generation, thereby reducing defects such as pores and slag inclusions in the casting.
5) Wide range of materials:
This process is suitable for a variety of alloy materials, including alloy steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, etc., and can produce thin-walled and complex-shaped castings.
(2) Disadvantages:
1) Weight handling restrictions:
It is mainly suitable for small and medium-sized castings, and there are certain restrictions on the production of large and heavy castings.
2) High cost:
The resin sand used in casting is expensive, and the template needs to be precisely processed, resulting in a high overall cost.
3) Complex process:
The process is relatively complex and has strict requirements on equipment and process parameters.
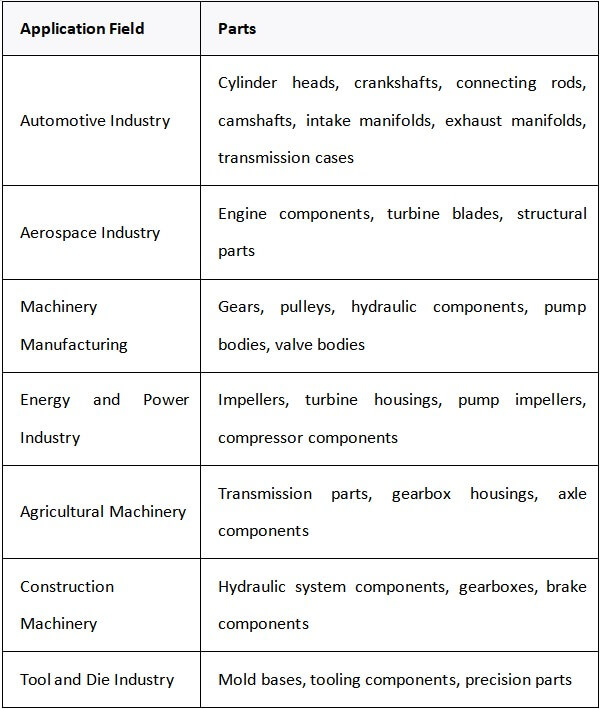
5.Application areas of shell casting
Shell casting is very effective and can replicate metal parts with precise dimensions in a short time. Therefore, shell casting products cover multiple industries, including automobiles, aerospace, energy, machinery, etc.
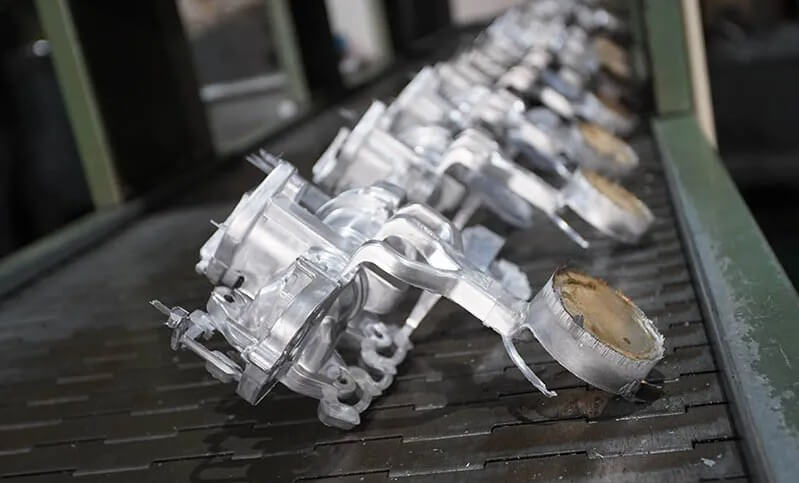
(1) Automobile industry
Key components: engine crankshafts, cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, connecting rods, etc.
Application advantages: Shell casting can produce castings with high dimensional accuracy and good surface finish to meet the high performance requirements of automobile engines.

(2) Aerospace
Key components: turbine blades, engine housings, structural frames, etc.
Application advantages: It is suitable for manufacturing complex components with high strength and high heat resistance to ensure flight safety and reliability.
(3) Mechanical manufacturing
Key components: gears, bearings, machine tool beds, etc.
Application advantages: Castings have excellent mechanical properties and wear resistance, which improve the operating stability and service life of mechanical equipment.
(4) Energy and power
Key components: wind turbine hub, generator housing, pump body, etc.
Application advantages: Ability to produce large and complex castings to meet the requirements of energy equipment for component strength and durability.
(5) Rail transit
Key components: wheels, axles, bogie components, etc.
Application advantages: The high precision and high quality of castings ensure the safety and stability of rail transit vehicle operation.
The following are some application summaries and extensions:
6.Comparison of shell casting with other casting processes
In order to better understand the characteristics and advantages of shell casting, it is compared with sand casting and investment casting as follows:
(1) Comparison of shell casting with sand casting
1) Process
○ Shell casting uses resin-coated sand to form a mold by heating and hardening. The process is complex but the precision is high.
○ Sand casting uses sand as the main molding material. The process is simple but the precision is relatively low.

2) Casting precision
○ Shell casting has high dimensional precision and good surface finish, which is suitable for high-precision castings.
○ Sand casting has low precision and high surface roughness, requiring more machining.
3) Scope of application
○ Shell casting is suitable for mass production of small and medium-sized castings.
○ Sand casting is widely used and suitable for the production of castings of various sizes and materials.
4) Production cost
○ Shell casting equipment investment is large and the resin material cost is high.
○ Sand casting has low cost and the material source is wide and cheap.
(2) Comparison between shell casting and investment casting
1) Process
○ Shell casting forms a mold by heating and hardening resin-coated sand.
○ Investment casting first makes a wax mold and then covers it with refractory material. The process is complicated.

2) Casting accuracy
○ Both castings have high casting accuracy, but investment casting has better surface finish.
3) Scope of application
○ Shell casting is suitable for mass production of small and medium-sized castings.
○ Investment casting is suitable for small castings with high precision and complex shapes.
4) Production cost
○ Shell casting costs are lower than investment casting, and the cost of wax mold materials and processes is higher.
(3) Comprehensive evaluation
● Shell casting finds a balance between accuracy and cost, and is suitable for mass production of small and medium-sized high-precision castings.
● Sand casting has strong versatility and is suitable for various castings, but has low accuracy.
● Investment casting has the highest accuracy, but also the highest cost, and is suitable for special high-requirement castings.
7.Summary
As a precision casting method, shell casting technology plays an increasingly important role in modern industrial production with its advantages of high precision, high efficiency and high material utilization.If you have related metal casting needs, please contact us!




