Explore the applications and advantages of die casting in various fields.
1.Definition and Development of Die Casting
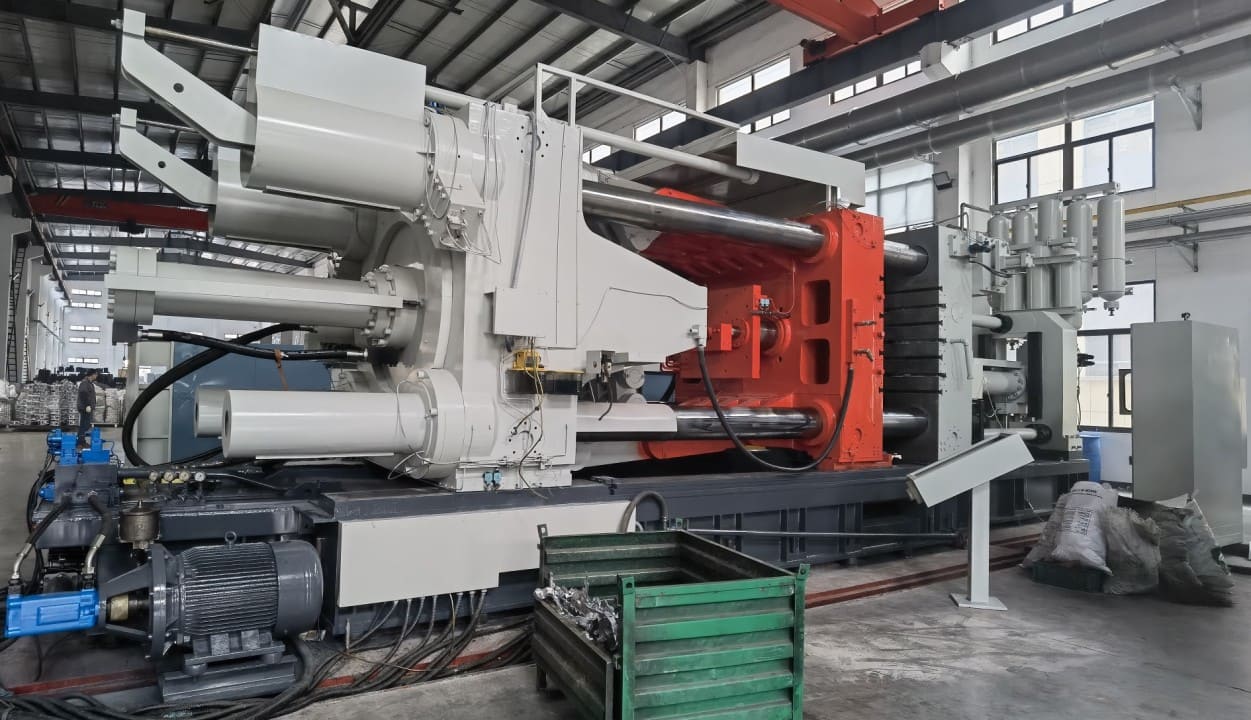
Die casting is an efficient metal casting process that uses reusable molds to inject molten metal under high pressure. It is particularly suitable for mass production of metal parts with high precision, high repeatability and high surface finish. It originated in the mid-19th century and initially served the printing industry. Later it spread to the automotive, aerospace, electronics and other fields. Today, it mainly uses non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc and magnesium, and has become an important process in the production of many products. Compared with other casting methods, die casting produces parts with tight tolerances, less post-processing requirements and high strength, which is highly sought after by manufacturers.
2.Working Principle of Die Casting
(1) Preparing the Mold
Die casting molds come in different sizes and design types. When considering the design and number of cavities, the following types are mainly distinguished:
1) Single-cavity mold: This is the simplest single-cavity mold and can only produce one part per cycle.
2) Multi-cavity form: The structure is more complex and is characterized by the presence of multiple identical cavities in one form. It can produce multiple identical parts in one cycle, which is very suitable for mass production of a single part.
3) Combination mold: There are different designed cavities inside the mold, so it is more flexible and can produce different types of parts in each cycle.
4) Unit mold: This is a special mold suitable for producing parts with complex geometries without losing precision, such as castings with molded inserts or thin walls.
(2) Process
The process depends on whether a hot chamber system or a cold chamber system is used. In a cold chamber system, the melting process occurs outside the casting machine; while in a hot chamber casting machine, the melting occurs inside the machine. The material is then injected into the mold under appropriate pressure.
(3) Cooling
The molten metal cools and solidifies in the mold to form the final part. Cooling should be carried out while the mold is still clamped.

(4) Pulling
Once the casting is completely hardened, the mold is released to activate the machine’s ejector pin, which ejects the hardened part.
(5) Trimming
The die casting is trimmed to remove burrs and other defects that leave excess material on the part.
3.Types of die-casting processes
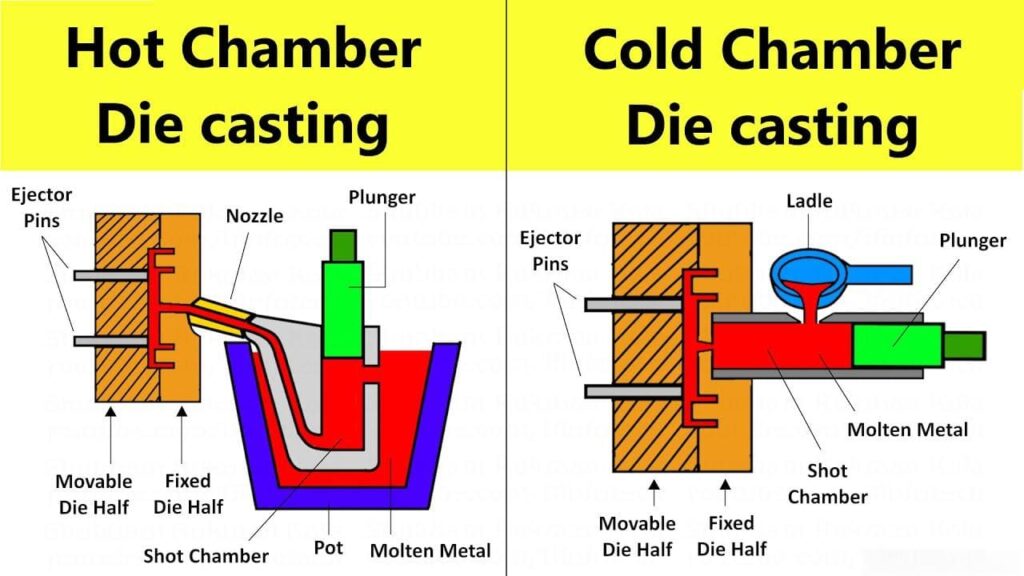
(1) Hot chamber die-casting:
Hot chamber die-casting machines are usually used for die-casting of low melting point metals such as zinc, magnesium and their alloys. The injection mechanism is immersed in the liquid metal in the heat-insulating crucible, and the molten metal is pushed into the mold cavity by the piston. The advantages of this process are simple production process and high efficiency, but the injection chamber and the injection punch are immersed in liquid metal for a long time, which affects the service life.
(2) Cold chamber die-casting:
When die-casting cannot be used for metals in hot chamber die-casting process, cold chamber die-casting can be used, including aluminum, magnesium, copper and zinc alloys with high aluminum content. In this process, the metal needs to be melted in a separate crucible first. Then a certain amount of molten metal is transferred to an unheated injection chamber or injection nozzle. The metal is injected into the mold through hydraulic or mechanical pressure. Due to the need to transfer the molten metal into the cold chamber, the biggest disadvantage of this process is the long cycle time.
(3) Pore-free die-casting process:
This process aims to reduce casting defects and eliminate pores, thereby improving the quality and performance of castings.
(4) Direct injection process:
It is mainly used for zinc processing, which can reduce waste and increase the yield rate. 3
(5) Precision die casting technology:
Invented by General Dynamics, this process is sometimes also called double punch die casting.
(6) Semi-solid die casting:
The core principle of this technology is: the metal melt that is undergoing the solidification process is violently stirred by a stirring device, and then the dendrites are fully broken by the stirring action to obtain a new spherical or ellipsoidal primary solid phase uniformly distributed in the metal melt, that is, a semi-solid slurry, and finally the prepared semi-solid slurry is processed.

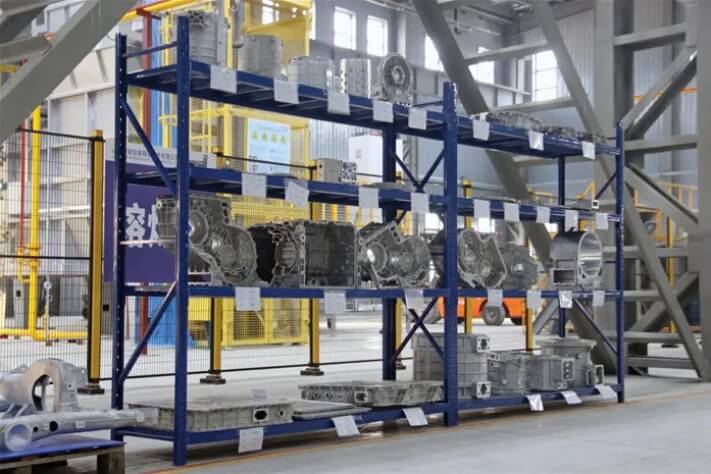
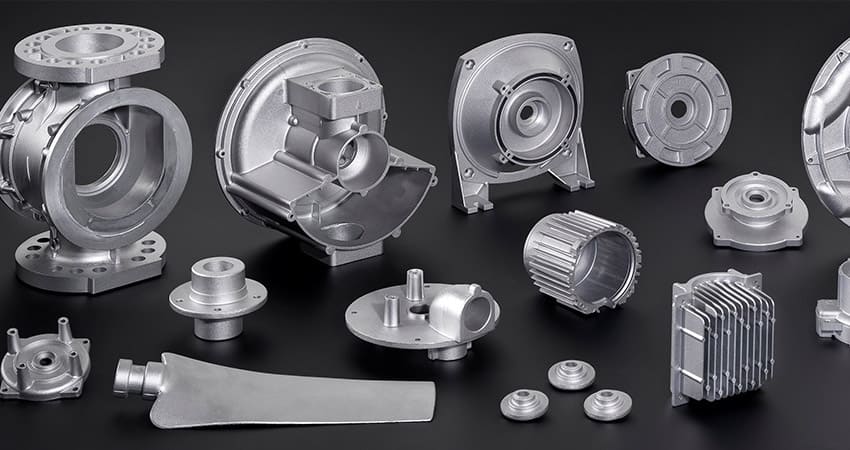
4.Application
(1) Aerospace industry
The aerospace industry often uses metal castings to manufacture aircraft engine parts. Die casting is suitable for materials widely used in this industry, can meet the needs of complex geometries and ensure dimensional accuracy. For example, the aircraft engine casing requires high-precision dimensions to adapt to high-speed flight and extreme conditions, and it can perfectly achieve this.
(2) Automobiles
In the automotive industry, die casting is used to produce engine parts (such as cylinder heads, transmission housings, engine blocks) and body parts (such as wheels and door handles). It allows you to create complex internal structures, provide sealing and strength, and achieve efficient mass production and reduce costs.
(3) Electronics
Aluminum alloys, zinc alloys and magnesium alloys are used to produce components such as connectors, heat sinks and housings for electronic products. It can accurately manufacture complex parts, such as mobile phone housings, to meet the appearance and performance requirements of electronic products.
(4) Consumer products
Many consumer products, such as kitchen appliances and power tools, are made of aluminum, zinc and tin alloys by die casting. The advantages of high productivity, large-scale production and cost-effectiveness meet the market demand for consumer products.
(5) Construction industry
Products such as hinges, window frames and accessories in the construction industry. When both functionality and aesthetics are important, this technology can produce complex product shapes to enhance the beauty of buildings, such as high-quality architectural window hinges that combine functionality and aesthetics.

Advantages of die casting
(1) High precision
It has very high dimensional accuracy and can achieve strict tolerances. For example, when making the body of a precision instrument, it can ensure that the body size matches the internal components perfectly, ensuring the performance and stability of the instrument.
(2) Complex parts
It can produce parts with complex geometric shapes, including casting inserts, thin walls, etc. Let’s take the cylinder head of an automobile engine as an example. It has many complex channels and structures, and these complex shapes can be easily produced to meet the performance requirements of the engine.
(3) Fast delivery and high output
It is a process suitable for large-scale production, and the unit cost of parts is low. For example, in the production of electronic products, the demand for mobile phone casings is very high. Through high-pressure casting and the use of multiple combined molds, the production speed and quantity can be quickly increased, the unit cost can be reduced, and the rapid demand of the market can be met.
(4) Surface treatment
When using methods such as low-pressure casting and semi-solid casting, the cast metal parts will have a smooth surface. For example, in the manufacture of high-end furniture metal accessories, good surface finish can improve the aesthetics of the product while reducing subsequent processing steps and improving production efficiency.
(5) Long mold life
Molds are usually made of high-quality steel, which is strong and durable and can withstand the high pressure and temperature during the casting process. Taking automobile manufacturing as an example, a set of high-quality die-casting molds can produce tens of thousands of auto parts, greatly reducing production costs. The strength and durability of steel ensures a long mold life, which is one of the main advantages of this process.




