Cast Iron Manufacturing: Process Details
Cast iron manufacturing is a long-standing metalworking process that involves pouring molten iron into a mold of a predetermined shape and cooling it to obtain the desired parts or products. This process is widely used in the automotive, machinery, construction and other fields, and is favored for its excellent strength, wear resistance and cost-effectiveness. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the types, process flow, heat treatment processes and application areas of cast iron manufacturing.
1.Types of Cast Iron Manufacturing
The classification of cast iron manufacturing is mainly based on the presence of carbon in cast iron and the form of graphite. According to these criteria, cast iron can be divided into the following types:
(1) Gray cast iron:
Carbon mainly exists in the form of flake graphite, and the fracture is dark gray. This cast iron has certain mechanical properties and good cutting performance, and is widely used in the manufacture of complex castings and wear-resistant parts.

(2) White cast iron:
Carbon mainly exists in the form of cementite, and the fracture is bright white, hard and brittle. This cast iron is difficult to cut and is mainly used as steelmaking raw material and for the production of malleable cast iron blanks.
(3) Mottled cast iron:
Carbon exists in the form of a mixture of graphite and cementite, and the fracture is grayish white. This type of cast iron is very brittle and is rarely used in industry.
(4) Malleable cast iron:
Obtained through high-temperature and long-term annealing treatment, the graphite is distributed in clusters and has good plasticity and toughness. It is used to manufacture parts with complex shapes and can withstand strong dynamic loads.
(5) Ductile cast iron:
Obtained through spheroidization treatment, the graphite is spherical, has high strength, toughness and plasticity, and is widely used in the manufacture of internal combustion engines, automobile parts, etc.

(6) Vermicular cast iron:
Obtained through vermicularization treatment, the graphite is in the form of worms, and its mechanical properties are similar to those of ductile iron. The casting properties are between gray cast iron and ductile iron. It is used to manufacture automobile parts.
2.Cast iron manufacturing process
(1) Material preparation:
First, prepare raw materials such as pig iron, scrap iron, and ferroalloy. According to the performance requirements of the required cast iron parts, these materials are mixed in a certain proportion.
(2) Melting and casting:
Put the prepared raw materials into a blast furnace or induction furnace for melting. During the melting process, the temperature and time must be strictly controlled to ensure that the molten iron has a uniform composition and is free of impurities. After melting, the molten iron is poured into a preheated mold for casting.
(3) Preparation of casting molds:
Before casting iron, a sand mold or a metal mold must be prepared. Sand casting uses sand and a binder to make a casting mold, while metal casting uses a metal mold. This step requires ensuring that the casting mold is accurate in size and has a smooth surface.
(4) Spheroidizing treatment (for ductile iron):
Before pouring the molten iron into the casting mold, spheroidizing treatment is required. Spheroidizing treatment is to add a spheroidizing agent (such as magnesium, rare earth elements, etc.) to the molten iron so that the graphite forms a spheroid during the solidification process, thereby improving the mechanical properties of the cast iron.
(5) Pouring and cooling:
Pour the treated molten iron into the casting mold, and control the pouring speed and temperature to ensure that the molten iron fills the casting mold evenly and has no defects such as pores and shrinkage holes. After pouring, the casting needs to be cooled to room temperature in the mold.
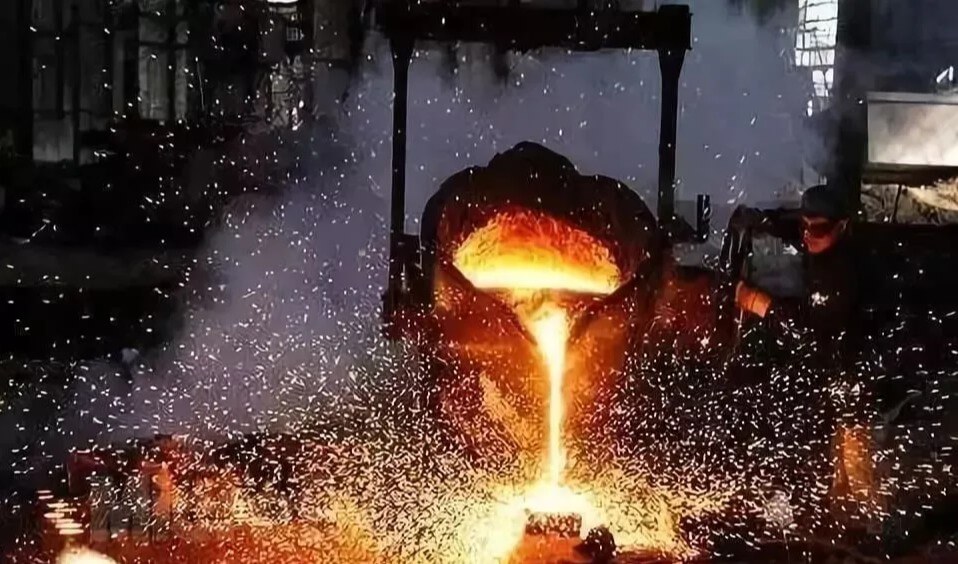

(6) Sand removal and cleaning:
After cooling, the casting is removed from the mold and sand is removed and cleaned. Sand removal is to remove sand particles on the surface of the casting, and cleaning is to remove defects such as flash and burrs.
(7) Heat treatment:
According to needs, heat treatment is performed on the cast iron parts, such as annealing, normalizing, quenching, etc., to improve their mechanical properties and structure.
(8) Machining:
Machining is performed on the cast iron parts, such as turning, milling, drilling, etc., to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
(9) Quality inspection:
After the cast iron manufacturing process is completed, the cast iron parts are inspected for quality, including dimensional inspection, surface quality inspection, mechanical property inspection, etc. to ensure that the product meets the design requirements.
(10) Painting and packaging:
Qualified cast iron parts are painted to prevent rust. After painting, they are packaged for shipment or storage.
3.Heat treatment process for cast iron manufacturing
The heat treatment process for cast iron manufacturing is an important way to improve the performance of cast iron, which mainly includes the following:
(1) Stress relief annealing:
By heating the casting to 500-550℃, keeping it warm for 2-8 hours, and then furnace cooling or air cooling, the internal stress of the casting can be eliminated to prevent deformation and cracking.
(2) High temperature graphitization annealing to eliminate the white cast of the casting:
Heating the casting to 850-950℃, keeping it warm for 2-5 hours, furnace cooling to 500-550℃ and then air cooling to eliminate the white cast structure, reduce the hardness and improve the machinability.
(3) Normalizing of ductile iron:
Heating the casting to the austenitizing temperature, keeping it warm and then air cooling to obtain the pearlite matrix structure, refine the grains, make the structure uniform and improve the mechanical properties.
(4) Quenching and tempering:
Including quenching and high temperature tempering to obtain the tempered troostite structure and improve the comprehensive mechanical properties.
(5) Isothermal quenching:
Applicable to complex parts that require high strength and good plasticity and toughness. By keeping the casting at a specific temperature and then cooling it in air, a lower bainite structure is obtained.
(6) Induction heating quenching:
By rapidly heating the surface of the casting and then rapidly cooling it, the surface hardness and wear resistance are improved.
(7) Electric contact heating quenching:
Surface quenching is performed using the resistance heat generated by the current passing through the casting. It is suitable for local hardening treatment.
(8) Artificial aging:
The casting is placed in a natural environment for a long time to release internal stress and stabilize the size.
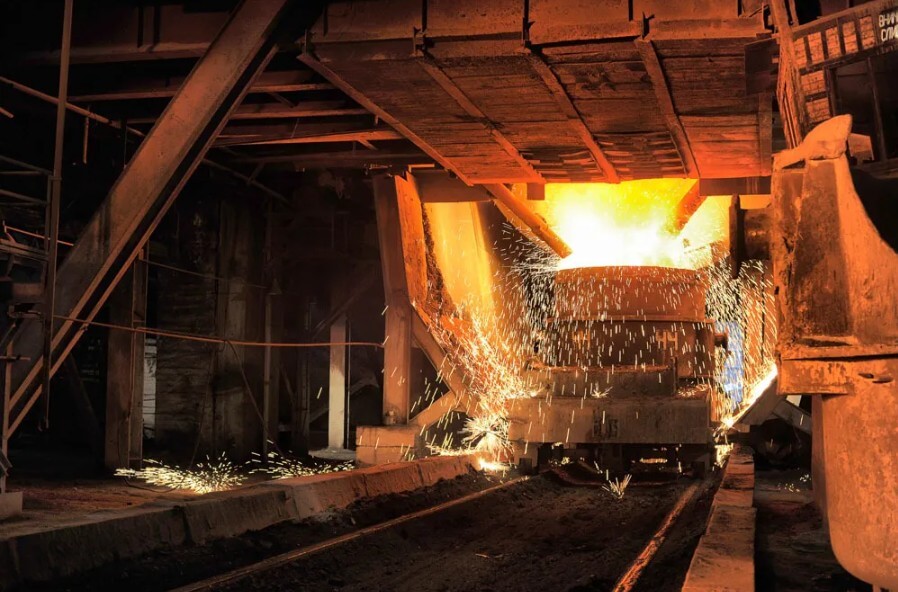

4.Application of cast iron manufacturing
Cast iron manufacturing parts are widely used in industrial production due to their good casting performance, wear resistance, shock absorption and relatively low cost. The following are the main application areas of cast iron manufacturing:
(1) Machine tool bed and base:
Gray cast iron is often used to manufacture the bed and base of machine tools due to its good shock absorption and wear resistance to improve the stability and precision of machine tools.
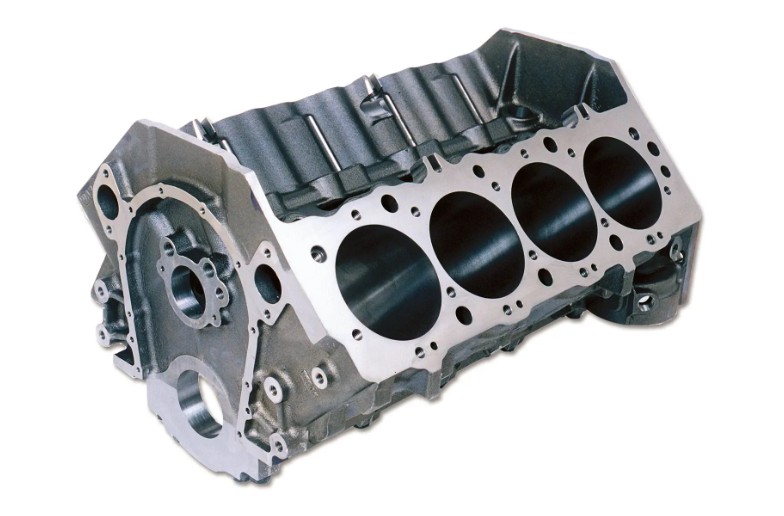
(2) Auto parts:
Ductile iron is often used to manufacture key parts such as automobile engine cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, crankshafts, etc. due to its high strength and toughness.

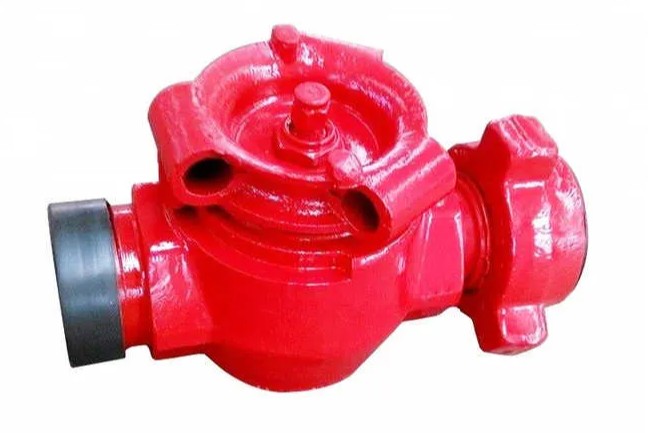
(3) Pipes and valves:
Gray cast iron and ductile iron are also widely used in the manufacture of pipes and valves, especially in water supply, drainage and gas systems.
(4) Agricultural machinery:
Cast iron is often used to manufacture parts of agricultural machinery such as plowshares and harrows due to its wear resistance and cost-effectiveness.
(5) Metallurgical and mining equipment:
In the metallurgical and mining industries, cast iron is used to manufacture highly wear-resistant parts such as rollers and grinding balls.
(6) Petrochemical equipment:
In the petrochemical field, cast iron is used to manufacture pump bodies, valves and other equipment due to its corrosion resistance.

(7) Power equipment:
Cast iron manufacturing is also used to manufacture parts in power equipment such as transformer housings, switchgear, etc.
5.Summary
As an important metal processing technology, cast iron manufacturing will continue to play an irreplaceable role in the future. Through continuous technological innovation and development, cast iron manufacturing technology will provide more high-quality, efficient and environmentally friendly products and services for all walks of life.




