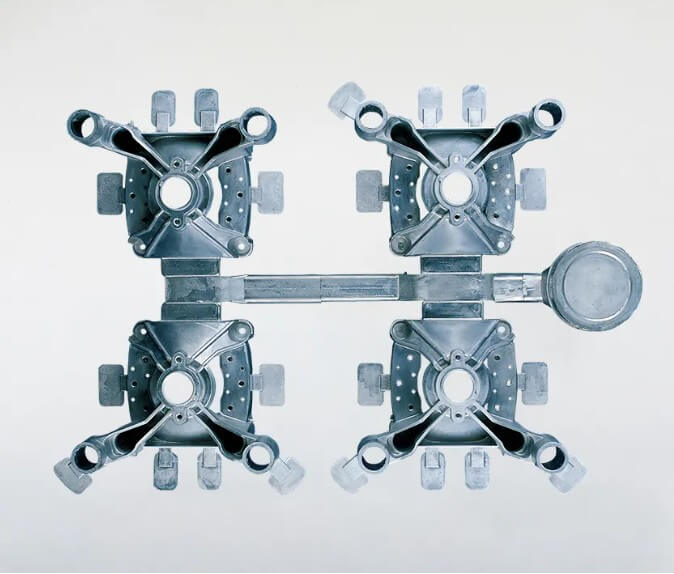
Aluminum die casting design: A Comprehensive Guide to Twelve Tips
Aluminum die casting design covers many aspects, from material selection to final product quality inspection, each step has its own specific design considerations. This article will introduce twelve aluminum die casting design tips to help designers optimize designs and improve product performance and production efficiency.
1.Aluminum die casting design tips one : material selection and ratio
(1) Material selection:
First, you need to select suitable aluminum alloy materials according to product requirements. Common aluminum alloys such as ADC12 and A380 are widely used due to their good mechanical properties and high thermal conductivity. ADC12 is suitable for parts requiring strength and wear resistance, while A380 is suitable for applications requiring higher toughness.
(2) Alloy ratio:
The composition of aluminum alloys has a significant impact on its properties. For example, the silicon and copper content can affect the fluidity and mechanical properties of the alloy. Appropriate adjustment of the ratio can improve the casting performance of the alloy while ensuring strength.

2.Aluminum die casting design skills two: mold design and manufacturing
(1) Mold design
When designing aluminum die-casting molds, product requirements and material properties must be clearly defined, such as the fluidity and thermal expansion coefficient of aluminum alloys. Subsequently, according to the product structure, the mold structure is designed, including the molding part, pouring system, mold base part, etc. The design of the gating system is particularly critical to ensure that the molten metal fills the mold cavity evenly and avoids bubbles and defects.
(2) Mold manufacturing and maintenance
During the manufacturing process, mold parts are first processed by high-precision CNC machine tools, such as milling, drilling, etc., and then assembled. Mold trial is a necessary step to verify the design. Parameters can be adjusted through trial until the desired effect is achieved. During use, regularly maintain the mold, clean the surface, check structural wear, and replace wearing parts to ensure long-term stable operation of the mold.

3.Aluminum die casting design tip three: temperature control
(1) Pouring temperature:
It needs to be controlled between 630-730℃, and the specific temperature depends on the casting structure. Thin-walled complex parts should use higher temperatures to improve fluidity, while thick-walled parts should use lower temperatures to reduce solidification shrinkage. If the temperature is too high, it will easily lead to pores and mold corrosion, while if the temperature is too low, cold shut and insufficient pouring will easily occur.
(2) Mold temperature:
The mold temperature should generally be kept at about 1/3 of the alloy liquid pouring temperature. The preheating temperature is usually 150-180℃, and the operating temperature should be maintained at 180-280℃. Reasonable mold temperature can prevent casting defects such as cold shut, under-casting, etc., and extend mold life.
(3) Cooling system:
Reasonable aluminum die casting design should involve the participation of cooling system. Commonly used methods include air cooling and water cooling to ensure uniform temperature in all parts of the mold.
4.Aluminum die casting design tip four: high-pressure injection
High-pressure injection is one of the key links in aluminum die casting design. Its core is to quickly inject molten aluminum liquid into the mold cavity through high pressure. This process requires precise control of pressure and speed to ensure that the aluminum liquid evenly fills the mold in a very short time, while avoiding the occurrence of defects such as pores and shrinkage cavities.
(1) Pressure setting
Appropriate pressure can ensure that molten aluminum fully fills molds with complex structures, while reducing filling time and improving production efficiency. The selection of pressure needs to be comprehensively considered based on factors such as casting structure, wall thickness and material properties.
(2) Injection speed control
A reasonable injection speed can prevent the aluminum liquid from generating vortices and splashes during the filling process, and avoid the entrainment of gas and oxidized inclusions, thereby obtaining high-quality castings. Typically, the injection speed should be optimized based on the mold geometry, casting size, and material properties.
5.Aluminum die casting design tips five: mold removal and post-processing
(1) Mold removal operation
During the mold removal process, common methods include the use of alcohol, water, gasoline and chemical solvents. Alcohol is cheap but volatile, water is easy to handle but may retain impurities, gasoline is effective but has safety hazards, and chemical solvents are effective but costly and require professional operation.
The specific choice depends on the actual situation.
(2) Post-processing
Post-processing includes orthopedics, aging treatment, machining, impregnation treatment and surface treatment. Orthopedics are used to correct deformation, aging treatment stabilizes dimensions through heating, mechanical processing performs necessary cutting and grinding, impregnation treatment is used to seal micropore defects, and surface treatment is improved through chemical conversion, anodizing, electroplating and painting. Corrosion resistance and decoration.

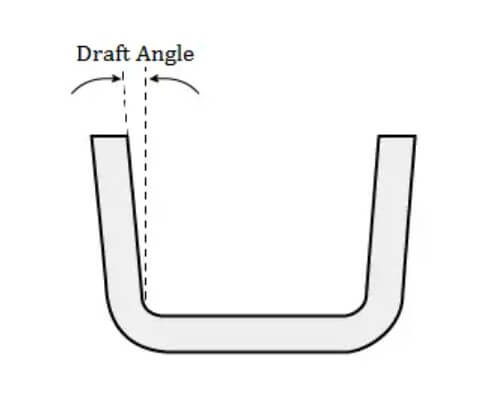
6.Aluminum die casting design tip six: draft angle
Draft angle, which is the slope, angle, or taper of the part’s core and surface at a 90-degree angle to the mold parting line.
Draft lines are important because they make it easier for aluminum parts to pop out after they are die cast. Without sufficient draft, the mold or part may be damaged during the ejection stage.
The draft angle depends on the type of aluminum alloy, the type and thickness of the walls, and the depth of the surface. However, a draft angle of 1 – 2 degrees is usually sufficient for optimal demolding of aluminum parts without damaging the die-cast part.
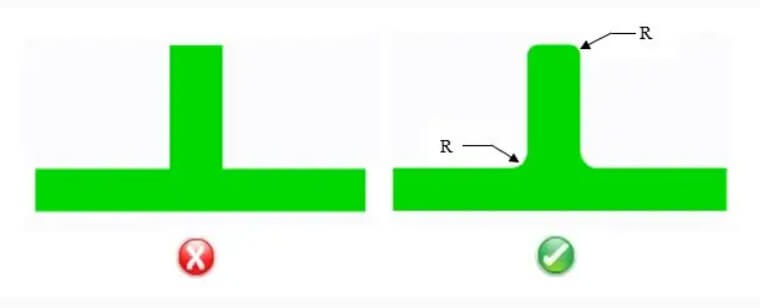
7.Aluminum die casting design tips seven: fillet and radius
Radius refers to the rounded outer edge of the part, while fillet refers to the internal fillet.
Proper fillets and radii contribute to smoother metal flow, and they also help reduce interference within the mold during the metal injection process, which can lead to sharp corners in the casting. These two characteristics are extremely important for any aluminum die-cast design, as they help the part achieve optimal structural integrity.
8.Aluminum die casting design tip eight: wall thickness design
First of all, it is necessary to ensure that the wall thickness is uniform. Taking aluminum alloy as an example, thin walls have higher strength and density than thick walls. Generally, the wall thickness of aluminum die casting parts is generally controlled at 2.0-2.5mm. The minimum wall thickness should not be less than 1.5mm, and the maximum wall thickness should not exceed 6mm. Wall thickness that is too thin may lead to poor metal welding and affect the strength; wall thickness that is too thick or uneven can easily produce defects such as pores and shrinkage, which also reduces the strength of the casting.
In addition, the design of the wall thickness also needs to consider the structural complexity and usage requirements of the casting. On the premise of meeting the strength and rigidity, the wall thickness should be reduced as much as possible to improve material utilization and production efficiency.
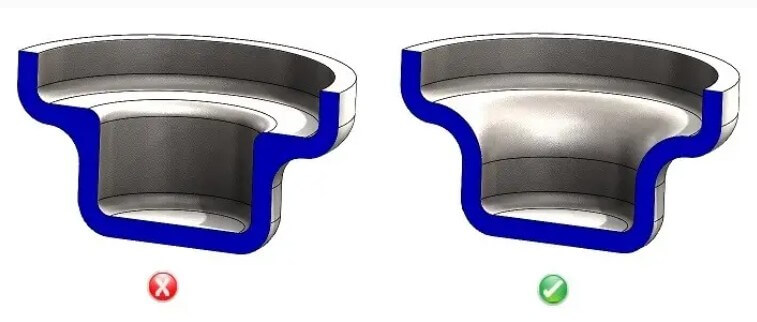
9.Aluminum die casting design tip nine: reinforcement design
Reinforcing ribs can significantly improve the strength and rigidity of die casting parts without increasing the wall thickness, thereby saving material usage, reducing weight, and reducing costs.
Reinforcing ribs effectively prevent the distortion and deformation of die castings by overcoming the problem of uneven stress caused by differences in wall thickness of castings. In addition, the reinforcing ribs can also serve as internal flow channels to assist in filling the mold cavity and improve the flow of plastic to make it smoother.
10.Aluminum die casting design tips ten: Mold draft design
The reasonable design of the mold draft can effectively avoid problems such as strain, deformation or even cracking of the casting during the demoulding process. Generally speaking, the draft angle should be determined based on the specific shape, size and material properties of the casting. Normally, a draft angle between 1° and 3° is appropriate, but for castings with deep cavities or complex structures, a larger draft angle may be required.
In addition, when designing the mold slope, factors such as the wall thickness of the casting, cooling rate, and mold wear must also be taken into consideration. By comprehensively considering these factors, a reasonable draft angle can be designed to ensure smooth demoulding of castings and improve the overall production efficiency and product quality of aluminum die castings.
11.Aluminum die casting design tips eleven: machining allowance design
The machining allowance design in aluminum die casting design is a key link to ensure the accuracy and quality of parts. The machining allowance refers to the difference between the design size and the actual size to account for the effects of material shrinkage, machining errors, surface treatment and other factors.
The material shrinkage is usually between 0.5% and 1%, and the machining allowance and surface treatment allowance are calculated based on the design size and specific proportions. When designing, it is necessary to consider the process requirements, maintain communication with the processing factory, pay attention to the accuracy and strength requirements of different parts, and set appropriate margins reasonably to ensure the performance and accuracy of the parts.
12.Aluminum die casting design tips twelve: spray design
Spray coating not only improves the aesthetics of the product, but also enhances its corrosion and wear resistance. When designing spray coatings, you first need to consider the selection of coatings. The appropriate coating type should be selected based on the use environment and functional requirements of aluminum die castings. For example, products used outdoors should choose coatings with good weather resistance.
Secondly, the spraying process parameters should be determined, such as spraying thickness, number of sprayings, etc., to ensure that the coating is uniform and meets performance requirements. In addition, surface treatment before spraying is also very important, including oil removal, rust removal, phosphating and other steps, which can improve the adhesion of the coating. Finally, quality inspection of the sprayed products, such as coating thickness test, adhesion test, etc., is required to ensure the quality and reliability of the product.
Summarize:
Aluminum die casting design is a complex process. Through the comprehensive application of the above twelve skills, the production efficiency, product quality and cost-effectiveness of aluminum die casting parts can be ensured.