Permanent mold casting: a high repetition rate metal casting process
Permanent mold casting is a process of metal casting using reusable metal molds, named because its molds can be used for a long time. This process occupies an important position in modern manufacturing, especially in the production of high-precision, complex-shaped parts. This article will introduce in detail its process principle, applicable process type, process characteristics, key technologies, mold materials that meet the requirements and material performance analysis. When you finish reading this article, you will have a comprehensive, systematic and profound understanding of permanent mold casting.
1.Permanent mold casting process principle
Permanent mold casting, also known as metal mold casting or hard mold casting, mainly relies on gravity to fill the molten metal into the mold. The mold is usually made of high-temperature resistant metals, such as copper alloys or steel. During the casting process, the mold is first preheated to a certain temperature, and then the molten metal is poured into the mold, and the gravity of the molten metal is used to evenly fill the mold cavity. After cooling and solidification, the casting is removed from the mold by the ejection mechanism to complete a casting process.
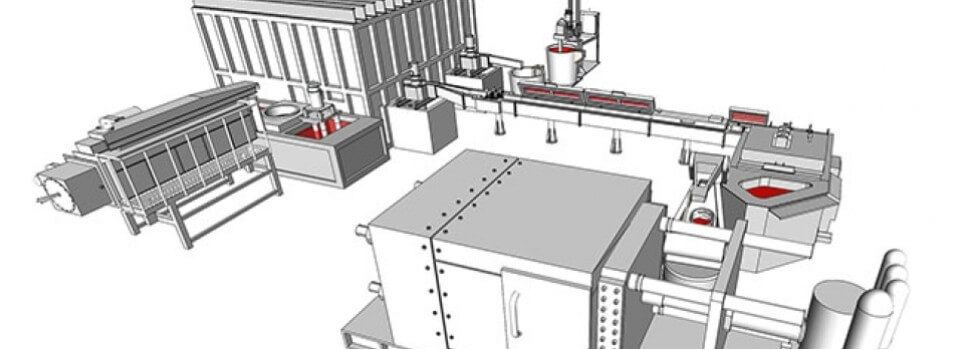
2.Types of permanent mold casting
The biggest feature of permanent mold casting is the use of reusable metal molds. Permanent mold casting can be divided into the following types according to different process characteristics and application requirements:
(1) Gravity casting:
This is the most traditional permanent mold casting method, which relies on gravity to pour the molten metal into the mold. It is suitable for producing castings with simple shapes and uniform wall thickness. Common applications include automotive parts, gears and gearboxes.
(2) Low-pressure casting:
During the low-pressure casting process, the molten metal is pressed into the mold under lower pressure. This method can form more complex shapes and reduce pores and defects in the casting. Low-pressure casting is often used to produce high-quality aluminum castings, such as automotive wheels and engine parts.
(3) High-pressure casting:
In contrast to low-pressure casting, high-pressure casting uses higher pressure to quickly press the molten metal into the mold. This method is suitable for producing thin-walled, complex castings, such as electronic equipment and aircraft parts.

(4) Centrifugal casting:
During the centrifugal casting process, the mold rotates around an axis, using centrifugal force to evenly distribute the molten metal on the inner wall of the mold. This method is particularly suitable for producing tubular or annular castings, such as pipes and bearings.
(5) Vacuum casting:
Vacuum casting is a process of pouring in a vacuum environment to reduce pores in the casting and improve the quality of the casting. This method is often used to produce castings with extremely high internal quality requirements, such as medical device components.
Summary:
Permanent mold casting is widely used in various industries due to its high efficiency, cost-effectiveness and ability to produce high-quality castings. The selection of the appropriate casting type depends on factors such as specific application requirements, material properties and production scale.
3.Process characteristics and greatest advantages of permanent mold casting

(1) Reusability:
The molds used in permanent mold casting are usually made of metal materials such as cast iron, carbon steel or low alloy steel, and can be reused hundreds to tens of thousands of times, thereby reducing the cost of a single casting.
(2) Casting quality:
Due to the high thermal conductivity and heat capacity of the metal mold, the cooling rate is fast, the casting structure is dense, and the mechanical properties are about 15% higher than those of sand castings.
(3) Accuracy and surface quality:
It is possible to obtain castings with higher dimensional accuracy and lower surface roughness values, and the quality stability is good.
(4) Fast cooling speed:
The thermal conductivity of metal molds is better than that of traditional sand molds, resulting in fast cooling speed, dense structure and excellent mechanical properties of castings.
(5) Material saving:
The process yield of castings is high, and the consumption of liquid metal is reduced, which can generally save 15-30%; no sand or less sand can generally save 80-100% of molding materials.
(6) Production efficiency:
Permanent mold casting is suitable for mass production and can improve production efficiency.
(7) Cost-effectiveness:
Although the initial mold cost is high, the unit cost is significantly reduced in the long run because the mold can be reused.
(8) Environmental friendliness:
Compared with traditional sand molds, metal molds reduce the use of sand, improve the working environment, reduce dust and harmful gases, and reduce labor intensity.
4.Key technologies of permanent mold casting

(1) Mold design and manufacturing:
Permanent mold casting uses reusable metal molds, usually made of steel or cast iron. The design of the mold needs to consider the shape, size and material properties of the casting to ensure that the molten metal can evenly fill the mold cavity and cool and solidify smoothly.
(2) Mold preheating and coating:
Before pouring, the mold needs to be preheated to a certain temperature to reduce the temperature difference between the molten metal and the mold, improve metal flow, and reduce defects. At the same time, a ceramic coating is applied to the surface of the mold cavity to facilitate casting disassembly and extend the life of the mold.
(3) Pouring system:
The pouring system is the channel for the molten metal to enter the mold, and its design is crucial to the quality of the casting. A reasonable pouring system can ensure that the molten metal flows smoothly into the mold, avoid turbulence and oxidation, and reduce the generation of pores and inclusions.
(4) Metal smelting and pouring:
During the metal smelting process, it is necessary to control the appropriate temperature and composition to ensure that the molten metal has good fluidity and filling properties. The pouring speed should be controlled during pouring to avoid being too fast or too slow, so as not to affect the quality of the casting.
(5) Cooling and mold opening:
After pouring, the molten metal cools and solidifies in the mold. During the cooling process, the cooling rate should be controlled appropriately to prevent cracks or deformation of the casting. After the metal solidifies, the mold is opened and the casting is taken out.
(6) Post-processing of castings:
After the casting is taken out, it needs to be trimmed to remove excess parts such as the pouring system and riser. Then, post-processing processes such as heat treatment and surface treatment are carried out to meet the performance and use requirements of the casting.
5.What are the special requirements for permanent mold casting materials?
(1) Heat resistance and chemical stability:
During the permanent mold casting process, the mold will repeatedly contact the high-temperature molten metal. Therefore, the mold material needs to have sufficient heat resistance and chemical stability to ensure that the mold does not deform at high temperatures and does not react chemically with the molten metal.
(2) Thermal conductivity:
The mold material should have a certain thermal conductivity to help the molten metal cool and solidify quickly, thereby improving production efficiency.
(3) Fluidity:
The coating should maintain good fluidity at high temperatures so that it can be evenly applied to the mold surface to form a protective film.

(4) Low gas emission:
The coating and mold material should have low gas emission at high temperature to avoid defects such as pores during the casting process.
(5) No cracking and flaking:
The coating should not crack or flake when the temperature changes drastically to ensure the surface quality of the casting.
(6) Easy demoulding:
The mold surface should be smooth and the coating should facilitate demoulding between the molten metal and the mold to reduce surface defects of the casting.
(7) Reusability:
The mold for permanent mold casting needs to be able to withstand multiple casting cycles, so the mold material should have sufficient strength and durability.
6.Some mold materials that can meet the special requirements of permanent mold casting:
(1) Steel:
Carbon steel and alloy steel are often used to make permanent mold casting molds due to their good strength and durability.
(2) Cast iron mold:
It has the advantages of high strength, high hardness, good processability, low cost and long service life, and is the first choice for mass casting production.
(3) Aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy and copper alloy:
These non-ferrous metals are commonly used materials for casting due to their good fluidity and casting properties.

(4) Steel and iron:
Although not as commonly used as non-ferrous metals, permanent mold casting can also be performed under certain conditions, such as using graphite molds.
7.Conclusion
Permanent mold casting, as an efficient and precise metal casting process, plays an irreplaceable role in modern manufacturing. With the continuous development of materials science and manufacturing technology, the permanent mold casting process will continue to improve and provide more high-quality and high-precision metal parts for the manufacturing industry.





What do you think?
[…] Mold design is the basis of copper mold casting, and its rationality directly affects the formation and quality of metallic glass. Copper molds are usually made of copper alloys with high thermal conductivity, which can quickly cool the melt and promote the formation of amorphous structure. The design of the mold needs to consider the following aspects: […]
Comments are closed.