Cast iron vs cast aluminium: How to choose?
When it comes to casting materials, cast iron vs cast aluminium are undoubtedly two names that cannot be ignored. Cast iron, with its low cost and good mechanical properties, occupies an important position in traditional manufacturing; cast aluminum, with its light weight and good processing performance, is highly favored in modern manufacturing.
This paper aims to systematically compare and analyze the basic characteristics, production processes, application fields, economy and environmental protection of cast iron vs cast aluminium, in order to provide a scientific basis for understanding the selection and application of these two materials.
1.Cast iron vs cast aluminium: comparison of basic characteristics
(1) Basic characteristics of cast iron
Cast iron is mainly an alloy composed of iron, carbon and silicon. First, cast iron has a high carbon content and is brittle in nature, but its casting performance is excellent and it can easily shape complex parts. Second, cast iron has good wear resistance and vibration absorption, and the presence of graphite makes it perform well in friction environments. In addition, the compressive strength and hardness of cast iron are close to those of carbon steel, and it is widely used in heavy-duty parts.

There are many types of cast iron, including gray cast iron, ductile iron, and vermicular cast iron, each with its own characteristics. Gray cast iron has excellent casting performance and machinability, and is relatively low in cost; ductile iron undergoes spheroidization to make graphite distributed in a spherical shape, significantly improving the strength and toughness of the material; vermicular cast iron has good thermal conductivity and fatigue resistance, and is suitable for manufacturing parts working under high temperature and high load conditions.
(2) Basic characteristics of cast aluminium
Cast aluminium is an alloy composed of aluminum and other elements. Common cast aluminium materials include aluminium alloy A380 and aluminum alloy A356. Cast aluminum is lightweight and high-strength, with high specific strength, and is suitable for making parts that bear large loads. It has good thermal conductivity, and heat can be quickly transferred to the mold, shortening the casting cycle. Cast aluminum has strong corrosion resistance, and an aluminum oxide protective layer is easily formed on the surface. It is resistant to oxidation and corrosion, which prolongs the service life of the product.

In terms of processing performance, cast aluminum exhibits good plasticity and casting processability, and can produce parts of various complex shapes. In addition, cast aluminum also has good weldability and certain heat resistance, which can meet the needs of various usage environments. Due to its low density, cast aluminum products are light in weight and easier to install and maintain. These characteristics make cast aluminum very popular in modern industry.
2.Cast iron vs cast aluminium: comparison of production processes
(1) Cast iron production process
The production process of cast iron mainly includes three steps: melting, molding and pouring. First, raw materials such as iron ore, coke and limestone are smelted in a blast furnace to obtain molten iron. Then, the molten iron is poured into a sand mold or a metal mold, and after cooling and solidification, a casting is formed. Finally, the casting is cleaned and heat treated to improve its mechanical properties.
The production process of cast iron is simple, the cost is low, and it is suitable for large-scale production. However, the melting point and density of cast iron are high, the energy consumption in the production process is large, and it is easy to cause environmental pollution.

(2) Cast aluminium production process
The production process of cast aluminum also includes three steps: melting, molding and pouring. First, aluminium ingots and other alloy elements are heated and melted in a furnace to obtain aluminum liquid. Then, the aluminum liquid is poured into a sand mold, metal mold or die-casting mold, and after cooling and solidification, a casting is formed. Finally, the casting is cleaned and heat treated to improve its mechanical properties.
The cast aluminum production process has the advantages of low melting temperature, fast solidification speed, and high casting precision, and is suitable for manufacturing parts with complex shapes. However, the smelting process of cast aluminium is prone to produce oxide inclusions, which affects the quality of the casting, and the cost of die-casting molds is relatively high.

3.Cast iron vs cast aluminium: comparison of application areas
(1) Application areas of cast iron
Due to its excellent wear resistance and cost-effectiveness, cast iron is mainly used in the fields of automobiles, pipelines and mechanical parts. In the automotive industry, cast iron is often used to manufacture key components such as engine cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts and brake discs. These components require materials with high strength and wear resistance, and cast iron meets these requirements. In the piping system, cast iron pipes are widely used in water supply, gas and sewage treatment due to their good corrosion resistance and long-term stability. In addition, cast iron is also widely used in machinery manufacturing to manufacture various machine tools, tools and structural parts.

(2) Application fields of cast aluminium
Cast aluminum is mainly used in the automotive, aviation and construction fields due to its light weight and good corrosion resistance. In the automotive industry, cast aluminum is widely used to manufacture engine blocks, cylinder heads, gearboxes and wheels. These parts require materials with low density and high strength, and cast aluminum meets these requirements. In the aviation industry, the lightweight characteristics of cast aluminum make it an important material for manufacturing aircraft parts, such as aircraft fuselages, wings and engine parts. In addition, cast aluminum is also widely used in the construction field to manufacture doors, windows, curtain walls and decorative parts.

4.Cast iron vs cast aluminium: comparison of economic and environmental performance
(1) Economic comparison
From the perspective of production cost, cast iron is usually cheaper than cast aluminum. The production process of cast iron is simple and the raw material cost is low, while cast aluminum requires higher melting temperatures and more complex processing, resulting in higher production costs.
However, from the perspective of service life and maintenance cost, cast iron parts usually have longer service life and lower maintenance costs due to their higher wear resistance and corrosion resistance. In the automotive industry, although cast aluminum engines have the advantage of being lightweight, their manufacturing and maintenance costs are high, while cast iron engines are still widely used in mid- and low-end models due to their high durability and low cost.
(2) Comparison of environmental protection
In terms of environmental protection, the production process of cast aluminum has a low melting temperature, relatively low energy consumption, and aluminum materials can be recycled many times, so the impact on the environment is relatively small. In contrast, the production process of cast iron produces more waste gas and waste slag, which pollutes the environment more. However, cast iron materials can also be recycled and reused to reduce the impact on the environment.

With the increasingly stringent environmental regulations, the production processes of cast iron vs cast aluminium are constantly improving to reduce the impact on the environment. For example, green casting technology and equipment are used to improve material utilization and reduce waste generation.
5.Summary
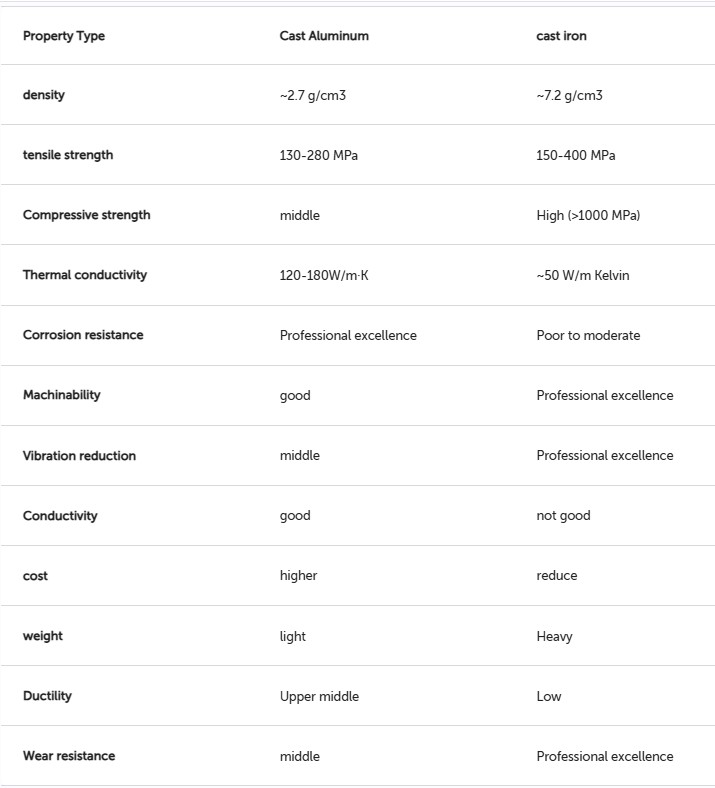
Comparison table of some key differences between cast iron vs cast aluminum
Cast iron vs cast aluminium have their own strengths and weaknesses. In practical applications, we need to flexibly select the most suitable material according to specific needs and conditions. Only in this way can we give full play to the advantages of the material and create products with excellent performance and reliable quality.




