How to choose a suitable die casting machine?
Choosing a suitable die casting machine is crucial to ensure the quality of castings and production efficiency. So what kind of machine is suitable? This article will answer your questions. I believe it will be helpful to you after reading it.
1.Definition of die casting machine and its working principle
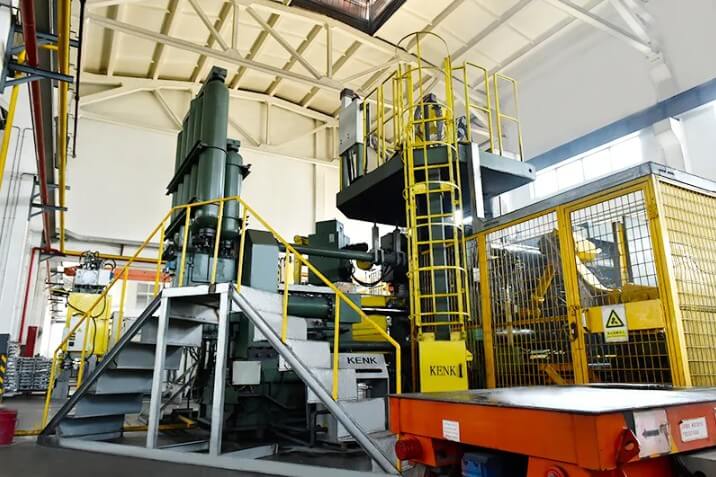
A die casting machine is a machine that injects molten metal into the mold cavity under high pressure and then cools and solidifies to form precision metal parts. Its main working principle includes two core steps: first, the melting of the metal, and then high-pressure injection. The metal is usually heated to a liquid state in the furnace of the die casting machine, and then quickly injected into the pre-designed mold through a high-pressure system. Under high pressure, the molten metal quickly fills every detail of the mold, and then cools and solidifies to form the desired part shape.
2.Analysis of the basic structure of the die casting machine
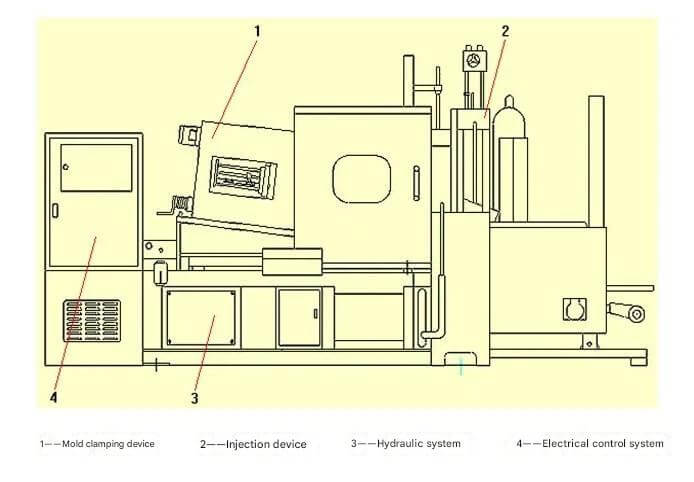
The basic structure of the die casting machine can be divided into five parts: mold clamping mechanism, injection mechanism, hydraulic transmission system, electrical control system and safety protection device.
(1) Mold clamping mechanism:
Responsible for the opening, closing and locking of the mold, ensuring that the mold is tightly closed under high pressure to prevent the molten metal from overflowing. Its core components include the dynamic mold base plate, the fixed mold base plate, the tie rod (coring column) and the ejection mechanism, which are used to eject the molded casting.
(2) Injection mechanism:
The molten metal is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure and speed. It is mainly composed of the injection hydraulic cylinder, the injection chamber (feeding barrel), the punch (hammer) assembly, etc. The injection speed and pressure have a decisive influence on the quality of the casting.
(3) Hydraulic transmission system:
The power is transmitted through hydraulic pumps, hydraulic cylinders, control valves and other components to realize the various actions of the die casting machine. The hydraulic system is the core of the power transmission of the die casting machine and ensures the coordinated work of all parts.
(4) Electrical control system:
Includes electrical cabinets, operating tables and sensors, etc., to monitor and control the entire die casting process. Modern die casting machines mostly use PLC or DCS control systems to achieve automated and intelligent management.
Summary:
These components of the die casting machine cooperate with each other and work together to enable it to efficiently and stably produce high-quality castings, which are widely used in many fields such as automobiles, aerospace, and 3C products.
3.Classification and characteristics of die casting machines
Classification by structure:
(1) Hot chamber die casting machine
Its pressure chamber is directly immersed in the liquid metal in the insulated crucible, and the injection mechanism is located above the crucible. This structure keeps the molten metal in a molten state, reduces the generation of oxide inclusions, and improves the quality of die casting parts. The main features include:
1) Simple structure, easy operation, and high productivity.
2) Applicable to low melting point alloys such as zinc, aluminum, magnesium, etc.
3) Small temperature fluctuation of the molten metal and stable process.
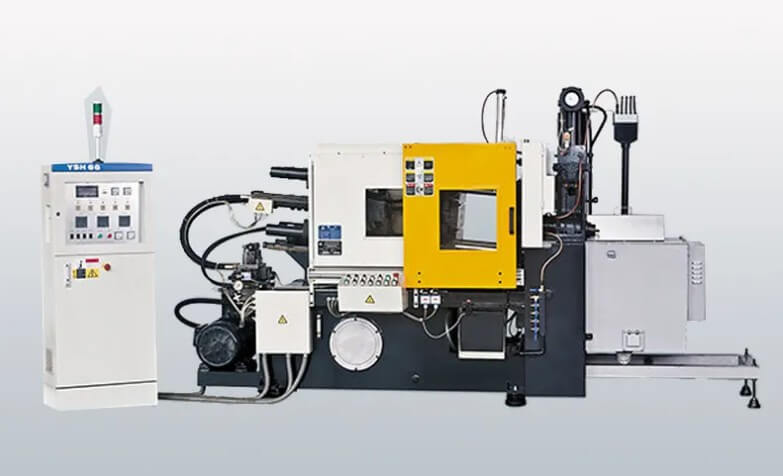

(2) Cold chamber die casting machine
Its pressure chamber is separated from the furnace. During die casting, the molten metal needs to be taken out of the insulated furnace and poured into the pressure chamber. It can be divided into three types according to the position of the pressure chamber and the injection mechanism: horizontal, vertical, and fully vertical.
1) Horizontal cold chamber die casting machine:
The pressure chamber and the injection mechanism are in a horizontal position. It is characterized by high pressure, easy operation, and high production efficiency. It is widely used in the die casting of various non-ferrous metals and ferrous metals.
2) Vertical cold chamber die casting machine:
The pressure chamber and injection mechanism are in a vertical position. It occupies a small area, but the structure is relatively complex. It is suitable for the production of die castings with a central gate.
3) Fully vertical cold chamber die casting machine:
The injection mechanism and clamping mechanism are placed vertically, and the mold is installed horizontally. The process of molten metal entering the mold is short, and the pressure loss is small. It is suitable for various non-ferrous metal die castings, but the structure is complex and maintenance is inconvenient.
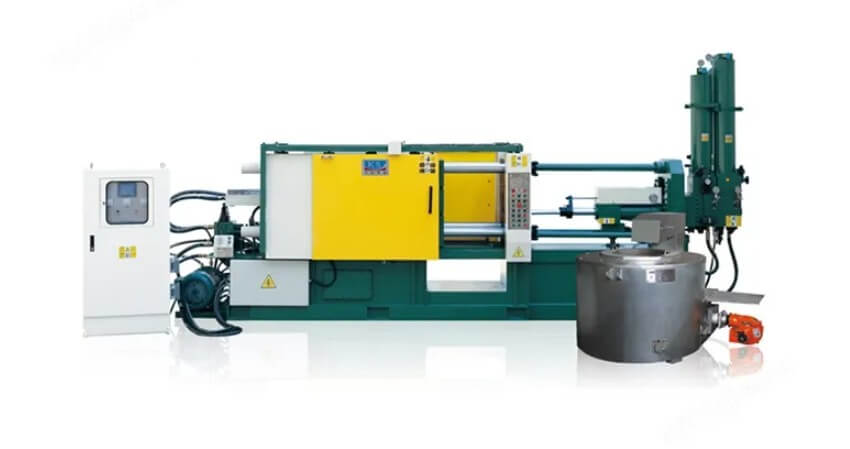

Classification by function and use:
(1) General die casting machine
It is suitable for the production of die castings of various metals and different specifications, and has strong flexibility and adaptability. Its clamping force ranges from a small few hundred kilonewtons to a large several thousand kilonewtons, which can meet the die casting needs of different sizes and materials.
(2) Special die casting machine
It is a production equipment designed for die castings of specific alloys or specific shapes. For example, a special machine for the production of automotive parts, or a special equipment for the production of motor rotors. This type of die casting machine usually has specific process parameters and a degree of automation, which can improve production efficiency and yield rate.
Summary:
Die casting machines have various classifications and characteristics, and each type has its unique advantages and application scenarios. Choosing the right machine is the key to ensuring production efficiency and product quality.
4.How to choose a suitable die casting machine?
The following are some key considerations when choosing:
(1) Product design requirements:
Product size, shape, material and quantity requirements will affect the choice of machine. For example, for products with high requirements for dimensional accuracy, casting density and surface finish, it is necessary to choose a machine with high precision, high stability and high clamping force.
(2) Production capacity and efficiency:
Based on the quantity and cycle requirements of the product, choose a machine that suits the production needs. When mass production is carried out, you can consider producing multiple machines at the same time or choose a high-speed die casting machine to improve production efficiency.
(3) Ease of operation and maintenance cost:
Choose a machine that is easy to operate and has low maintenance costs to avoid increasing production costs and reducing market competitiveness.
(4) Supplier reputation and service:
Choose a supplier with good reputation and high-quality service to ensure the hardware support and after-sales service of the equipment.
(5) Type of die casting machine:
Choose a hot chamber or a cold chamber according to the type of alloy and the requirements of the die casting process. Hot chambers are suitable for low-melting-point alloys, while cold chambers are suitable for the production of non-ferrous alloys such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper.
(6) Calculation of clamping force:
Calculate whether the clamping force of the machine meets the requirements, ensure that the clamping force is greater than the expansion force generated by the product during die casting, and reserve a safety factor.
(7) Injection performance:
Among the various technical indicators and performance parameters of the die casting machine, injection performance is the primary consideration. Models with a wider range of injection performance parameters are preferred.
(8) Automation device:
When possible, equip with mechanized or automated devices to improve product quality, production efficiency, safe production, and enterprise management efficiency.
(9) Cost-effectiveness:
On the premise of ensuring that the performance is met, comprehensively consider the cost-effectiveness, reliability, operability, and maintainability of the machine.

5.How do novices use a die casting machine? And related precautions
(1) Preparation before starting the machine:
Ensure that the surface of each part of the machine is clean, check the lubrication points and lubricate them on time.
Check the oil level in the oil tank to ensure that the oil is sufficient and the filter element is clean.
Ensure that the cooling system is working properly and avoid excessive oil temperature.
(2) Safe operation:
Use a safety protection door to prevent metal liquid from splashing and injuring people.
Wear protective glasses to prevent metal liquid from splashing.
Do not stand opposite the contact point of the mold parting surface.
Do not bring open flames near the oil tank.
(3) Operation process:
Before starting the motor, put the pressure relief valve handle in the pressure relief position and release it after the motor runs normally.
Heat the mold to the specified temperature.
Use tools to remove metal debris on the mold.
After work, stop the oil pump, close all valves, and turn off the power.
(4) Maintenance and care:
Clean the oil pump suction port filter regularly.
Keep the moving parts of the machine lubricated and clean.
When the machine is stopped for a long time, the pump should be turned off and the machine should be shut down.
When a fault or alarm occurs, stop the machine for maintenance immediately.
When adjusting the mold thickness, avoid starting the mold adjustment motor in the mold closing state.

6.Workflow and main steps of the die casting machine
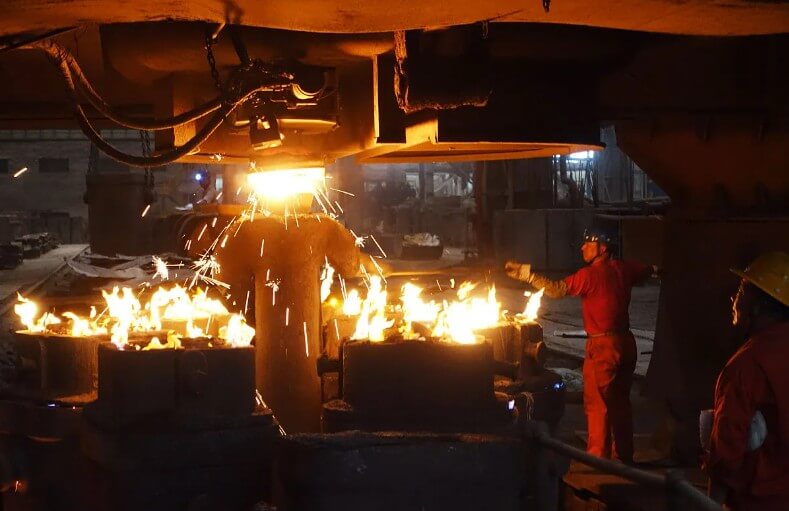
(1) Melting metal:
First, the metal raw materials (such as aluminum, magnesium, copper, etc.) need to be heated to a molten state in a melting furnace, and necessary refining treatment is carried out to remove impurities.
(2) Preparing the mold:
Design and prepare the corresponding die casting mold according to the shape and size of the required casting. The mold usually consists of two halves with a pouring system and vents in the middle.
(3) Spraying mold release agent:
Spray a layer of mold release agent on the mold surface to prevent the casting from sticking to the mold, which is convenient for subsequent mold opening and removal.
(4) Closing the mold:
Close the two halves of the mold and lock them through the clamping mechanism to ensure that the mold does not expand during the injection process.
(5) Pouring:
The molten metal is injected into the cavity of the die casting mold through the pouring system.

(6) Injection:
The injection mechanism of the die casting machine is started to press the metal into the mold cavity at high speed and high pressure.
(7) Maintaining pressure:
After the molten metal fills the cavity, a certain pressure is maintained to ensure that the casting solidifies under high pressure, thereby obtaining a dense casting.
(8) Mold opening:
After solidification, the mold is opened and the casting is taken out.
(9) Cleaning:
Clean the release agent and other residues on the casting for subsequent processing or treatment.
(10) Heat treatment:
According to needs, the casting is heat treated to improve its mechanical properties or eliminate internal stress.
7.Summary
When you understand the above knowledge first, it will be easy to choose a suitable die casting machine. The correct selection can provide sufficient clamping force and injection performance to meet the needs of different materials and processes, thereby improving the yield and qualified rate and reducing production costs.




