Revealing the secrets of weathering steel: How to make an anti-corrosion “golden bell”?
Weathering steel, as a low-alloy high-strength steel that has good corrosion resistance in the atmosphere by adding a small amount of alloying elements, has gained popularity in recent years in industries such as construction, bridges, chemical industry, landscape, railway vehicles, and container manufacturing. Wide range of applications.
This kind of steel not only has excellent mechanical properties and welding properties, but its atmospheric corrosion resistance is 2-8 times that of ordinary carbon steel. The longer it is used, the more prominent its corrosion resistance. This article will delve into the concept and characteristics of weathering steel, its working principle, the role of alloying elements, and the technical difficulties in its production.
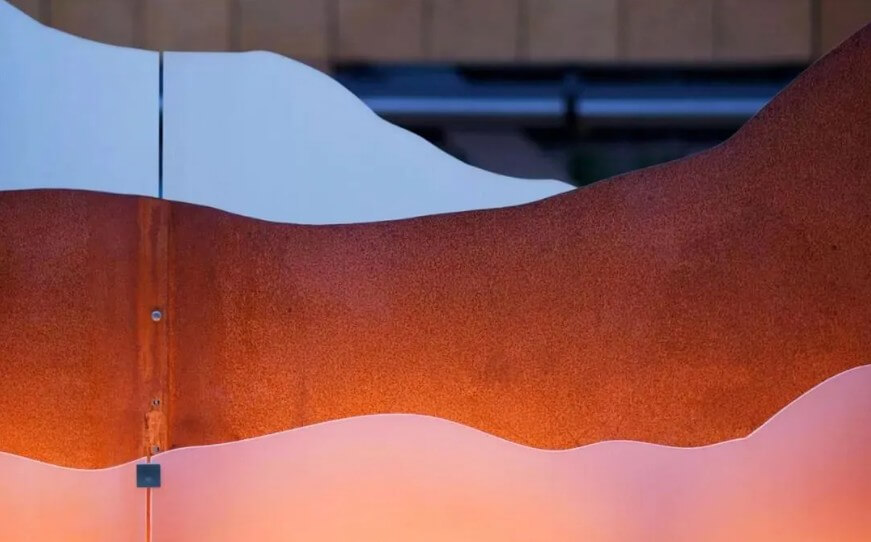

1.Concept and characteristics of weathering steel
(1) Concept
Weathering steel, also known as atmospheric corrosion-resistant steel, is a low-alloy high-strength steel containing a small amount of alloying elements (such as copper, phosphorus, chromium, nickel, etc.). By adding specific alloying elements to ordinary steel, this kind of steel can form a dense protective rust layer in the atmospheric environment, thereby significantly improving its corrosion resistance.
(2) Features
1) It has the characteristics of strength, plastic extension, molding, welding and cutting, abrasion, high temperature, fatigue resistance, etc.
2) The weather resistance is 2 to 8 times that of ordinary carbon steel, and the paintability is 1.5 to 10 times that of ordinary carbon steel.
3) It has the characteristics of being rust-resistant, making the components resistant to corrosion, prolonging the life of the components, thinning and reducing consumption, saving labor and energy, etc.
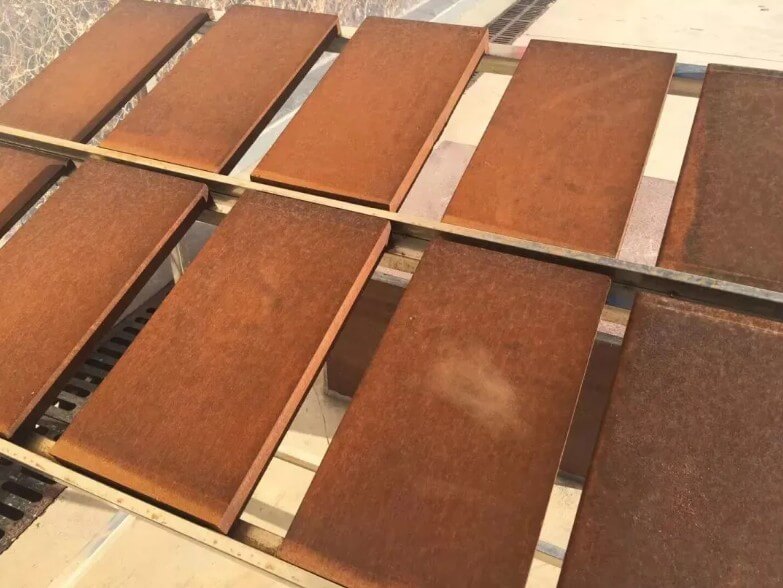

2.Working principle of weathering steel and formation process of rust layer
(1) Working principle
The working principle of weathering steel is based on the reaction of alloy elements on its surface with oxygen and moisture in the atmosphere to form a stable oxide film. This oxide film can effectively prevent further intrusion of external corrosive media, thereby protecting the steel matrix from corrosion. The formation of this protective film is a dynamic balance process. As time goes by, the rust layer gradually becomes stable, and its protective effect becomes increasingly significant.
(2) The formation process of the rust layer
Weathering steel is not stainless steel, but a low-alloy steel series between ordinary steel and stainless steel. In the early stage, it will rust like ordinary carbon steel, but in the later stage, the situation is different.
After weathering steel corrodes for a period of time, due to the enrichment of trace elements such as Cu and P on the steel surface, an amorphous spinel-type oxide layer about 50 μm to 100 μm thick is formed between the rust layer and the matrix, which is dense and adheres to the base metal. Due to the existence of this dense oxide film, it prevents oxygen and water in the atmosphere from penetrating into the steel matrix, slows down the development of corrosion into the steel material, and greatly improves the atmospheric corrosion resistance of the steel material.
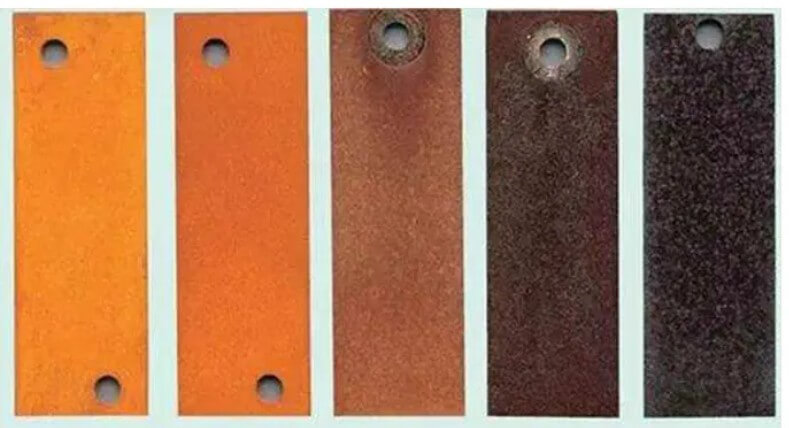

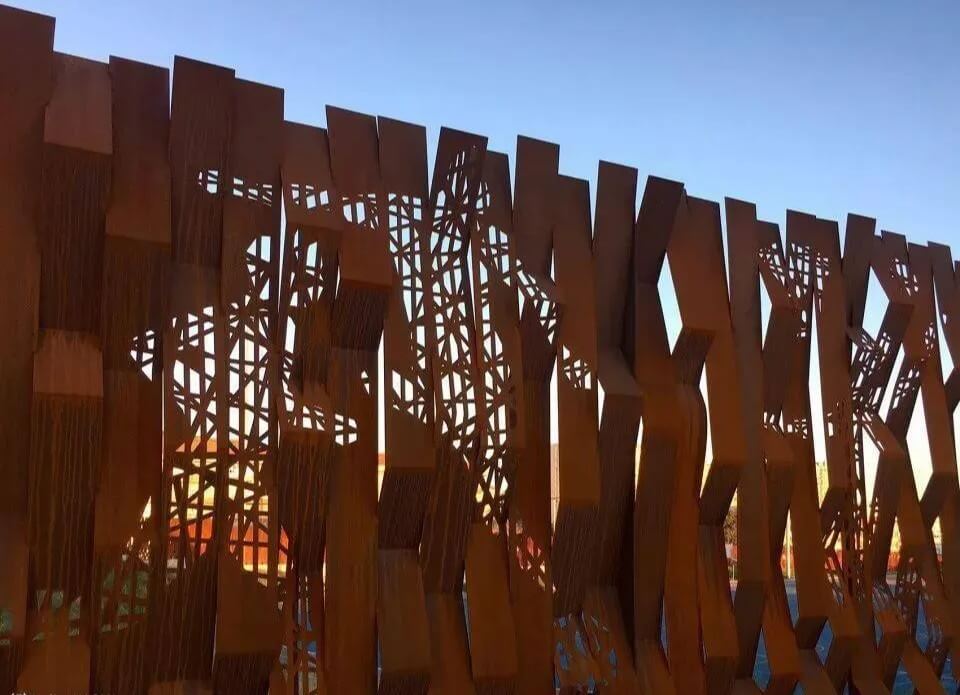
As time goes by, this layer of rust gradually stabilizes, and its protective effect on the steel also increases. During this process, the color of weathering steel gradually changes from bright yellow to earthy yellow, orange, reddish brown, and brown, and finally forms a unique chocolate color.
3.The role of alloy elements in weathering steel
The reason why weathering steel has good resistance to atmospheric corrosion is that alloying elements play a decisive role. The following are the specific functions of each alloy element:
(1) Copper:
Copper mainly plays the role of forming an anti-embroidery barrier layer in weathering steel, which can effectively slow down the atmospheric corrosion rate. When copper is combined with the steel matrix, a dense protective film can be formed to prevent the penetration of corrosive media.
(2) Phosphorus:
Phosphorus is one of the important elements that improves the atmospheric corrosion resistance of weathering steel. It can increase the electrical potential of steel by forming a solid solution with iron, thereby enhancing corrosion resistance. However, excessive phosphorus content will cause segregation and affect mechanical properties and welding performance.

(3) Chromium:
Chromium forms a dense oxide film on the surface of steel, which improves the passivation ability of steel, thereby enhancing its corrosion resistance. The addition of chromium can also stabilize the rust layer and further reduce the corrosion rate.
(4) Nickel:
Nickel is a relatively stable element that can change the corrosion potential of steel in the positive direction, increase the stability of steel, and improve its ability to resist marine corrosion. At the same time, nickel can also promote the formation of a dense rust layer.
(5) Silicon:
Silicon helps refine the FeO2H in the rust layer and reduces the overall corrosion rate of the steel. Silicon is used in combination with elements such as copper, chromium, and phosphorus to further improve the weather resistance of steel.

(6) Calcium:
Trace amounts of calcium can not only significantly improve the overall corrosion resistance of steel, but can also form dissolved CaO and CaS in the electrolyte of the steel surface film, increase the alkalinity of the corrosion interface, reduce its corrosion performance, and transform the rust layer into a dense and Maintain FeO2H.
(7)Molybdenum:
The addition of molybdenum can significantly reduce the corrosion rate of steel in atmospheric environments, especially in environments containing chloride ions.
4.Manufacturing technology of weathering steel
(1) Smelting technology:
An electric furnace or converter is used for primary refining, scrap steel and alloy elements (such as Cu, P, Cr, Ni, etc.) are added, and impurities are removed through argon blowing treatment. The addition of rare earth elements can further purify steel, reduce inclusion content, and improve the purity of steel. The refining process is usually carried out in an LF/VD furnace to ensure uniform chemical composition.

(2) Continuous casting technology:
The refined molten steel is cast into slabs or billets through a continuous casting machine. Low superheat continuous casting technology helps reduce internal defects and improve billet quality. Feeding rare earth wire can improve the morphology of inclusions and improve the mechanical properties and weather resistance of steel.
(3) Rolling technology:
The continuous cast billet is heated to the appropriate temperature and rolled through the rolling mill. Controlled rolling and controlled cooling technology is the key. By accurately controlling the rolling temperature and cooling rate, a uniform and fine grain structure is formed to improve the strength and toughness of the steel. The rolling process of weathering steel requires attention to prevent surface cracks and oxide scale.
(4) Heat treatment technology:
Depending on specific needs, weathering steel can undergo different heat treatments, such as normalizing, annealing, etc. Normalizing treatment can improve the strength and hardness of steel, while annealing treatment can help eliminate internal stress and improve plasticity and toughness. The temperature and time need to be strictly controlled during the heat treatment process to ensure stable performance of the steel.

(5) Surface treatment technology:
In order to accelerate the weathering process on the surface of weathering steel and form a uniform protective oxide layer, surface treatment techniques such as pickling can be used. Pickling can remove the oxide scale on the surface, promote the rust reaction, and quickly form a dense protective film on the steel surface. In addition, sandblasting, coating and other treatments can also be carried out to meet different application needs.
(6) Cutting and processing technology:
Depending on the design requirements, weathering steel can be cut, drilled, welded, etc. Cutting processes include CNC plasma cutting, CNC laser cutting and CNC flame cutting, etc. Choosing the appropriate cutting method can ensure cutting accuracy and surface quality.
summary:
The manufacturing technology of weathering steel covers all aspects from raw material selection, smelting, refining, continuous casting, rolling, heat treatment to surface treatment and processing. Through scientific process control and strict quality management, weather-resistant steel is ensured to have excellent weather resistance, mechanical properties and processing properties to meet the needs of various application fields.

5.Application fields of weathering steel
(1) Construction projects:
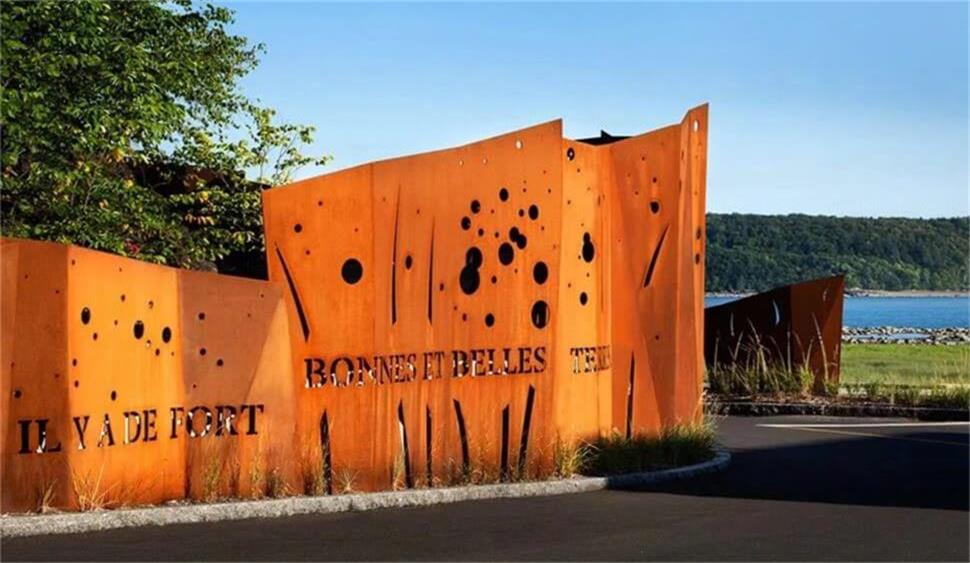
Weathering steel is widely used in the construction field, including the decorative design of large residential buildings, exhibition halls, multi-functional halls and other public places. Its unique rust-red appearance is not only beautiful, but also shows different textures over time. For example, the Luxembourg Pavilion and the Australian Pavilion at the Shanghai World Expo both use weathering steel as exterior wall materials.
(2) Landscape design:
Weathering steel plates are often used as plant planting troughs and tree pond deck decorations in landscape design. Their rust-red texture contrasts sharply with the green plants, adding artistic value to the landscape.
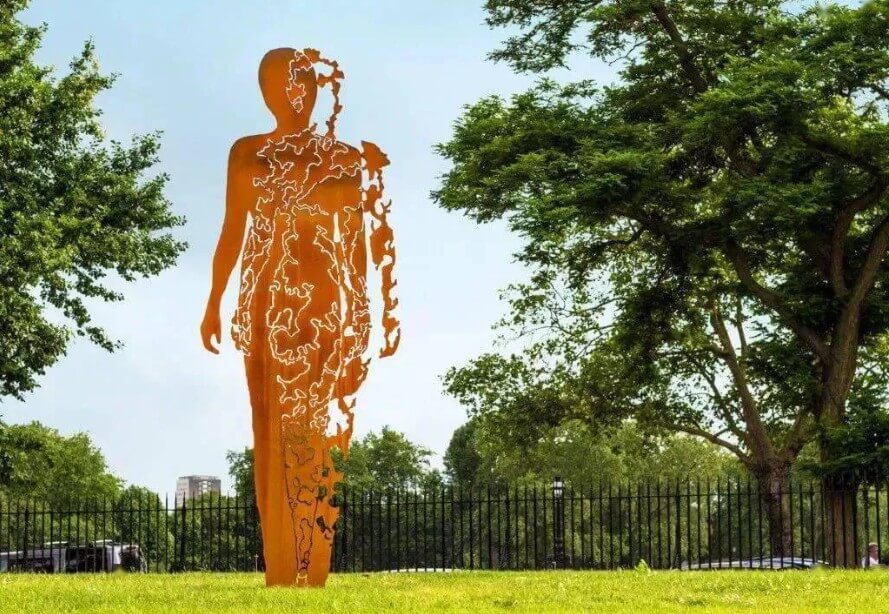

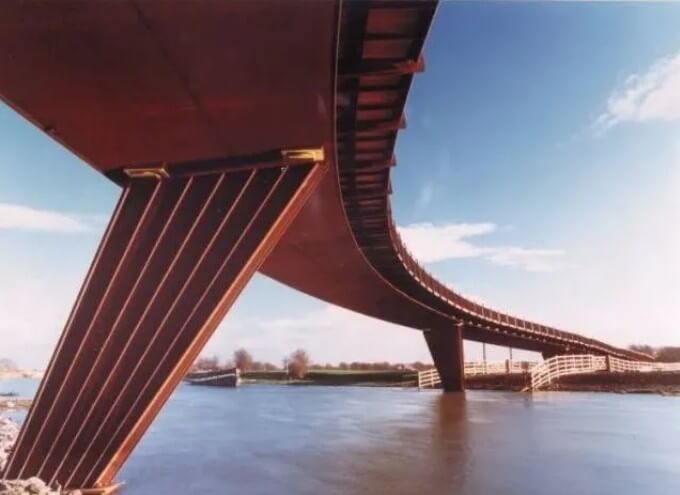
(3) Bridge engineering:
The high strength and good corrosion resistance of weathering steel give it significant advantages in bridge construction. It has been successfully used in the construction of many bridges, reducing maintenance costs and extending the service life of the bridge.
(4) Railway rolling stock
The application of weathering steel in railway vehicle manufacturing is also very common. Train carriages made of this material can withstand harsh environments such as strong winds and sand, low temperatures, and ensure the safety and durability of railway vehicles.
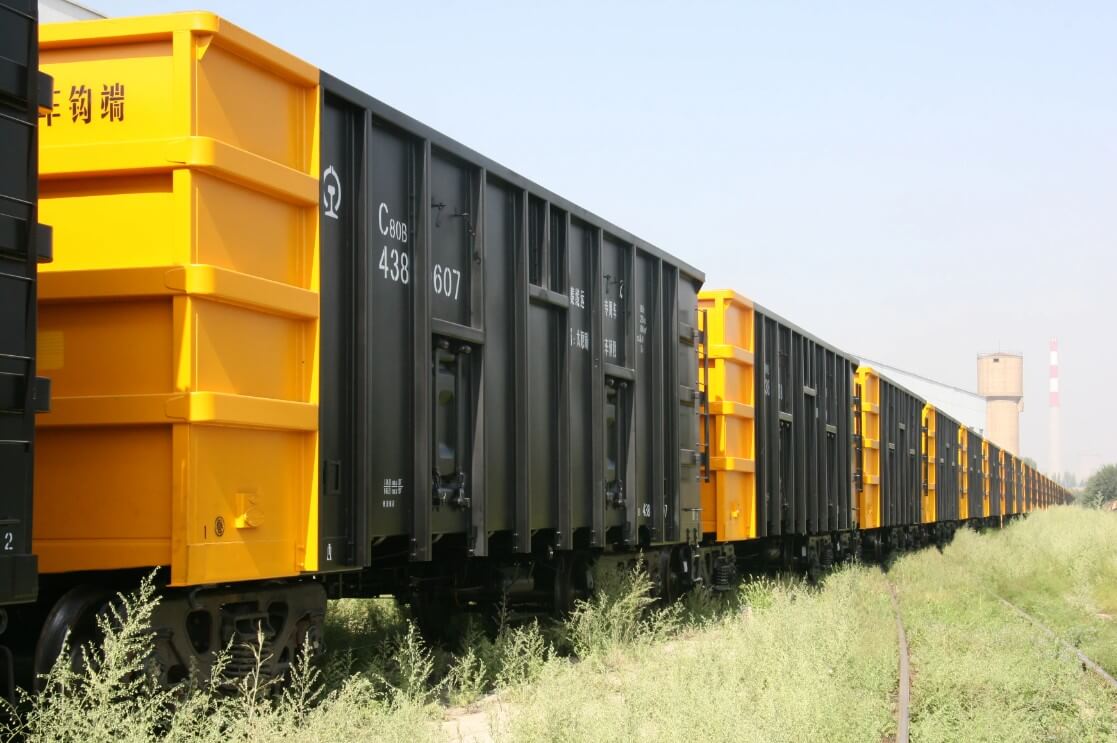

(5) Container manufacturing:
The rust-resistant properties of weathering steel make it an ideal material for manufacturing containers, which can significantly improve the corrosion resistance of the container and reduce maintenance costs.
(6) Offshore platforms and chemical equipment:
This material is suitable for manufacturing structural parts such as oil derricks, harbor buildings, oil production platforms, and containers for corrosive media containing hydrogen sulfide in chemical and petroleum equipment. Its corrosion resistance is particularly critical in harsh environments.
6.Summary
The dense oxide film on the surface of the steel plate acts as an anti-corrosion “shield”, while weathering steel turns this shield into a “golden bell”. With its excellent corrosion resistance, it has been widely used in construction, bridges, chemical industry, railway vehicles and other fields, and has become an indispensable material in modern industry.




What do you think?
[…] weathered steel is a high-strength low-alloy steel between ordinary steel and stainless steel. With its excellent […]