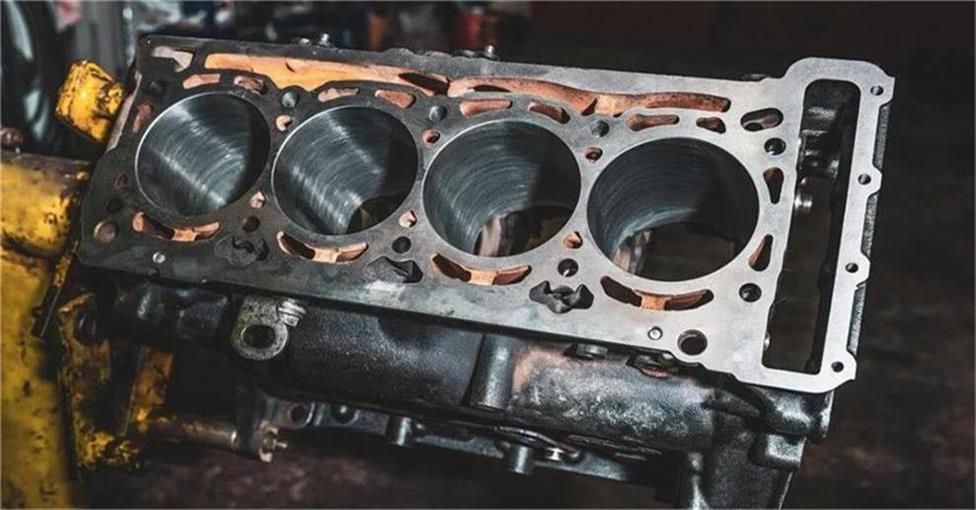
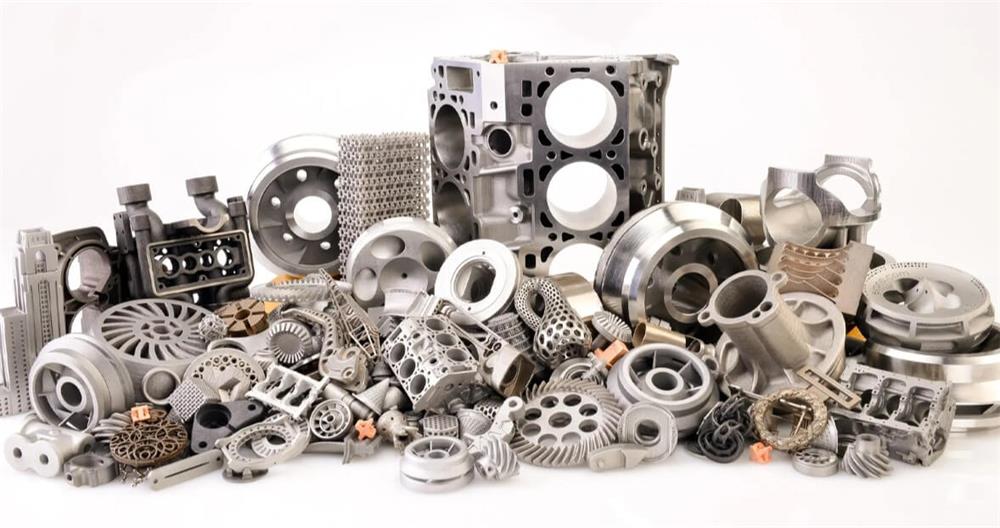
Exploring the difference between engine cylinder block and engine block in production and processing
As the heart of a car, the engine has an internal structure that is more precise and complex than one can imagine.
As the core components of an engine, although the names of engine cylinder block and engine block are only one letter different, there are many differences in production and processing.
This article will explore the differences between the two in production and processing from the aspects of material selection, production process, processing accuracy and quality control.
1.Differences in material selection between engine cylinder block and engine block
Engine cylinder block and engine block have different focuses in material selection, which is mainly based on their respective functional requirements and working environment.
(1) Material selection of engine block
As the main structure of the engine, the engine block needs to withstand large mechanical and thermal loads. Therefore, its material selection must have good strength, rigidity and heat resistance. At present, cast iron and aluminum alloy are the two most commonly used materials for engine blocks.
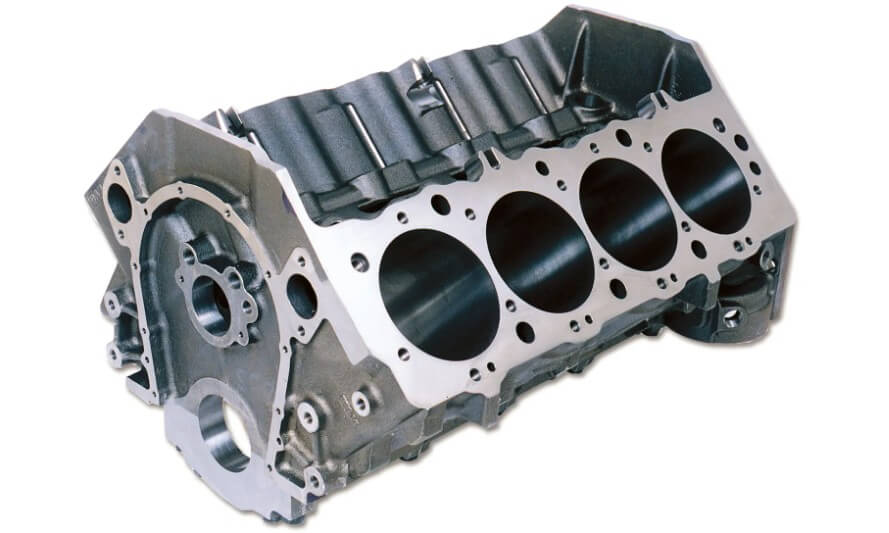
Cast iron materials have been widely used in traditional engines due to their good casting performance, wear resistance and cost advantages. However, cast iron cylinder blocks are heavy, which is not conducive to the lightweight development of automobiles.
With the advancement of automobile technology, aluminum alloy materials are increasingly used in engine blocks. Aluminum alloys have the advantages of low density and good thermal conductivity, which can effectively reduce engine weight and improve fuel economy. At the same time, aluminum alloy cylinder blocks can also improve the heat dissipation performance of the engine by optimizing structural design.
(2) Material selection for engine cylinder blocks
The engine cylinder block is mainly responsible for guiding the piston to move linearly in the cylinder, and its material selection also needs to consider strength, wear resistance and heat resistance. In addition to cast iron and aluminum alloy, engine cylinder blocks are also often made of cast steel.
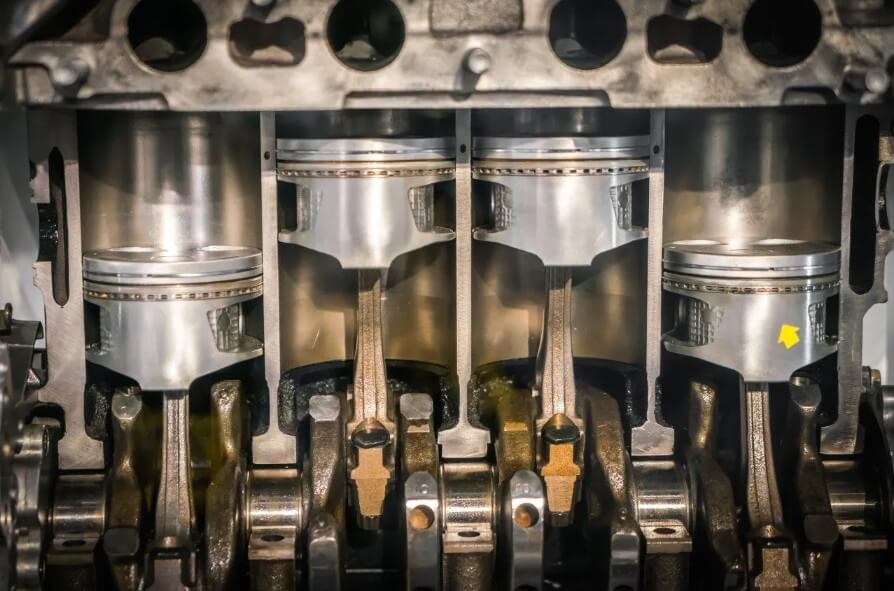

Cast steel materials have higher strength and toughness and can meet the needs of high-power engines. However, the weight and manufacturing cost of cast steel cylinder blocks are relatively high, so their application is subject to certain restrictions.
In addition, some high-performance engines also use ceramic materials or composite materials to manufacture cylinder blocks to further improve the heat resistance and wear resistance of the engine. Although these new materials are more expensive, they can meet the performance requirements under extreme working environments.
2.Differences in production process between engine block and engine cylinder block
There are differences in production process between engine block and engine cylinder block, which are mainly reflected in casting process and processing flow.
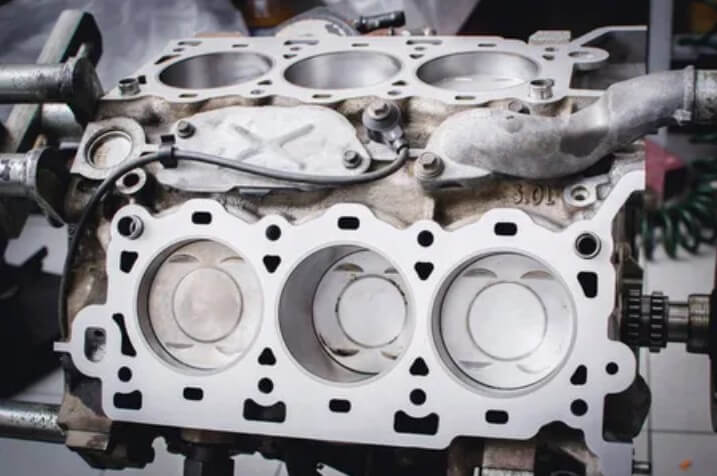
(1) Production process of engine block
The production of engine block mainly adopts casting process, including sand casting, pressure casting and lost foam casting. Among them, pressure casting is one of the most commonly used methods. Die casting has high dimensional accuracy, low surface roughness and high productivity.
In order to improve the accuracy and performance of engine block, metal mold casting and pressure casting are gradually used. Metal mold casting can improve the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of castings, while pressure casting can produce castings with complex shapes and high strength.
After casting, the engine block needs to undergo a series of mechanical processing, including rough machining, semi-finishing and finishing. These processing processes are designed to ensure that the dimensional accuracy, surface roughness and geometric tolerance of the cylinder block meet the design requirements.
(2) Production process of engine cylinder block
The production of engine cylinder block also mainly adopts casting process, but its accuracy and surface quality requirements are higher. Therefore, engine cylinder blocks usually adopt high-precision casting processes, such as precision casting and centrifugal casting.
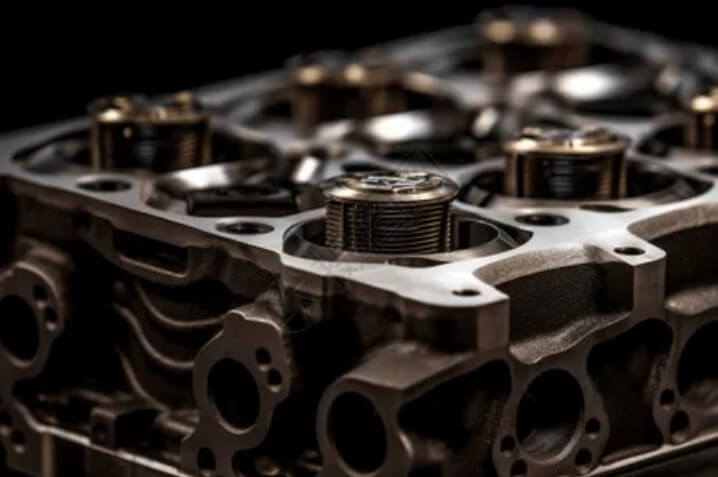

Precision casting can produce castings with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface, reducing the subsequent machining process. Centrifugal casting can improve the density and wear resistance of the cylinder block and extend the service life of the engine.
After casting, the engine cylinder block also needs to undergo special honing. Honing is a high-precision surface processing method that can further improve the surface roughness and cylindricity of the cylinder block and ensure the smooth movement of the piston in it.
3.The requirements for machining accuracy of engine cylinder block and engine block
There are certain differences in the requirements for machining accuracy of engine cylinder block and engine block, which are mainly reflected in dimensional accuracy, surface roughness and form and position tolerance.
(1) Machining accuracy requirements of engine block
The machining accuracy of the engine block is mainly reflected in the dimensional accuracy and surface roughness of important parts such as cylinder bore, crankshaft bore and camshaft bore. The dimensional accuracy and surface roughness of these parts directly affect the performance and reliability of the engine.
For example, the dimensional accuracy and cylindricity of the cylinder bore are very high to ensure that the piston moves smoothly in it and reduce wear and leakage. The dimensional accuracy and positional accuracy of the crankshaft hole and camshaft hole are also very important, which directly affects the running smoothness and service life of the crankshaft and camshaft.
(2) Machining accuracy requirements of engine cylinder block
The machining accuracy requirements of the engine cylinder block are higher than those of the cylinder block, especially in terms of the dimensional accuracy, surface roughness and cylindricity of the cylinder bore. The dimensional accuracy and cylindricity of the cylinder bore directly affect the sealing performance of the piston ring and the compression ratio of the cylinder, which in turn affects the power and fuel economy of the engine.
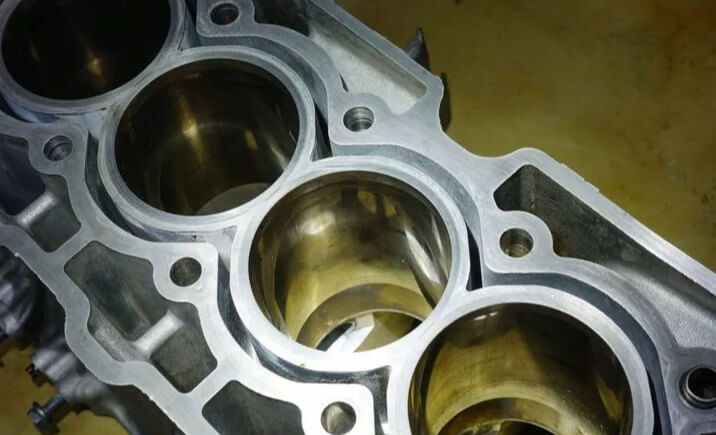

In addition, the surface roughness of the engine cylinder block is also required to be very high to reduce friction and wear and improve the efficiency and reliability of the engine. In order to meet these high-precision requirements, the engine cylinder block usually needs to undergo multiple machining and honing processes.
4.The difference between engine block and engine cylinder block in quality control
Engine block and engine cylinder block need to be strictly controlled during production and processing to ensure that the performance and quality of the product meet the design requirements.
(1) Quality control of engine blocks
The quality control of engine blocks mainly includes raw material inspection, casting process control, mechanical processing process control and finished product inspection. In the raw material inspection stage, the chemical composition and mechanical properties of cast iron or aluminum alloy need to be tested to ensure that the quality of the raw materials meets the requirements.
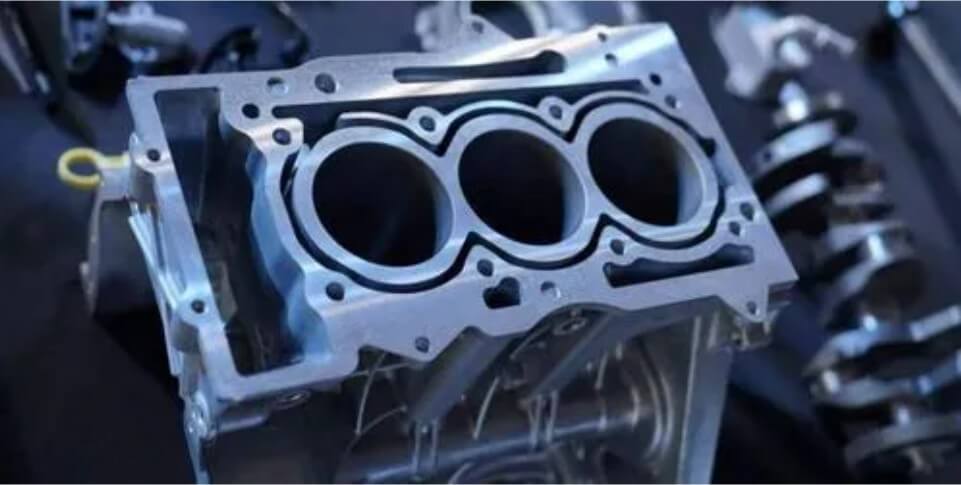

In the casting process control, the casting process parameters need to be strictly controlled, such as pouring temperature, cooling rate, etc., to ensure the quality of the casting. In the mechanical processing process control, the dimensional accuracy, surface roughness and form and position tolerances during the processing process need to be monitored and controlled in real time.
In the finished product inspection stage, it is necessary to conduct comprehensive inspections on various performance indicators of the engine block, such as air tightness, water pressure test, etc., to ensure that the product quality meets the design requirements.
(2) Quality control of engine cylinder blocks
The quality control requirements of engine cylinder blocks are more stringent. In addition to the above-mentioned raw material inspection, casting process control, mechanical processing process control and finished product inspection, special inspections are also required for the dimensional accuracy, surface roughness and cylindricity of the cylinder bore.
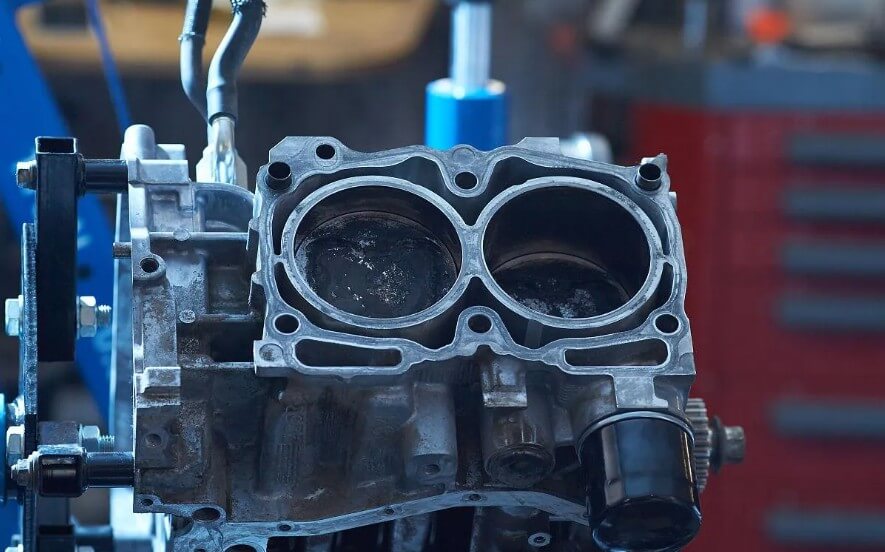

These tests are usually carried out using high-precision measuring instruments and methods, such as three-dimensional coordinate measuring machines, surface roughness meters, etc. In addition, the engine cylinder block also needs to undergo dynamic performance tests, such as cylinder compression pressure tests, air leakage tests, etc., to ensure that the performance of the cylinder block meets the working requirements of the engine.
5.Summary
In summary, the differences between the production and processing of the engine cylinder block and the engine block are mainly reflected in material selection, production process, processing accuracy and quality control. These differences reflect their respective functional requirements and working environments, and also reflect the continuous progress and development of engine manufacturing technology.




