Amorphous steel: application expansion of high-performance magnetic materials
Amorphous steel, as a new type of material, has become a hot spot in many fields due to its high strength, high hardness, excellent soft magnetic properties and good corrosion resistance. Among them, due to the strong demand for high-performance magnetic materials in the power electronics industry, amorphous steel has shown huge application advantages. This article will discuss the definition, importance, preparation technology, performance characteristics and related applications of amorphous steel.
1.The definition and importance of amorphous steel
Amorphous steel, also known as iron-based amorphous alloy, is a metal material with unique properties. It is composed of iron and other elements such as silicon and boron. Its disordered atomic structure shows completely different characteristics from traditional crystal materials. characteristic. Due to its disordered atomic arrangement, this material exhibits extremely high strength, hardness and excellent magnetic properties, making it occupy an extremely important position in modern industry. Especially in fields such as electric power and electronics, amorphous steel is increasingly used because it can significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of equipment and reduce energy consumption and maintenance costs.

For example, in the power industry, the application of amorphous steel can significantly reduce the energy consumption of transformers and improve the transmission efficiency of the power grid, which is of great significance to energy conservation and emission reduction. In addition, due to its excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance, amorphous steel also shows great application potential in the fields of machinery manufacturing and aerospace, which can significantly improve the service life and reliability of parts.
2.Preparation technology of amorphous steel
(1) Vapor deposition method
Vapor deposition is a technology widely used in the preparation of amorphous steel, including physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In the PVD process, iron-based materials are deposited on the substrate in the form of atoms or molecules through vacuum evaporation, sputtering or glow discharge to form an amorphous structure.
The advantage of this method is that the thickness and composition of the film can be precisely controlled, making it suitable for preparing high-performance surface coatings. CVD deposits a thin film on the surface of the substrate through a chemical reaction, which can achieve amorphization of the material at a lower temperature and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
(2) Liquid phase quenching method
The liquid phase quenching method is to cool the molten alloy at an extremely fast speed, so that it has no time to form a crystal structure, thereby forming an amorphous state. In specific operations, commonly used technologies include single-roller spin quenching and double-roller spin quenching. These technologies work by injecting molten alloy onto a high-speed rotating cooling roll, where it is rapidly cooled to form an amorphous thin ribbon.
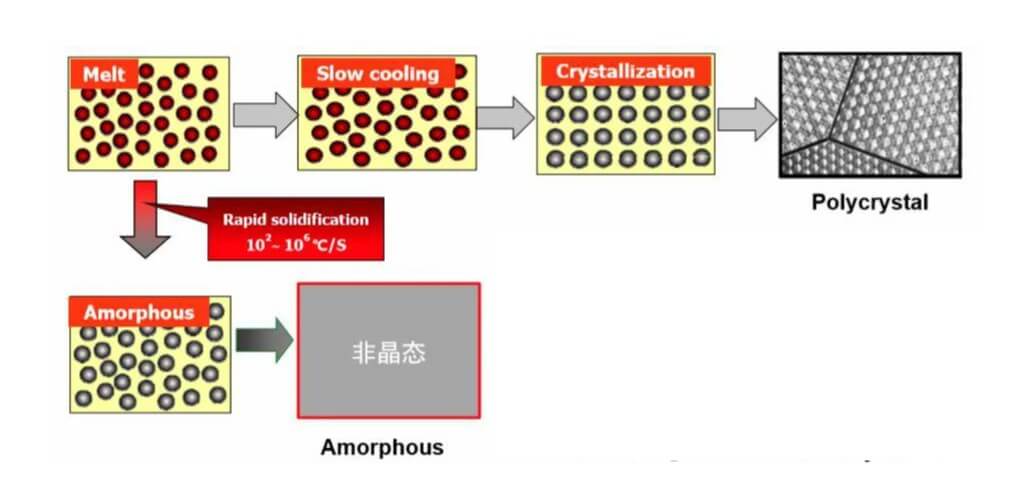
The cooling rate of the liquid phase quenching method is usually as high as 10^6 to 10^8 K/s. This extremely fast cooling rate is the key to forming an amorphous structure. The amorphous steel prepared by this method has excellent magnetic and mechanical properties and is widely used in power electronic devices.
(3) High-energy particle injection method
The high-energy particle injection method irradiates the metal surface with high-energy laser or electron beam, causing the surface to locally melt and cool rapidly to form an amorphous layer. This method can precisely control the thickness and properties of the amorphous layer and is suitable for preparing surface modification layers with special performance requirements.
The advantage of high-energy particle injection method is that it can significantly improve the wear resistance, corrosion resistance and magnetic properties of the material surface without changing the properties of the matrix material, thereby expanding its application range.
3.Performance characteristics of amorphous steel
(1) Excellent soft magnetic properties
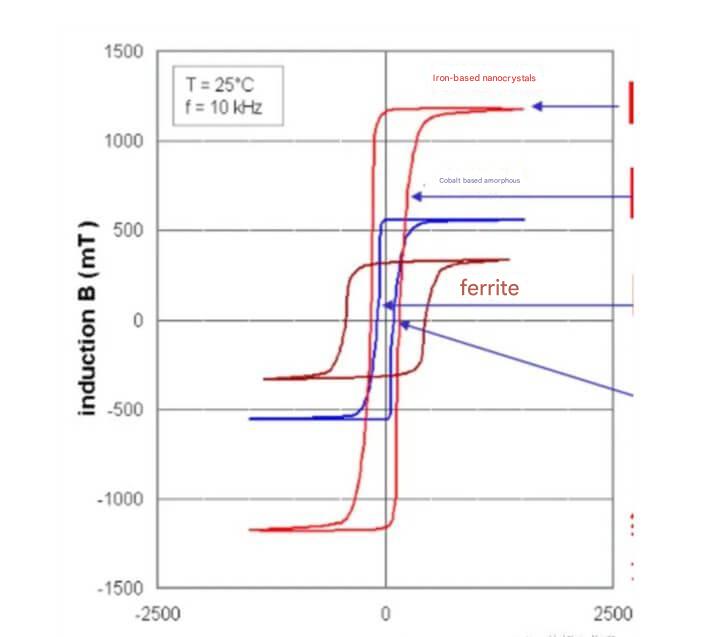
Amorphous steel has the characteristics of high magnetic permeability, low coercivity and low iron loss. Its magnetic permeability is much higher than that of traditional silicon steel sheets, which can significantly reduce the excitation current of transformers and other devices and reduce energy loss. Due to the disordered nature of its atomic arrangement, it exhibits extremely low magnetocrystalline anisotropy, resulting in excellent soft magnetic properties.
For example, under a magnetic field of 50Hz and 1.3T, the iron loss of amorphous steel is less than 0.25 W/kg. In comparison, the iron loss of silicon steel sheets is 1.2 W/kg, and the energy saving effect is significant.
(2) High strength and hardness
There are no microstructural defects inside amorphous steel, and the bonds between atoms are tight, giving it higher strength and hardness than crystalline alloys. Its tensile strength can reach 1500 MPa and Vickers hardness exceeds 900, which is much higher than conventional iron-based alloys.
This high-strength characteristic gives it great advantages in manufacturing wear-resistant, high-strength parts such as high-pressure valves and aviation parts.
(3) Good corrosion resistance
There are no structural defects such as grain boundaries and dislocations inside amorphous steel, and there is no component segregation. Therefore, it has a highly uniform structure and composition and exhibits good corrosion resistance. In harsh environments, it can still maintain stable performance and extend the service life of the device.
(4) High thermal stability
Amorphous steel has high Curie temperature and crystallization temperature, and can maintain its excellent performance in high temperature environments. For example, its Curie temperature is about 410°C and its crystallization temperature is as high as 550°C, making it suitable for high-temperature working environments.
(5) High resistivity
The resistivity of amorphous steel is much higher than that of crystalline alloys, usually 2-3 times that of the latter. High resistivity helps reduce eddy current losses, further reducing device energy consumption. This feature makes it excellent in applications such as transformer cores and induction heaters.
4.Application fields of amorphous steel
Amorphous steel is a new type of metal functional material with excellent magnetism, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, as well as high strength, high hardness and high toughness. The following are its wide range of applications in multiple fields:
(1) Electric power field
1) Transformer core:
Amorphous steel has high saturation magnetic induction intensity and low iron loss characteristics, making it very suitable for use as core materials for distribution transformers and medium frequency transformers. Compared with traditional silicon steel sheets, the use of amorphous steel can significantly reduce energy consumption and achieve energy savings of 60%-70%.

2) Motor core:
The application in motor stator cores can significantly improve motor efficiency and reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The low loss characteristics of amorphous steel give it significant advantages in the field of motors, especially in medium and high frequency motors.
(2) Electronic products
1) Reactor:
Because amorphous steel has low coercivity and high magnetic permeability, it is very suitable as the core material for high-power switching power supply reactors, and the use frequency can reach 50KHz.
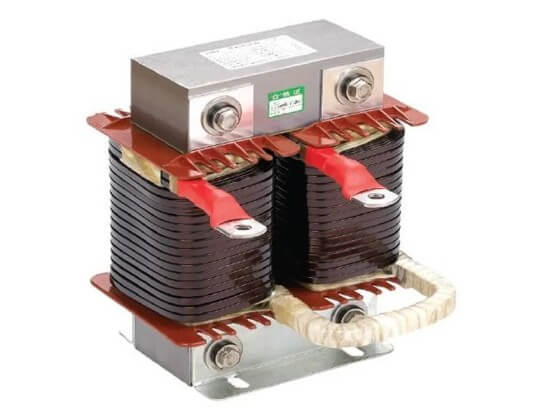

2) Wireless charging equipment:
Utilizing its excellent magnetic properties, amorphous alloys are used in wireless charging technology to create charging equipment with higher efficiency and smaller size.
(3)Industrial application
1) Sensor:
Its high magnetic permeability and low magnetostriction coefficient give it great potential in manufacturing high-precision magnetic sensors.

2) Mechanical parts:
The super hardness and wear resistance of amorphous steel make it excellent in manufacturing various industrial machinery parts, such as cutting tools, bearings, etc., which can extend the service life of parts and improve equipment operation efficiency.
(4) Medical equipment
The corrosion resistance and high strength of amorphous steel make it useful in the medical field, where it is used to manufacture surgical tools and human implants, such as orthopedic fixation materials, artificial joints, etc.
(5) Aerospace field
Due to its low density, it can be used to manufacture lightweight structural parts for aerospace vehicles, reducing aircraft weight and improving fuel efficiency. In addition, amorphous steel is also used to manufacture precision components such as sensors and actuators for aerospace vehicles.

5.Summary
As a new material with broad application prospects, amorphous steel will make important contributions to the miniaturization, lightweight, high efficiency, and energy saving of many industries with the advancement of technology and market development.




