Aluminum investment casting: Technical key points analysis
Aluminum investment casting, as an indispensable part of modern industry, is widely used in various fields with its unique advantages. Therefore, this article will take you to explore the technical details and technical key points of aluminum investment casting.
1.Definition and application of aluminum investment casting
Aluminum investment casting is a high-precision metal casting process. The process first uses wax to make a model, and then coats the surface of the model with multiple layers of refractory materials to form a shell. After hardening and drying, the wax model is melted and drained by heating, and finally an empty shell cavity is formed. At this time, liquid aluminum alloy is injected into the cavity, and the required casting can be obtained after cooling and solidification. This process has a wide range of applications in aerospace, automotive industry, and high-precision instrument manufacturing, especially in the manufacture of aluminum alloy parts with complex structures.
2.Overview of aluminum investment casting process
The basic process of aluminum investment casting includes the following steps:
(1) Investment casting:
First, it is necessary to make an investment mold, usually using fusible materials such as wax or plastic to make an accurate model. The production of wax patterns requires the use of high-precision pressing molds (molds) to ensure the dimensional accuracy and surface finish of the molten mold.
(2) Shell manufacturing:
The surface of the manufactured molten mold is coated with several layers of refractory materials, and each layer is sprinkled with sand or powder, and then dried and hardened to form a multi-layer shell. Commonly used refractory materials include quartz sand, zirconium sand, etc., and the binder is silica sol, ethyl silicate, etc.
(3) Lost wax mold:
The manufactured shell is heated to melt the wax pattern and flow out, thereby forming a cavity. The temperature and time of this process must be controlled to ensure that the wax pattern is completely lost and the shell is not damaged.
(4) Firing and pouring:
The shell is fired at high temperature to remove residual wax and moisture, and to improve the strength and high temperature resistance of the shell. The fired shell can be poured with aluminum liquid.
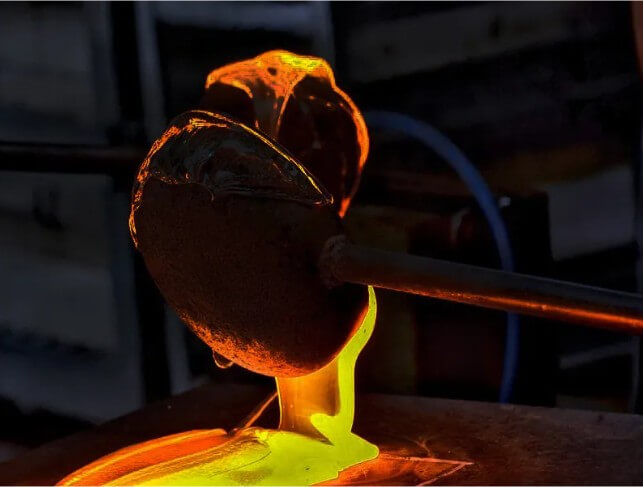

(5) Cooling and cleaning:
After pouring, the casting needs to be cooled to room temperature, then the shell is removed, and necessary cleaning and heat treatment are performed to obtain the final product.
3.Material selection for aluminum investment casting
Material selection for aluminum investment casting needs to consider multiple factors. The following are some key points and suggestions:
(1) Aluminum material selection
In aluminum investment casting, commonly used aluminum alloy types include A356, ZL101A and ZL114A. These alloys have good casting properties, high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. A356 alloy is widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries due to its good fluidity and thermal cracking resistance; ZL101A alloy is often used to manufacture high-load mechanical parts due to its high strength and toughness; ZL114A alloy is widely used in high-end manufacturing fields due to its excellent comprehensive performance.
Considering the purity of aluminum, aluminum materials of different purities have a significant effect on the mechanical properties and surface quality of castings.
(2) Mold material selection
1) Wax-based mold material:
Paraffin wax, microcrystalline wax, etc. are often used to make wax molds, with good fluidity and formability.
2) Resin-based mold material:
Such as polystyrene and epoxy resin, with high strength and dimensional stability, suitable for precision casting.
3) High molecular polymer mold material:
Such as polyethylene and polypropylene, with good heat resistance and chemical stability.
(3) Shell material
1) Refractory material:
Such as quartz sand, zircon sand and high alumina sand, used to make shells, providing the necessary high temperature strength and thermal stability.
2) Binder:
Such as silica sol, water glass and ceramic glue, used to bond refractory materials into shells.
3) Sanding material:
Such as aluminum powder, ferrosilicon powder, etc., used to improve the thermal expansion performance of the shell.
(4) Auxiliary materials
1) Release agent:
Used to reduce the friction between the casting and the mold to facilitate demolding.
2) Refining agent:
Used to remove gas and inclusions in aluminum liquid and improve the quality of castings.
3) Modifier:
Used to improve the microstructure of aluminum alloy and improve its mechanical properties.

Summary:
Selecting the right material is one of the keys to the success of aluminum investment casting, and it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as product performance, production efficiency and cost. At the same time, the selection of materials should also match the casting process to ensure the quality and production efficiency of castings.
4.Factors affecting material properties in aluminum investment casting
Aluminum investment casting is a precision casting process that is widely used in industries such as aviation, automobiles and electronics. However, in the aluminum investment casting process, many factors will affect the performance of the final material. The following are several key influencing factors:
(1) Chemical composition:
Various elements in aluminum alloys such as silicon, copper, magnesium, and iron have a significant effect on the performance of the material. For example, silicon can improve fluidity but may reduce cutting performance; copper can improve mechanical properties but may reduce corrosion resistance. Therefore, strict control of chemical composition is crucial to ensure material performance.
(2) Melting process:
Temperature control and impurity removal during the melting process have a direct impact on the performance of aluminum alloys. Too high a temperature may cause the alloy elements to burn out, while too low a temperature may make it impossible to effectively remove impurities. In addition, effective degassing can reduce the pores in the casting and improve the material properties.
(3) Casting process parameters:
Including pouring temperature, mold temperature, injection speed, etc. Pouring temperature that is too high or too low will cause casting defects such as cold shut and pores. The control of mold temperature is also very critical. Proper preheating can reduce thermal stress and prevent deformation of the casting. Too fast or too slow injection speed will also affect the density and surface quality of the casting.
(4) Mold design:
The design and manufacturing accuracy of the mold directly affect the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of the casting. Reasonable design of the pouring system and exhaust system can ensure smooth filling of the molten metal and reduce defects such as pores and undercasting.
(5) Post-processing process:
Including heat treatment, surface treatment, etc. Proper heat treatment can improve the mechanical properties of aluminum alloys and eliminate internal stress. Surface treatment can improve the corrosion resistance and aesthetics of castings.
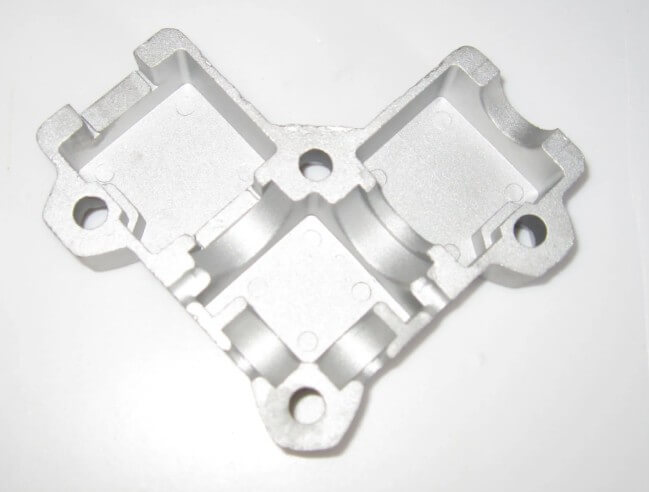
5.Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of aluminum investment casting
(1) Advantages
1) High precision:
Aluminum investment casting can achieve high dimensional accuracy and low surface roughness. Usually, the dimensional tolerance grade can reach CT4CT7, and the roughness Ra can reach 6.31.6μm, which reduces the need for mechanical processing.
2) Complex shape:
It is suitable for the production of castings with complex shapes that are difficult to machine, such as castings with fine grooves and curved fine holes.
3) Wide range of materials:
It is almost not limited by alloy materials and is suitable for various aluminum alloys, including high melting point and difficult to process high alloy steel.
4) High flexibility:
Aluminum investment casting is suitable for both large-scale production and small-scale or even single-piece production, and has high production flexibility.
(2) Disadvantages
1) Complex process:
The production process is relatively complex and involves multiple steps, such as wax mold pressing, mold assembly, mold repair, coating, etc., resulting in high production costs.
2) Casting limitations:
Due to the easy softening of wax molds and the limited strength of the mold shell, it is not suitable for the production of large castings, and the size and weight of the castings are limited.
3) Defect risks:
Surface and internal defects such as cold shut, shrinkage, pores, slag inclusions, hot cracks and cold cracks may occur during aluminum investment casting, which requires strict quality control.
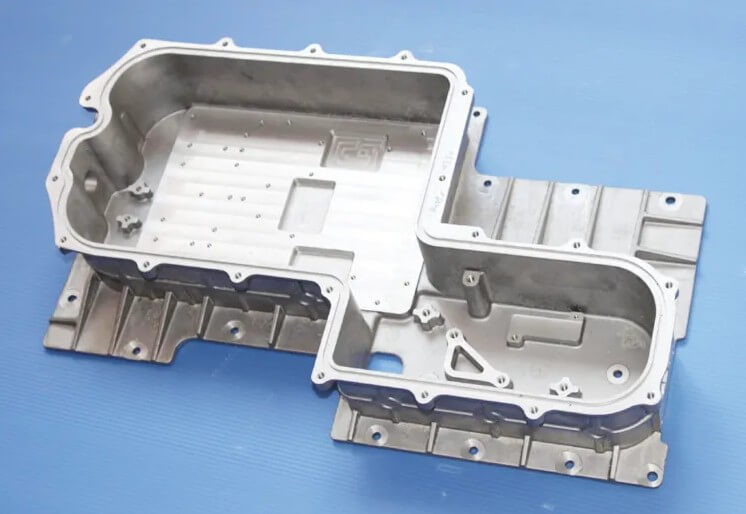
6.Common defects and control measures of aluminum investment casting
Various casting defects may be encountered during aluminum investment casting. The following are some common defects and their causes and preventive measures:
(1) Shrinkage and shrinkage:
The holes on the casting caused by poor shrinkage compensation are irregular in shape and rough in wall. They may be caused by unreasonable casting structure, poor shrinkage compensation of the pouring head or excessively high pouring temperature.
Preventive measures include improving the casting structure, rationally designing the riser and lowering the pouring temperature.
(2) Cold cracks:
Cracks mostly pass through the grains, with a bright surface. This may be caused by unreasonable casting structure, unreasonable gating system design, or impact of the casting during transportation and sand cleaning.
Preventive measures include improving the casting structure and gating system design to avoid impact and throwing of the casting.
(3) Hot cracks:
Cracks grow along the grain boundaries, with an oxidized color on the surface. This may be caused by low mold temperature, too fast cooling speed, or poor mold shell yieldability.
Preventive measures include increasing the mold temperature, improving the mold shell yieldability and collapse.

(4) Metal thorns:
Dense or scattered small thorns appear on the surface of the casting. This may be caused by a low powder-to-liquid ratio of the surface coating, poor wettability of the coating and the wax mold surface, or unwashed wax on the wax mold surface.
Preventive measures include increasing the powder-to-liquid ratio and viscosity of the surface coating, and increasing the amount of surface coating wetting agent added.
(5) Sand sticking:
There is a sand sticking layer on the surface of the casting, and there are raised burrs or pits after sand blowing. This may be caused by excessive impurity content in the refractory powder and sanding material used in the surface coating or excessively high pouring temperature.
Preventive measures include reducing the impurity content in the powder and sanding material in the coating, and selecting appropriate refractory materials and binders.
(6) Insufficient pouring:
The casting product is incomplete, which may be caused by low pouring temperature, narrow pouring system channel or low aluminum liquid flow rate.
Preventive measures include redesigning and improving the pouring system and increasing the aluminum liquid flow rate.
(7) Shrinkage:
Due to the high aluminum alloy liquid temperature and pouring temperature, the cooling rate is slow and the shrinkage is large, resulting in coarse grains and loose structure, forming shrinkage casting waste.
Preventive measures include improving the process, careful operation, and controlling the alloy heating temperature and pouring temperature.
(8) Oxidation inclusions and pores:
Due to improper operation, aluminum liquid will splash when entering the mold cavity, forming bubbles that are wrapped inside the casting, causing the metal to oxidize and forming oxidation inclusions; when there is a large amount of small hydrogen in the aluminum liquid, irregular small holes will be formed, which are more common in thick sand castings, and the physical and chemical properties will be sharply reduced.
Preventive measures include careful operation, the flow rate of aluminum liquid should be smooth and gentle during pouring to reduce impact force, and the use of serpentine gates and bottom pouring systems is appropriate; strictly check the cleanliness of the furnace charge, formulate reasonable aluminum alloy melting temperature and pouring temperature, and carry out refining and degassing.
7.Analysis of aluminum investment casting application fields
Aluminum investment casting is a process that can produce high-precision and complex-shaped castings. It has a wide range of applications in multiple industrial fields, mainly including:
(1) Aerospace:
Aluminum investment casting is widely used in the aerospace field due to its high precision and ability to produce complex shapes, such as manufacturing aircraft engine parts, turbine blades, integral blades and combustion chambers.
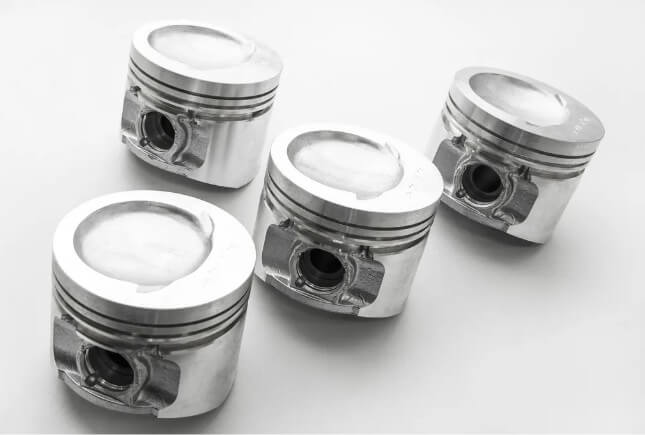
(2) Automotive industry:
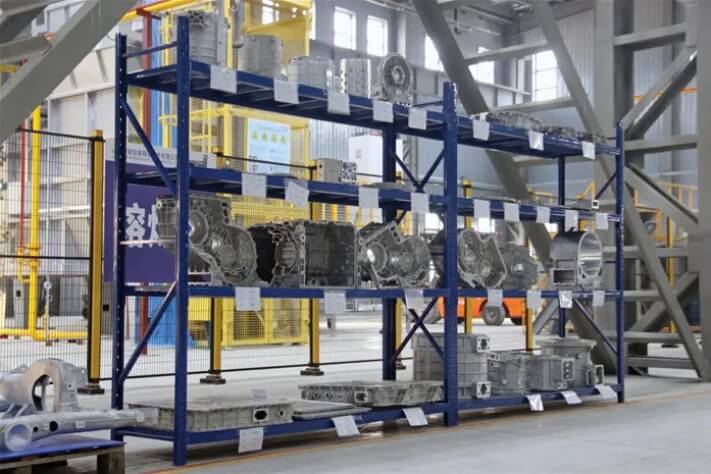
In the automotive field, aluminum investment casting is used to produce automotive parts such as engine pistons, brake discs, engine pistons and gearboxes, which helps to reduce weight and improve wear resistance.

(3) Electronic and optical instruments:
Due to the advantages of small thermal expansion coefficient, low density and good thermal conductivity, aluminum-based composite materials are suitable for manufacturing electronic devices such as packaging materials and heat sinks for electronic equipment.
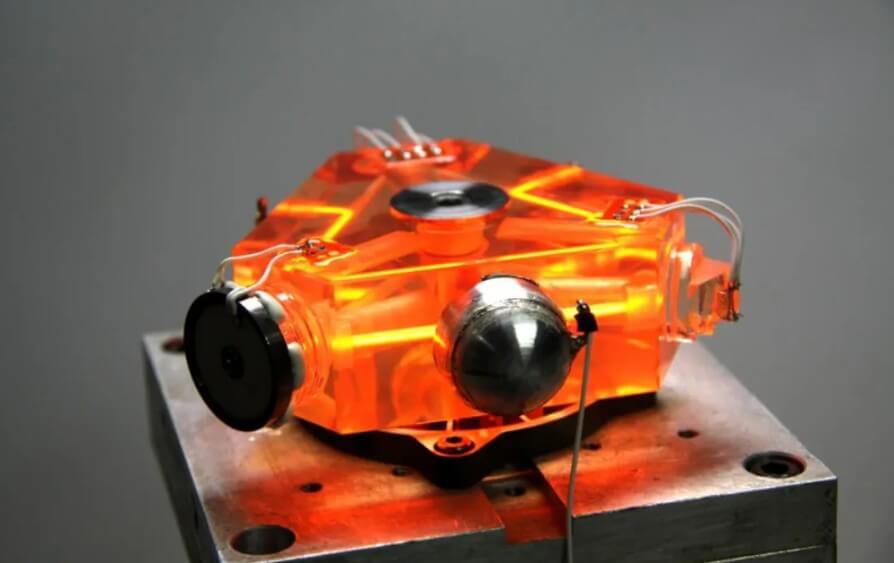
(4) Military industry:
The application of aluminum-based composite materials in the military industry includes the manufacture of precision parts for inertial navigation systems, rotating scanning mirrors, infrared observation mirrors, laser mirrors, laser gyroscopes, etc.

(5) Sports equipment:
Aluminum investment casting can also be used to make sports equipment such as tennis rackets, fishing rods, golf clubs and skis.
8.Summary
In addition, aluminum investment casting is also suitable for the production of small parts with complex shapes, high precision requirements or difficult cutting, such as blades, impellers, guides, guide wheels of steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbine engines, etc. and small parts on automobiles, tractors, pneumatic tools and machine tools.




